Full text
PDF

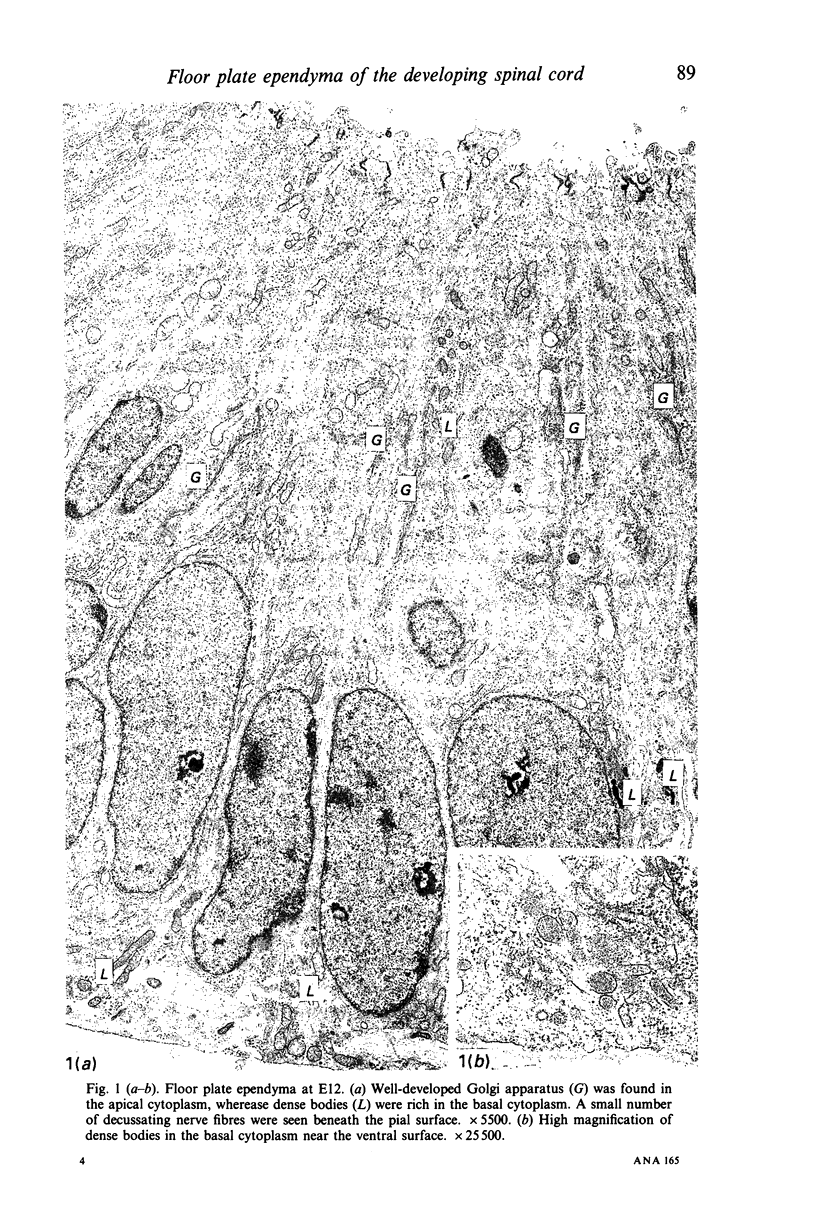
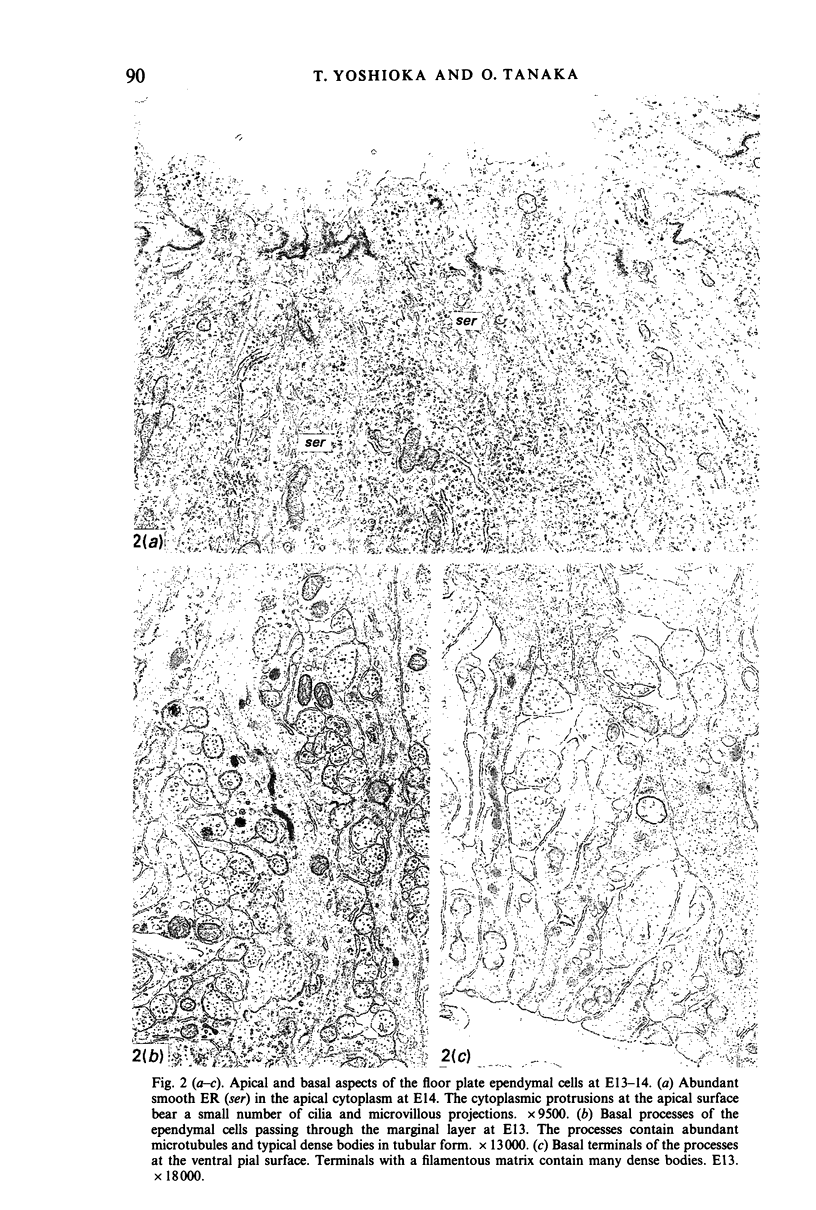
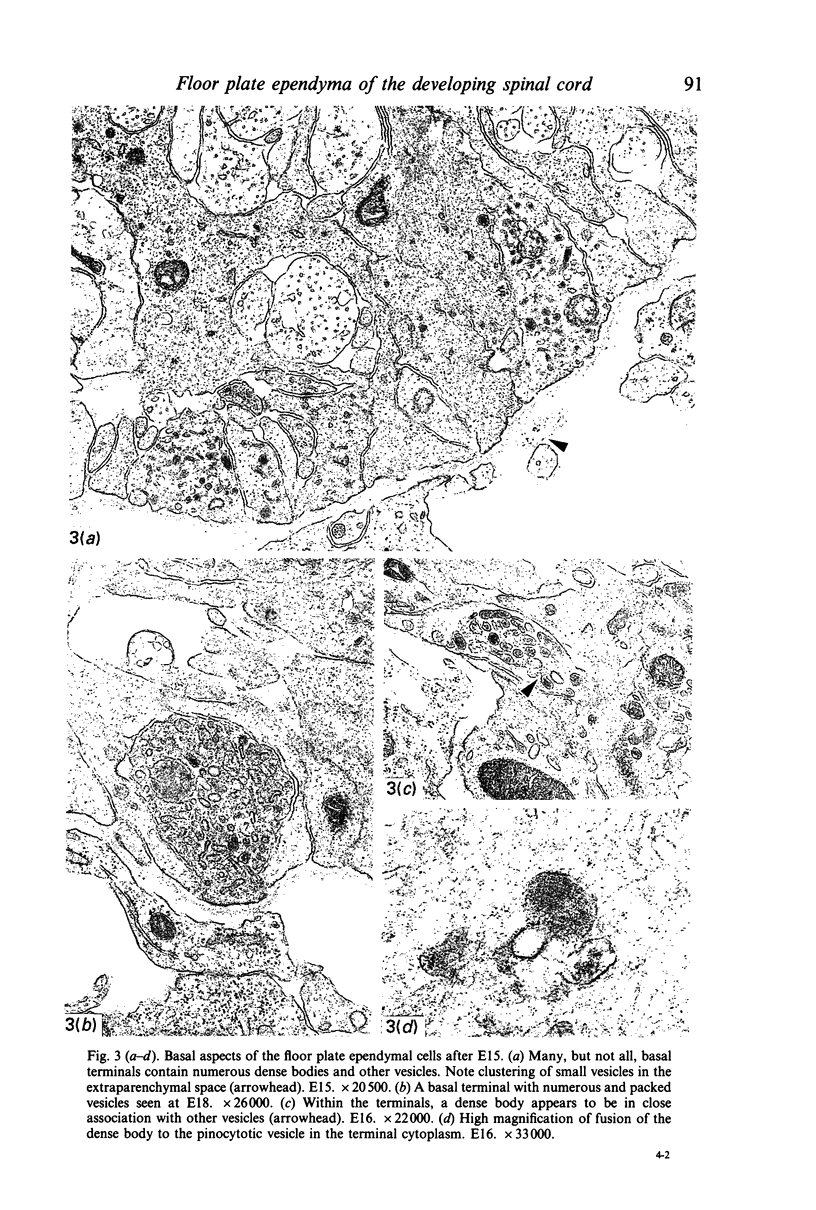
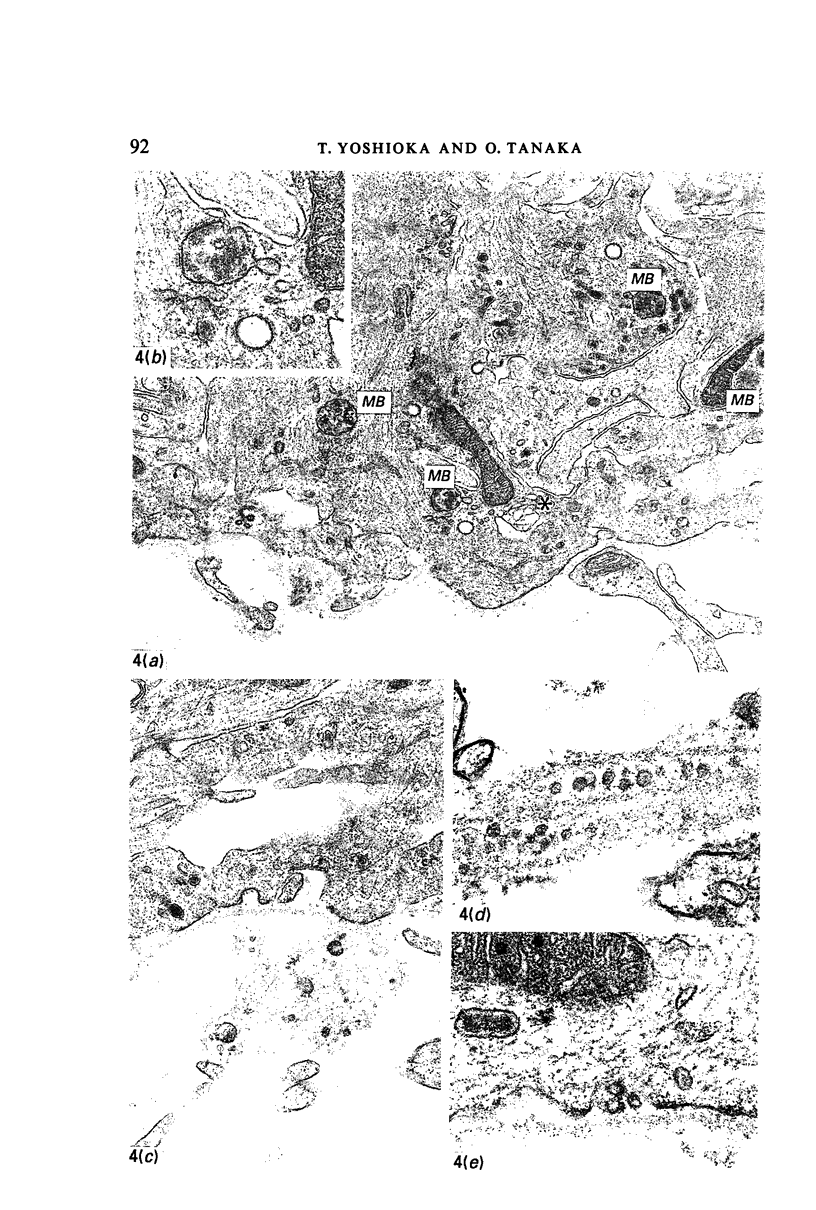

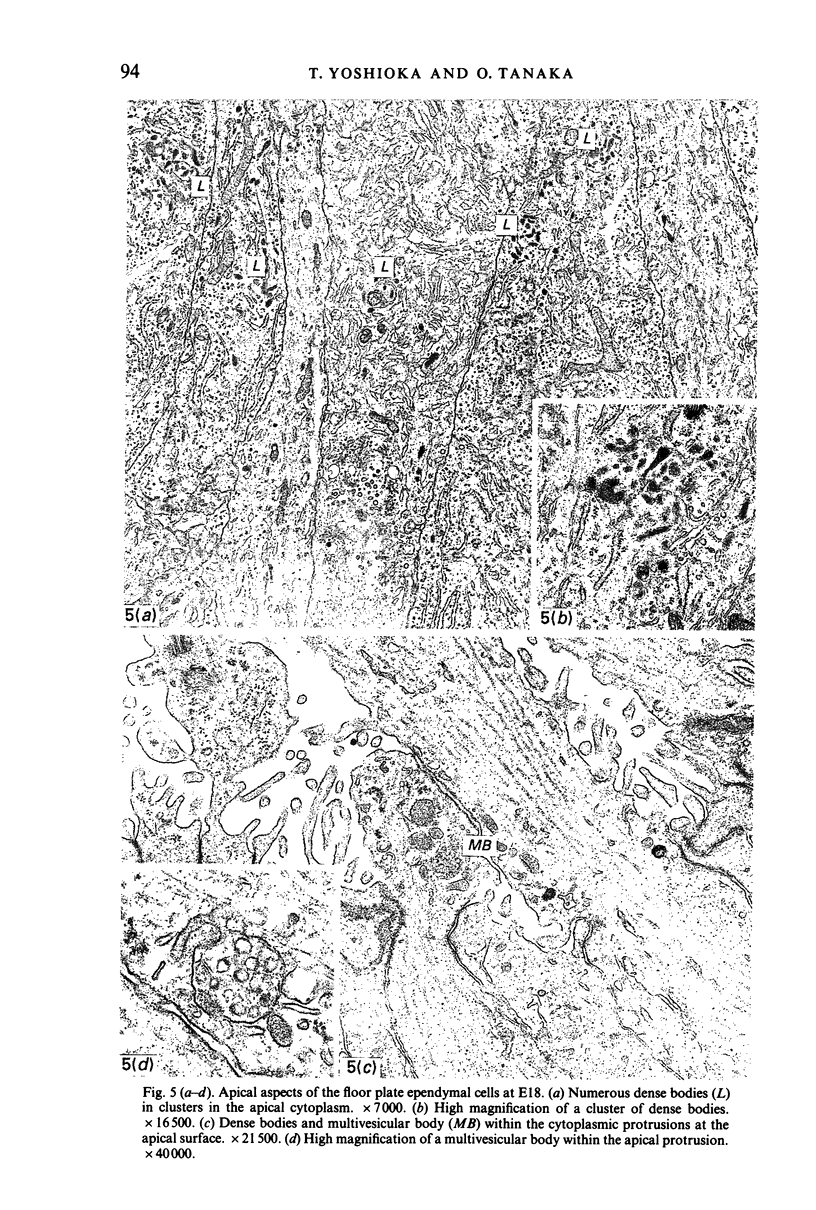

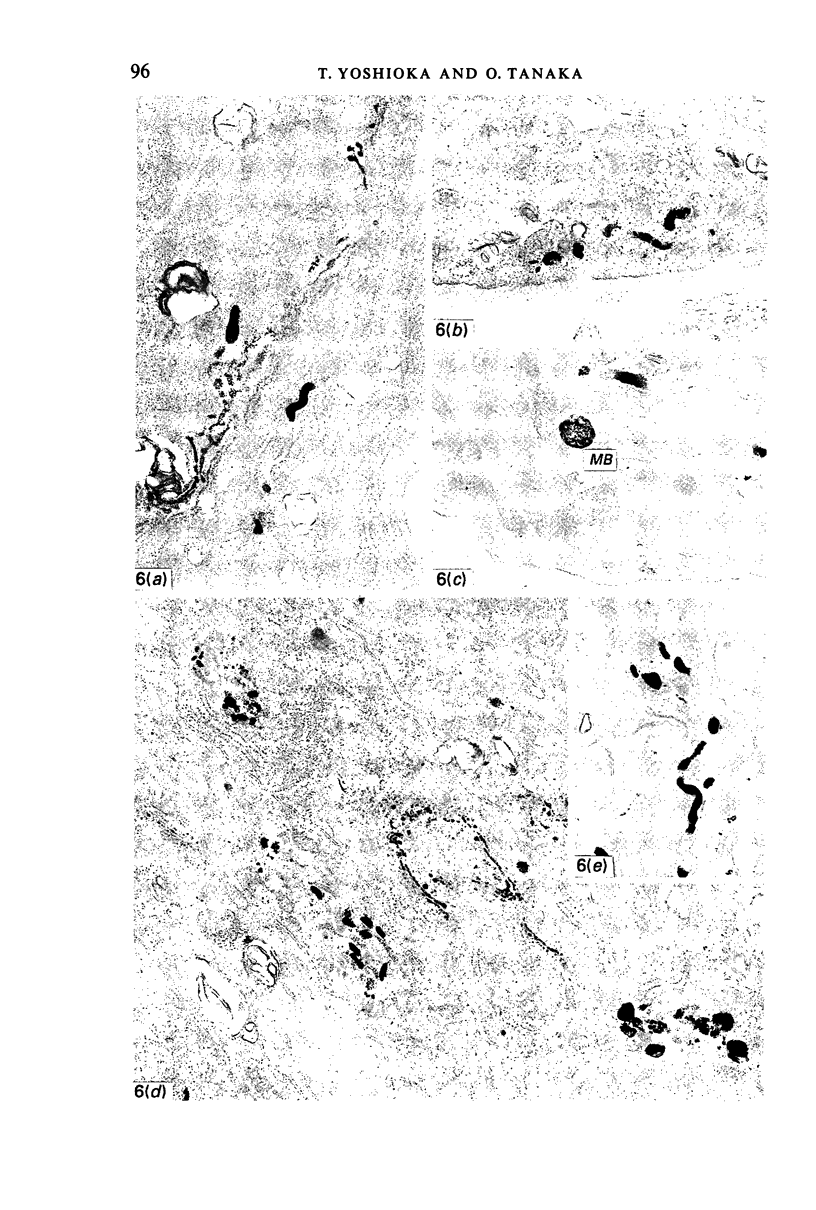




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein J. J., Bernstein M. E. Effect of glial-ependymal scar and teflon arrest on the regenerative capacity of goldfish spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 1967 Sep;19(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(67)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. E., Del Bigio M. R., Clattenburg R. E. Ependyma: normal and pathological. A review of the literature. Brain Res. 1985 Apr;356(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(85)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. E., Reddy K. Ependyma of the central canal of the rat spinal cord: a light and transmission electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1987 Jun;152:55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner G., Biesold D. Histochemistry of glycogen deposition in perinatal rat brain: importance of radial glial cells. J Neurocytol. 1981 Oct;10(5):749–757. doi: 10.1007/BF01262651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble H. J. Electron microscope observations on the human foetal and embryonic spinal cord. J Anat. 1969 May;104(Pt 3):435–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore S. A., Leiting J. E. Changes in the central canal area of immature rats following spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 10;201(1):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore S. A., Sims T. J., Leiting J. E. Central canal area in the early postnatal rat: normal development and radiation-induced changes. Brain Res. 1984 Jun;316(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(84)90301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrikson C. K., Vaughn J. E. Fine structural relationships between neurites and radial glial processes in developing mouse spinal cord. J Neurocytol. 1974 Dec;3(6):659–675. doi: 10.1007/BF01097190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W., Hinds P. L. Reconstruction of dendritic growth cones in neonatal mouse olfactory bulb. J Neurocytol. 1972 Sep;1(2):169–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01099183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan F. L., Rieke G. K., Thomas W. E. Presence and development of ependymal cells in primary tissue cultures derived from embryonic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1987 Sep;432(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKAY D. G., ADAMS E. C., HERTIG A. T., DANZIGER S. Histochemical horizones in human embryos. II. 6 And 7 millimeter embryos-Streeter horizon XIV. Anat Rec. 1956 Dec;126(4):433–463. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinský J., Brichová H. Fine structure of ependyma in spinal cord of human embryos. Folia Morphol (Praha) 1967;15(1):68–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., ADAMS E. C., HERTIG A. T., DANZIGER S. Histochemical horizons in human embryos. I. Five millimeter embryo, Streeter horizon XIII. Anat Rec. 1955 Jun;122(2):125–151. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091220202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannese E., Luciano L., Iurato S., Reale E. Lysosomes in normal and degenerating neuroblasts of the chick embryo spinal ganglia. A cytochemical and quantitative study by electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol. 1976 Nov 15;36(3):209–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00685365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G. Sub-lethal autolysis. Modification of cell periphery by lysosomal enzymes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90615-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall D. P. Transport through the ependymal linings. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:159–172. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Karnovsky M. J. Ultrastructural localization of several phosphatases with cerium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Oct;31(10):1197–1208. doi: 10.1177/31.10.6309949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenen J. Histoenzymology of the developing rat spinal cord. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Jan-Feb;4(1):37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz R., Löhler J., Schwendemann G. Ependyma and meninges of the spinal cord of the mouse. A light-and electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00209966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simón-Marín R., Vilanova J. R., Aguinagalde A., Barberá-Guillem E. Vascular architecture of the developing spinal cord in the rat: a suggested model. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Aug;76:27–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A quantitative and morphological study of vascularisation of the developing mouse spinal cord. J Anat. 1981 Mar;132(Pt 2):203–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. An electron microscopic study of the development of the ependyma of the central canal of the mouse spinal cord. J Anat. 1981 Jan;132(Pt 1):119–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R., Smart I. H. A morphological study of the mouse subependymal layer from embryonic life to old age. J Anat. 1980 Mar;130(Pt 2):391–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka O., Yoshioka T., Shinohara H. Secretory activity in the floor plate neuroepithelium of the developing human spinal cord: morphological evidence. Anat Rec. 1988 Oct;222(2):185–190. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092220211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara M., Ueshima T. Distribution of glycogen in the floor plate of the chick spinal cord during development. Anat Rec. 1984 May;209(1):105–113. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092090113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigh-Teichmann I., Vigh B. The system of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Arch Histol Jpn. 1983 Sep;46(4):427–468. doi: 10.1679/aohc.46.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigh B., Vigh-Teichmann I. Comparative ultrastructure of the cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Int Rev Cytol. 1973;35:189–251. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60355-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wender M., Kozik M., Sniatała-Kamasa M. Activity of acid phosphatase and TPP-ase at a fine structure level in the neuroglia as related to myelination of the brain. Acta Histochem. 1976;57(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(76)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Ultrastructural localization of acid phosphatase in the hindbrain of the mouse embryo. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Apr;34(4):507–512. doi: 10.1177/34.4.3950389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]