Abstract
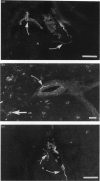
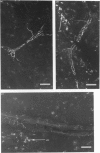
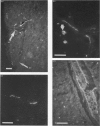
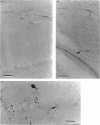
Sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the rat thymus is described using immunohistochemical, fluorescence histochemical and histochemical methods. Sympathetic innervation was found to enter the gland with the vasculature and to be distributed mainly in the subcapsular and corticomedullary junctional areas of the cortex. The parasympathetic innervation was also found to enter the gland with the vasculature, but was distributed to both cortex and medulla. Acetylcholinesterase-positive staining cells were seen in the medulla. Ideas about the function of thymus innervation are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTIN L., BERRY W. K. Two selective inhibitors of cholinesterase. Biochem J. 1953 Jul;54(4):695–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulloch K., Moore R. Y. Innervation of the thymus gland by brain stem and spinal cord in mouse and rat. Am J Anat. 1981 Oct;162(2):157–166. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001620207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulloch K., Pomerantz W. Autonomic nervous system innervation of thymic-related lymphoid tissue in wildtype and nude mice. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 1;228(1):57–68. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Do some sympathetic neurones synthesize and release both noradrenaline and acetylcholine? Prog Neurobiol. 1978;11(3-4):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R. J., Gomez M. M., Norgren R. Central origins of cranial nerve parasympathetic neurons in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Mar 15;190(2):373–394. doi: 10.1002/cne.901900211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L., Felten S. Y., Bellinger D. L., Carlson S. L., Ackerman K. D., Madden K. S., Olschowki J. A., Livnat S. Noradrenergic sympathetic neural interactions with the immune system: structure and function. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:225–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbenkian S., Wharton J., Polak J. M. The visualisation of cardiovascular innervation in the guinea pig using an antiserum to protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5). J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Mar;18(3):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Mesulam M. M. Brain stem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus complex in the cat: I. The cervical vagus and nodose ganglion. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Sep 15;193(2):435–465. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. D., al-Shawaf A., Zaidi S. A. The cholinergic and adrenergic innervation of the rat thymus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;237:255–261. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5535-9_39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzewa R. M., Jacobowitz D. M. Pharmacological actions of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Sep;26(3):199–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kása P., Silver A. The correlation between choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activity in different areas of the cerebellum of rat and guinea pig. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):386–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Fibiger H. C. Acetylcholinesterase and the cholinergic neuron. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 3;25(23):1939–1947. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90596-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O. Substance P hydrolysis by human serum cholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):106–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Fahrenkrug J., Hökfelt T., Mutt V. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cholinergic neurons of exocrine glands: functional significance of coexisting transmitters for vasodilation and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1651–1655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance D. M., Hopkins D. A., Bieger D. Re-investigation of the innervation of the thymus gland in mice and rats. Brain Behav Immun. 1987 Jun;1(2):134–147. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(87)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway C. A., Greenberg G. R. Interaction of vasoactive intestinal peptide with mouse lymphocytes: specific binding and the modulation of mitogen responses. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):417–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway C. A. In vitro alteration of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide changes the in vivo localization of mouse T cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1054–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. The pharmacology of 6-hydroxydopamine. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:169–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Doran J. F., Jackson P., Dhillon A. P., Rode J. PGP 9.5--a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 14;278(1-2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]