Abstract
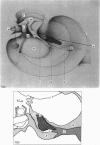
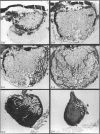
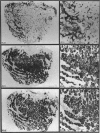
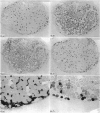
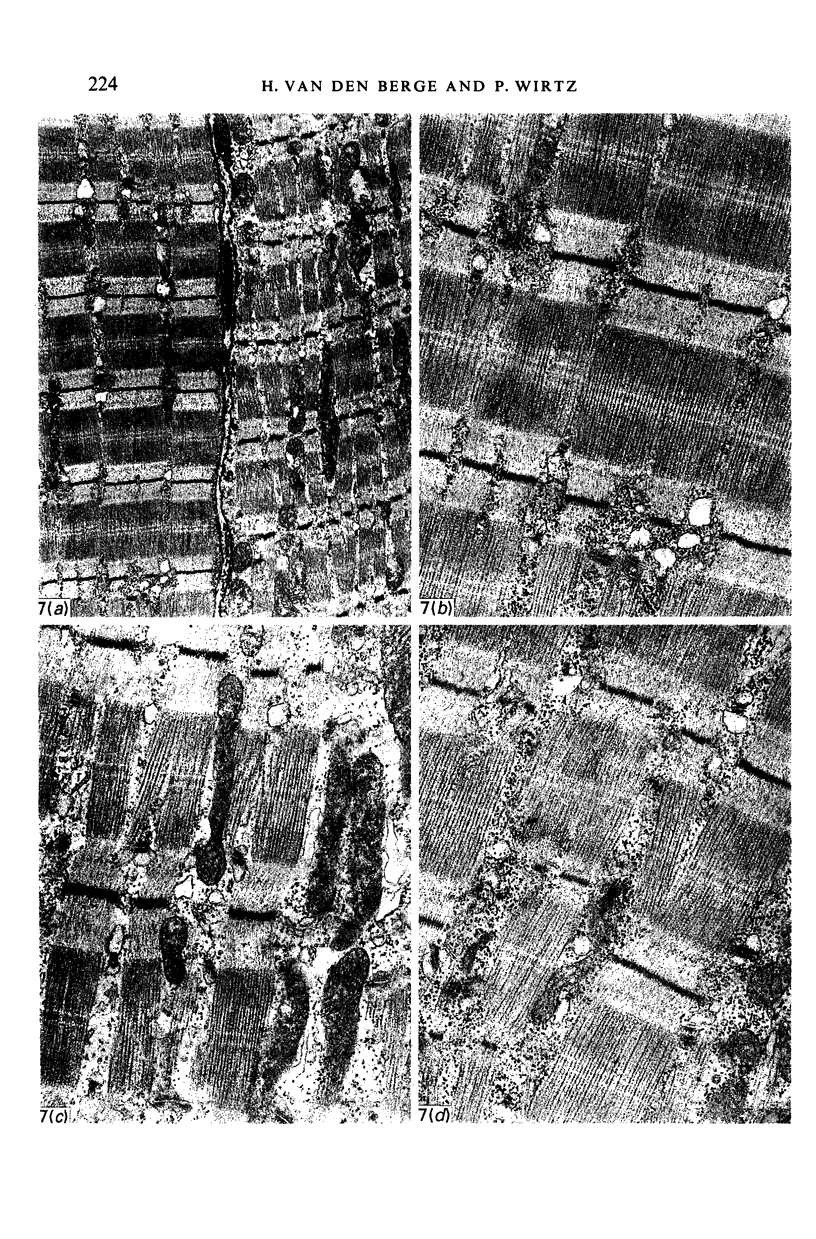
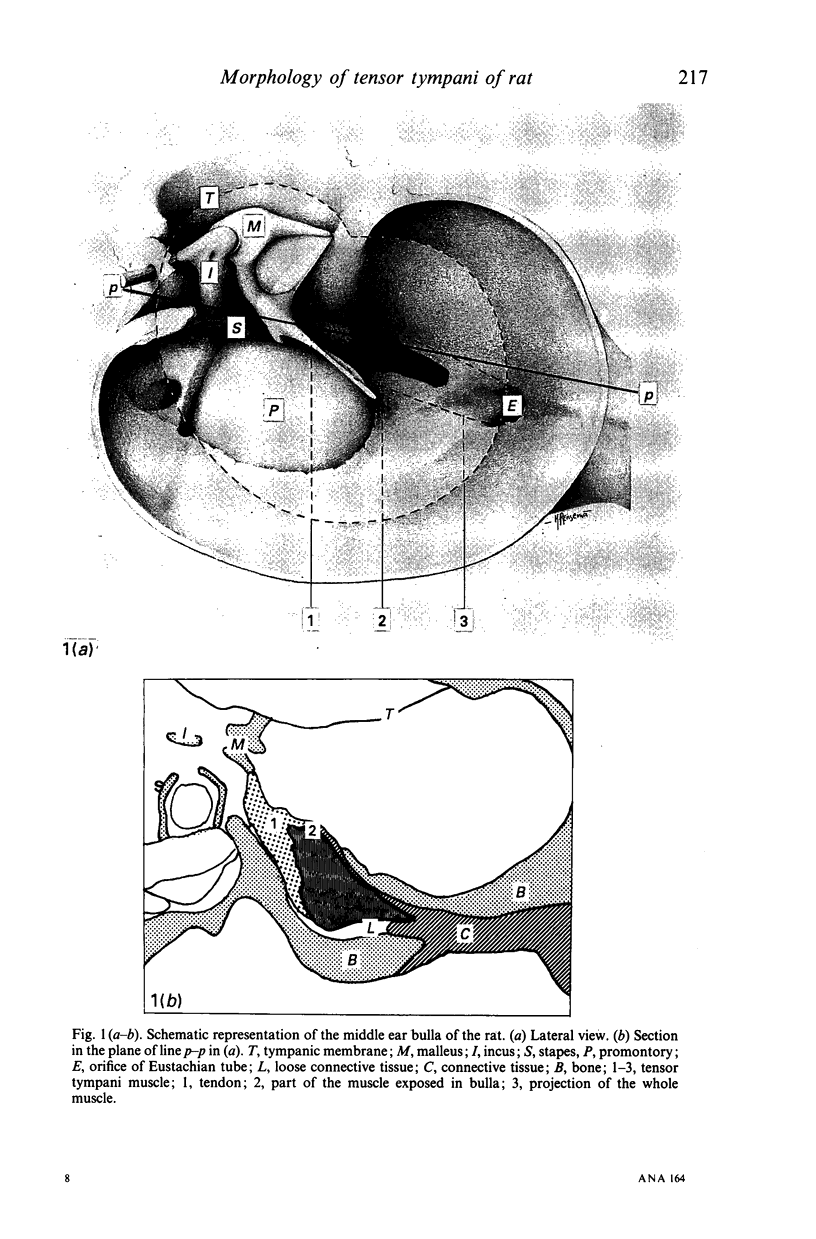
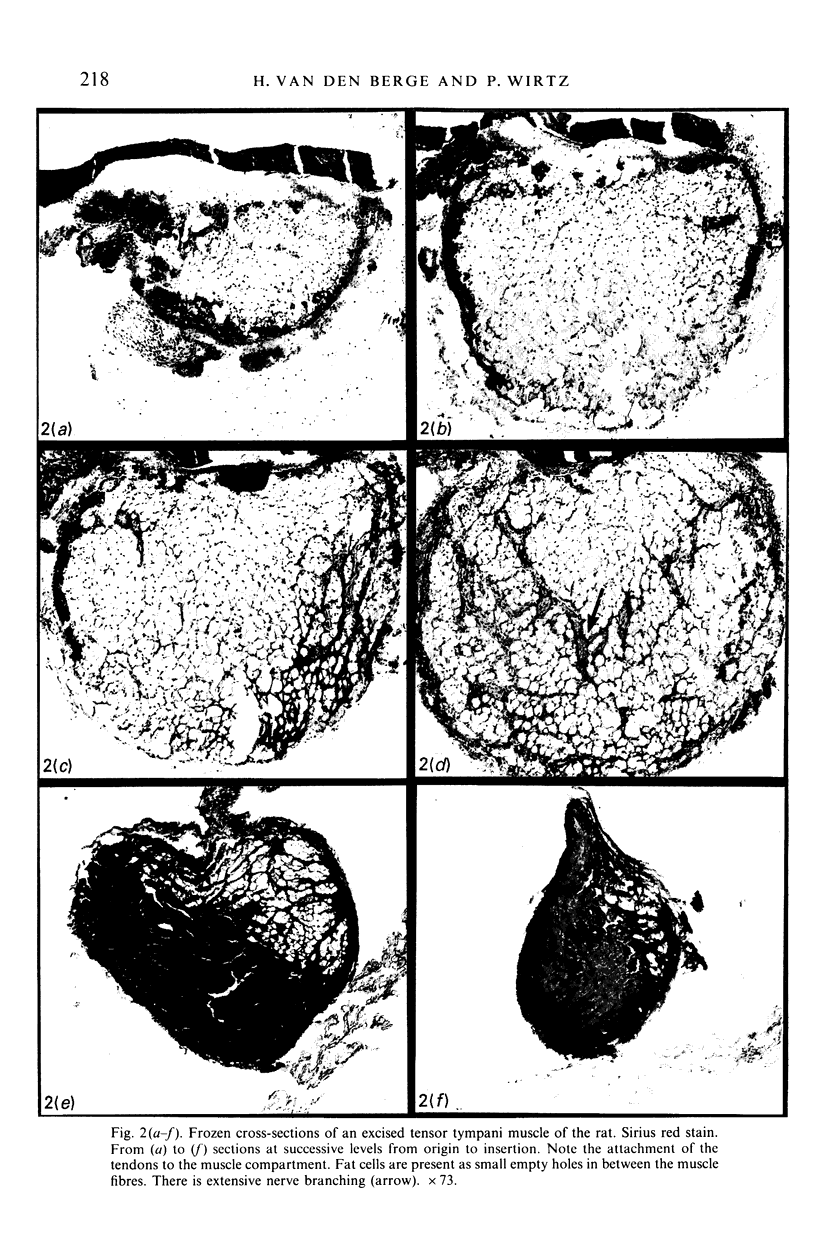
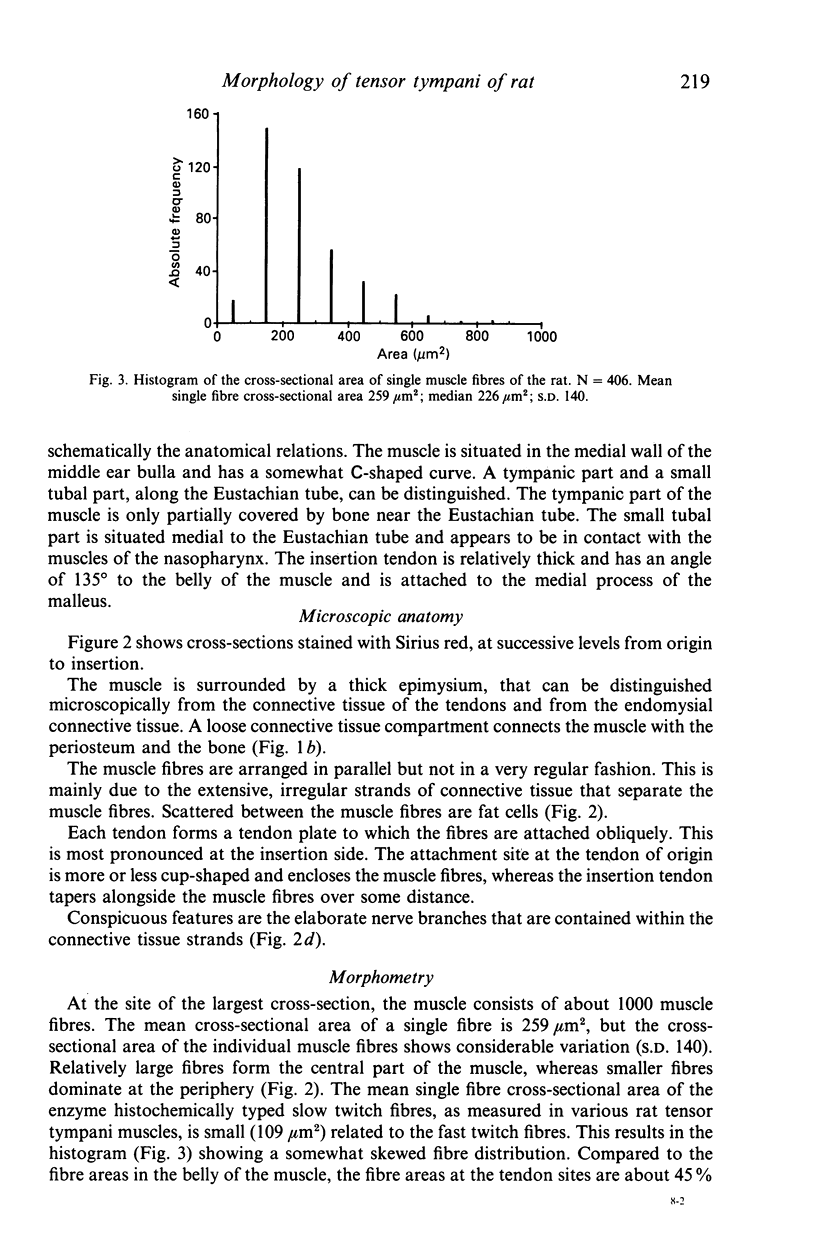
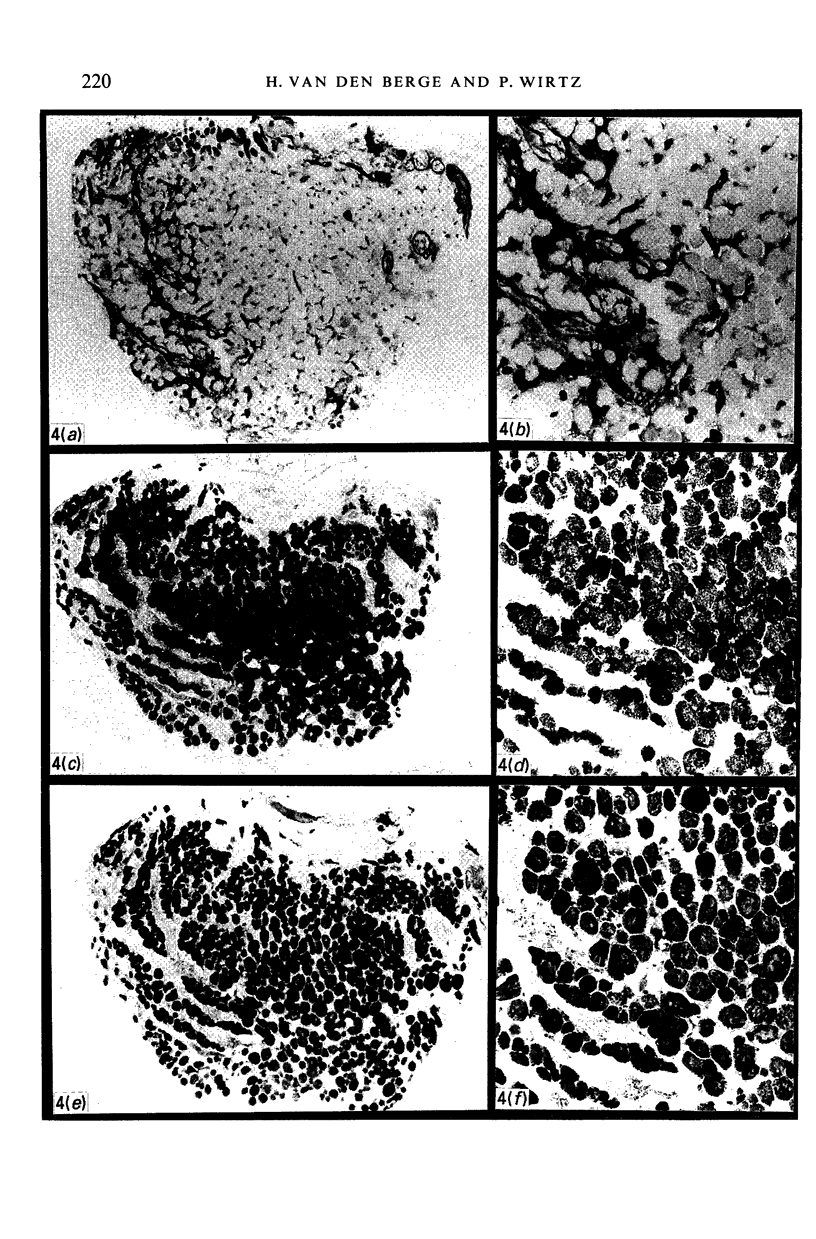
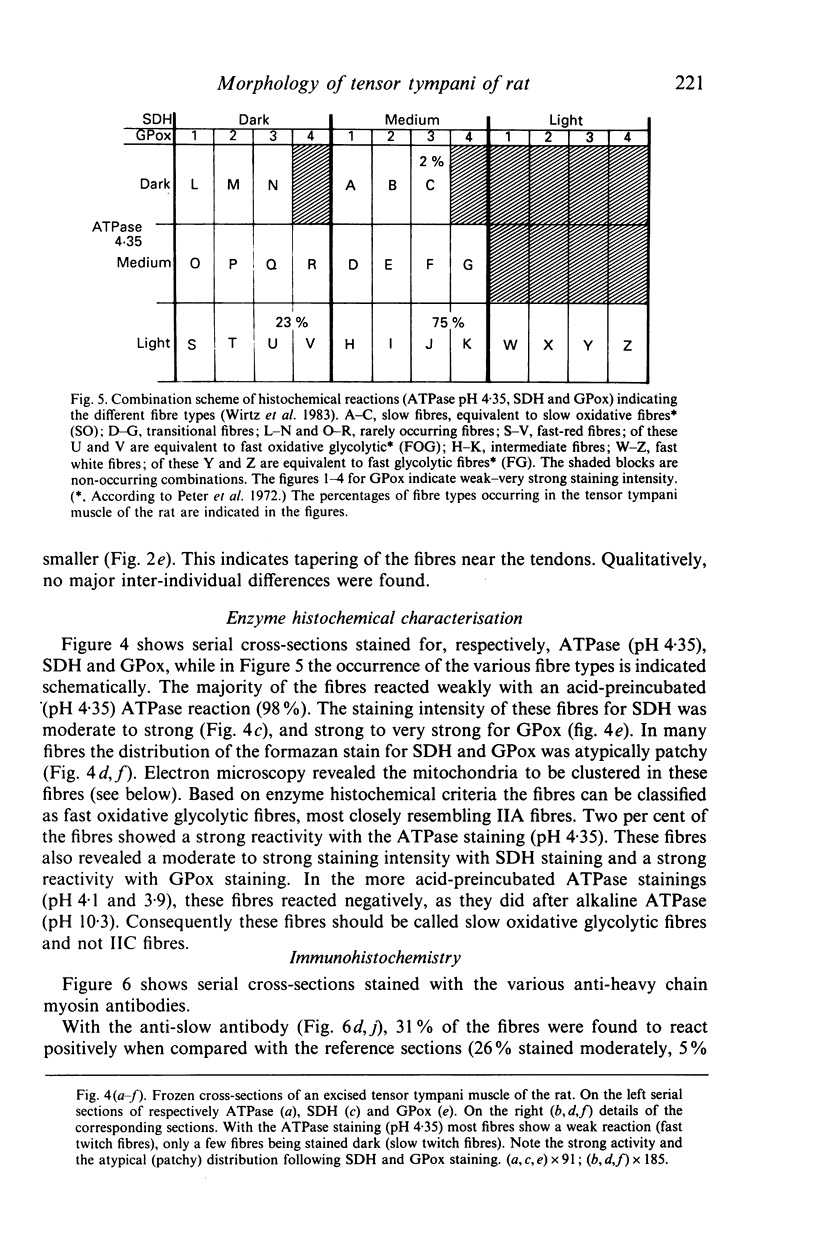
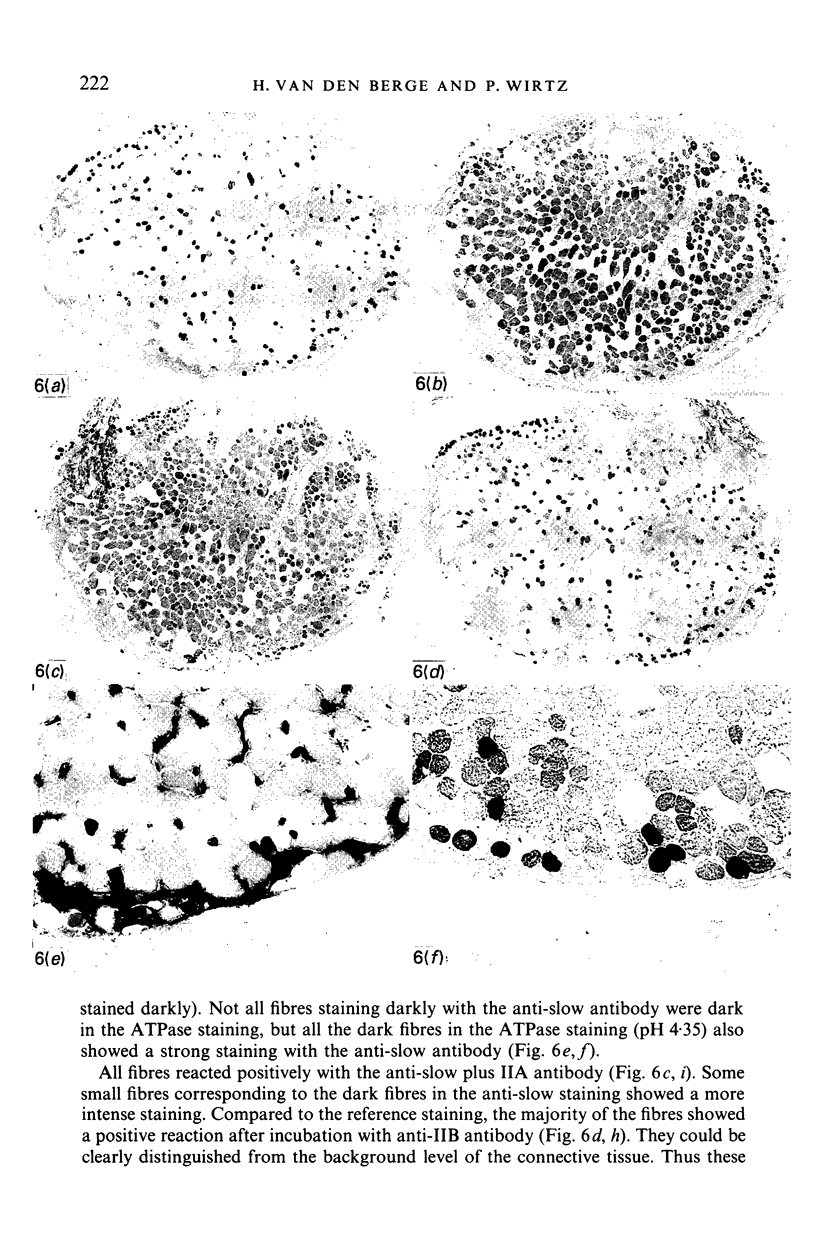
The gross anatomy, microscopical anatomy, morphometry, enzyme histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy of the tensor tympani muscle of the rat was studied. The aim of the study was to create an integrated insight into the morphology of the muscle and to discuss functional implications. The tensor tympani muscle of the rat is an atypical muscle. It is a small muscle composed of very small muscle fibres with a complex microscopical and submicroscopical architecture. Histochemically the muscle consists mainly of fast oxidative glycolytic fibres, but discrepancies are found when anti-heavy chain myosin antibodies are used for fibre typing. Different adult heavy chain myosin isotypes coexist in one single muscle fibre. The electron microscopical study shows that bundles of myofilaments branch and interconnect with other bundles of myofilaments. The findings suggest that the muscle is able to contract fast and is fatigue-resistant. Both features seem to suggest that the muscle has a function in protecting the inner ear against noise damage.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLEVINS C. E. INNERVATION OF THE TENSOR TYMPANI MUSCLE OF THE CAT. Am J Anat. 1963 Sep;113:287–301. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRZEZINSKI D. K. [Fine structure, muscle spindles and function of the muscles of the middle ear in man]. Arch Ohren Nasen Kehlkopfheilkd. 1962;179:550–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David H., Gerhardt H. J., Uerlings I. Die submikroskopische Struktur des Musculus Stapedius des Meerschweinchens. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;70(3):334–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernand V. S., Hess A. The occurrence, structure and innervation of slow and twitch muscle fibres in the tensor tympani and stapedius of the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):547–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugsten P., Dahl H. A., Teig E. Histochemical characteristics of the tensor tympani muscle in relation to the medial gastrocnemius muscle of the cat. Acta Otolaryngol. 1984 Sep-Oct;98(3-4):221–230. doi: 10.3109/00016488409107558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama M., Davidowitz J., Daly J. F. Ultrastructure of middle ear muscle in the rabbit. II. Tensor tympani. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Mar;77(3):171–175. doi: 10.3109/00016487409124614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMFORS T., WERSALL J. Innervation of the middle ear muscles in the rabbit with special reference to nerve calibres and motor units. I. Musculus tensor tympani. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. 1960;3:157–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello F., Carpenè E., Veggetti A., Rowlerson A., Jenny E. The tensor tympani muscle of cat and dog contains IIM and slow-tonic fibres: an unusual combination of fibre types. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):363–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00713043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello F., Veggetti A., Cerpenè E., Rowlerson A. An immunohistochemical study of the middle ear muscles of some carnivores and primates, with special reference to the IIM and slow-tonic fibre types. J Anat. 1983 Aug;137(Pt 1):95–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer A. E., Vries G. P. Enzyme histochemical studies on the Purkinje fibers of the atrioventricular system of the bovine and porcine hearts. Histochem J. 1978 Jul;10(4):399–408. doi: 10.1007/BF01003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., TSOU K. C., DE SOUZA E., CHENG C. S., SELIGMAN A. M. Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Jul;5(4):420–436. doi: 10.1177/5.4.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):170–195. doi: 10.1177/3.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B., Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Gillespie C. A., Stempel K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2627–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEAT F., PUCHTLER H., ROSENTHAL S. I. SIRIUS RED F3BA AS A STAIN FOR CONNECTIVE TISSUE. Arch Pathol. 1964 Jul;78:69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Gorza L., Pitton G., Saggin L., Ausoni S., Sartore S., Lømo T. Embryonic and neonatal myosin heavy chain in denervated and paralyzed rat skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veggetti A., Mascarello F., Carpenè E. A comparative histochemical study of fibre types in middle ear muscles. J Anat. 1982 Sep;135(Pt 2):333–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTENBERG L. W., LEONG J. L. Effects of coenzyme Q10 and menadione on succinic dehydrogenase activity as measured by tetrazolium salt reduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1960 Jul;8:296–303. doi: 10.1177/8.4.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz P., Loermans H. M., Peer P. G., Reintjes A. G. Postnatal growth and differentiation of muscle fibres in the mouse. I. A histochemical and morphometrical investigation of normal muscle. J Anat. 1983 Aug;137(Pt 1):109–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuurveld J. G., Wirtz P., Loermans H. M., Veerkamp J. H. Postnatal growth and differentiation in three hindlimb muscles of the rat. Characterization with biochemical and enzyme-histochemical methods. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(1):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00214640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong F. I., Kingma H., Wirtz P., vd Berge H., Marres E. H. Indications of a differentiated regulation of sound transmission by the middle ear muscles of the rat. Am J Otol. 1988 Jan;9(1):70–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]