Abstract
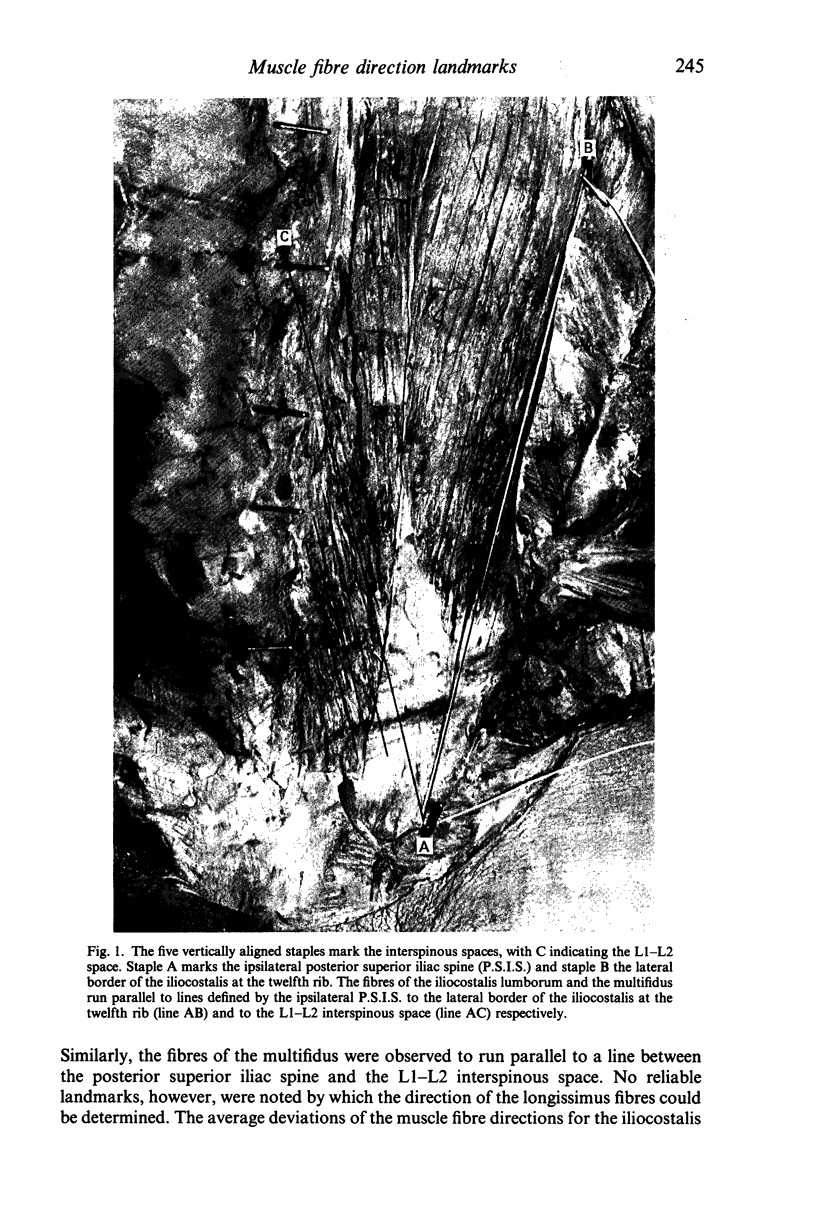
Considerable inter-individual variations in the fibre direction angles of the iliocostalis lumborum, longissimus and multifidus were observed, thus bringing the applicability of a two dimensional fixed angle grid system for fibre direction determination into question. However, the angulation of the fibres of the multifidus and iliocostalis lumborum were found to be easily identifiable by the use of three surface anatomical landmarks: the caudal tip of the superior iliac spine, the lateral border of the iliocostalis at the twelfth rib and the L1-L2 interspinous space. No reliable index was found for the longissimus. Suggested electrode placement sites for the electromyographic study of the iliocostalis lumborum and the multifidus are at the levels of the L2-L3 and the L4-L5 interspinous spaces respectively.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G. B., Ortengren R., Herberts P. Quantitative electromyographic studies of back muscle activity relatated to posture and loading. Orthop Clin North Am. 1977 Jan;8(1):85–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. A reappraisal of the anatomy of the human lumbar erector spinae. J Anat. 1980 Oct;131(Pt 3):525–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustami F. M. A new description of the lumbar erector spinae muscle in man. J Anat. 1986 Feb;144:81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca C. J. Myoelectrical manifestations of localized muscular fatigue in humans. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1984;11(4):251–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stulen F. B., DeLuca C. J. Frequency parameters of the myoelectric signal as a measure of muscle conduction velocity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1981 Jul;28(7):515–523. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1981.324738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]