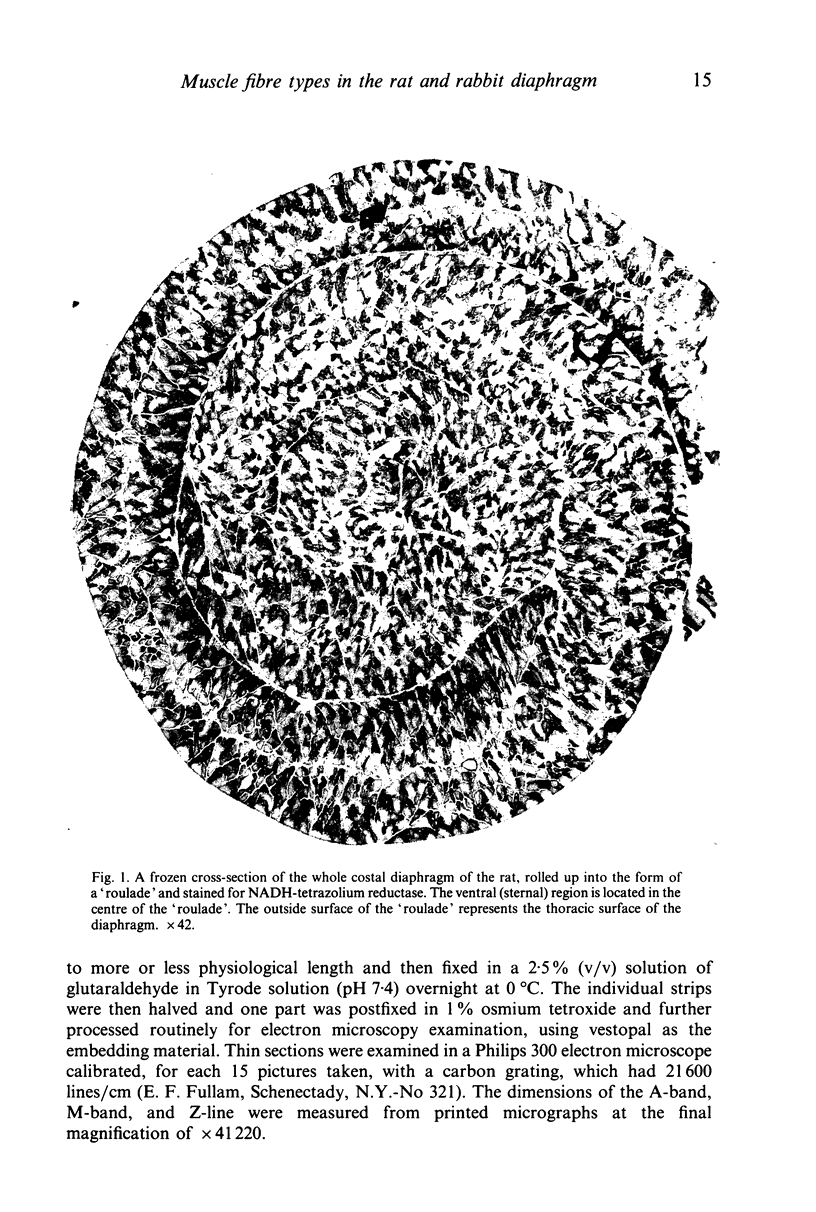
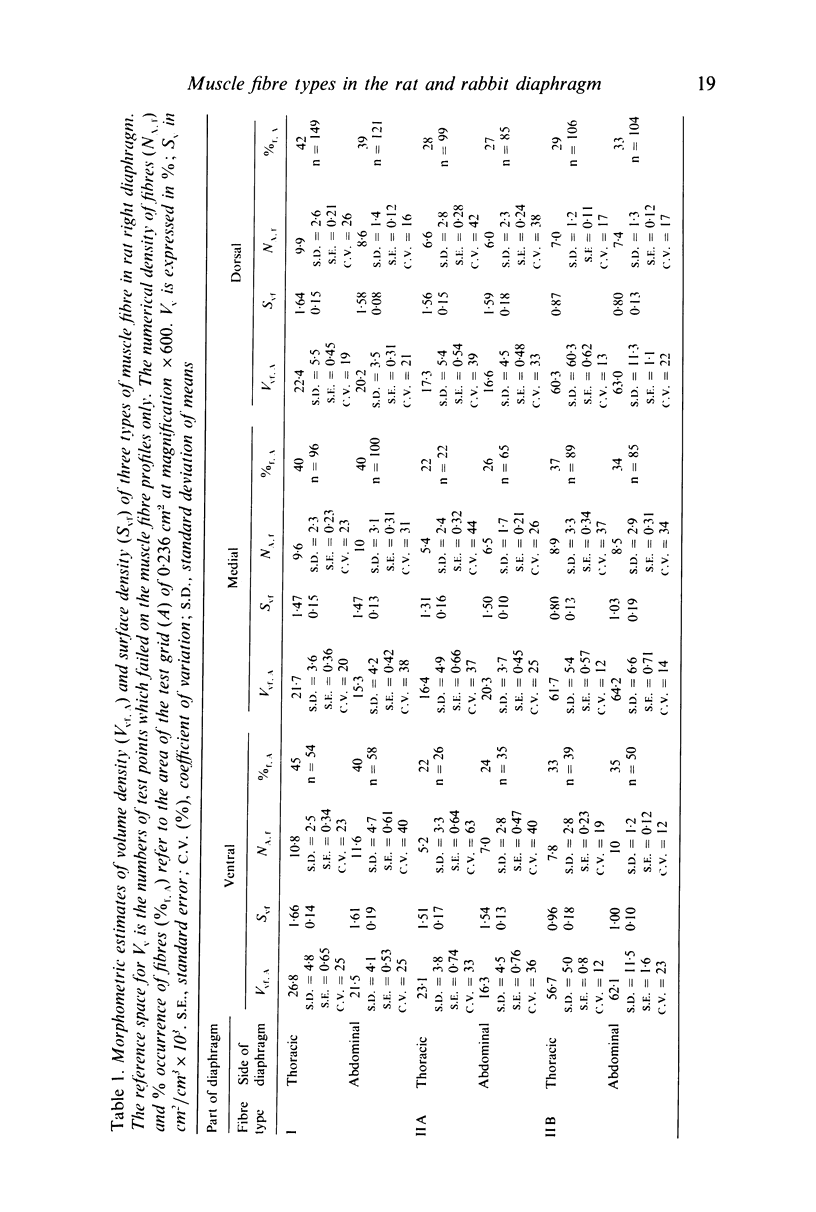
Abstract
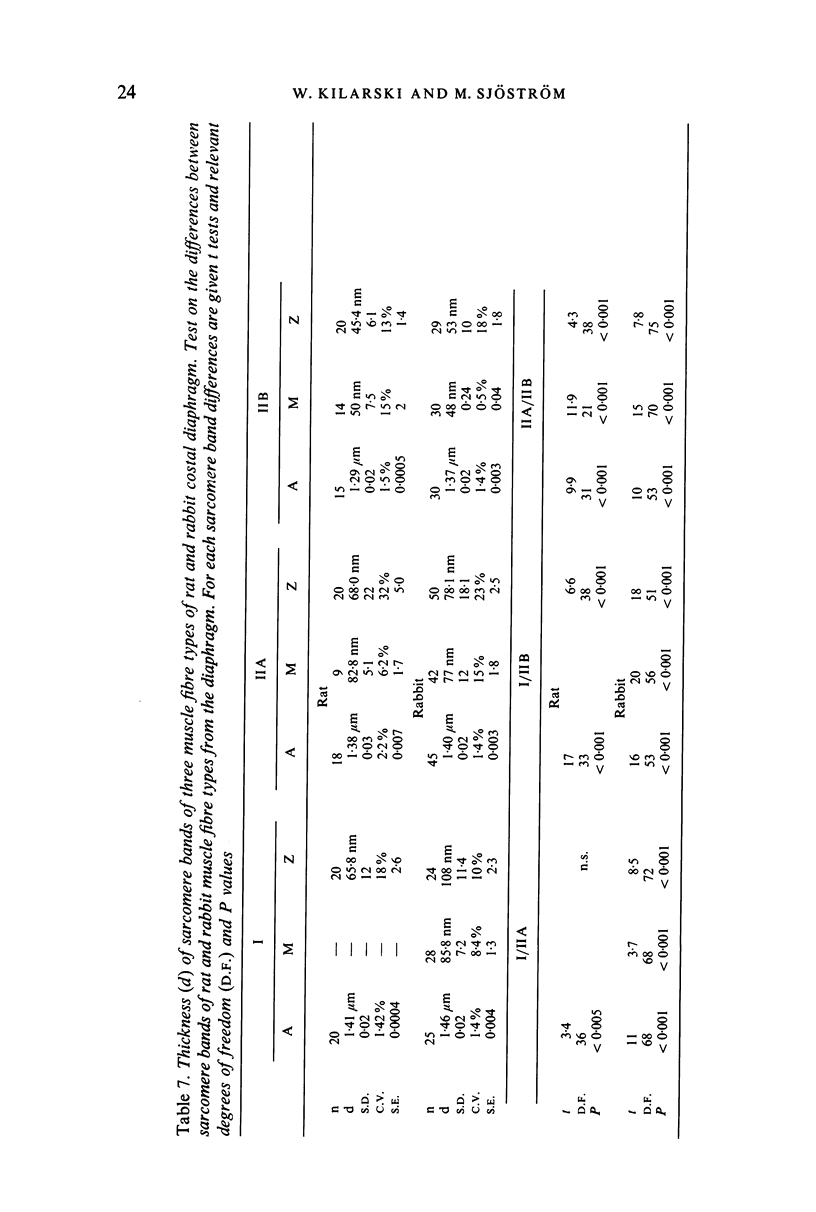
The histochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of the adult rat and rabbit costal diaphragm were investigated. On the basis of enzyme histochemistry, the rat diaphragm was found to contain 42% and 39% Type I, 24% and 25% Type II A and 33% and 34% Type II B fibres on the thoracic and abdominal surfaces respectively. The rabbit costal diaphragm contained 18% and 26% Type I, 46% and 39% Type II A and 35% and 34% Type II B fibres on the thoracic and abdominal surfaces respectively. Differences in the proportion of each muscle fibre type were also observed between diaphragmatic regions (ventral, medial and dorsal) in the rat as well as in the rabbit. Differences in muscle architecture were also noted on the basis of stereological analysis in estimation of volume density, surface density, numerical density and cross-sectional areas of each muscle fibre type. The fine structural analysis of all three fibre types also showed significant differences in the width of the A-bands and Z-lines between the muscle fibre types of the rat and rabbit costal diaphragm.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD W. H., BASMAJIAN J. V. Electromyography of the diaphragm in rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1963 May;204:943–948. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Salcman M., Tsairis P. Motor units in cat soleus muscle: physiological, histochemical and morphological characteristics. J Physiol. 1974 May;238(3):503–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Zajac F. E., 3rd Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Tsairis P. Trophic functions of the neuron. II. Denervation and regulation of muscle. The correlation of physiological properties with histochemical characteristics in single muscle units. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Mar 22;228(0):145–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Sampson M., Sigrist S., Macklem P. T. The diaphragm: two muscles. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):237–238. doi: 10.1126/science.7244632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decramer M., De Troyer A., Kelly S., Zocchi L., Macklem P. T. Regional differences in abdominal pressure swings in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Dec;57(6):1682–1687. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.6.1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner J. A., Maxwell L. C., Ruff G. L., White T. P. The diaphragm as a muscle. Contractile properties. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2 Pt 2):89–92. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2P2.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNTHER P. G. Das muskuläre Substrat der Bewegungsund Halteleistung des menschlichen Zwerchfells. Acta Anat (Basel) 1953;17(4):348–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNTHER P. G. Die Morphologischen Grundlagen der Bewegungs und Halteleistung (Tetanus und Tonus) des Zwerchfells. Acta Anat (Basel) 1952;14(1-2):54–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Padykula H. A. Cytological studies of fiber types in skeletal muscle. A comparative study of the mammalian diaphragm. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):333–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschall J. The diaphragm of the rat and its innervation. Muscle fiber composition; perikarya and axons of efferent and afferent neurons. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1981;161(4):405–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00316051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E., Edström L. Differential histochemical effects of muscle contractions on phosphorylase and glycogen in various types of fibres: relation to fatigue. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):415–423. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, contraction speed and fatiguability of rat soleus motor units. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):177–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Scheidt K. B., Fitts R. H. Histochemical and physiological characteristics of the rat diaphragm. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Apr;58(4):1085–1091. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.4.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A. Histochemical studies on the red, white and intermediate muscle fibers of some skeletal muscles. 3. Histochemical demonstration of oxidative enzymes, phosphorylase and glycogen in respiratory muscle fibers. Acta Med Okayama. 1966 Jun;20(3):137–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Stern L. Z., Curless R. G., Hannapel L. K. Ultrastructural fiber typing in normal and diseased human muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1975 May;25(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B., Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Gillespie C. A., Stempel K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2627–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. A., Berger A. J. A regional histochemical and electromyographic analysis of the cat respiratory diaphragm. Exp Neurol. 1979 Dec;66(3):636–649. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(79)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G., Saibene F. Contractile properties of the diaphragm in some mammals. Respir Physiol. 1970 Oct;10(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieck G. C., Roy R. R., Powell P., Blanco C., Edgerton V. R., Harper R. M. Muscle fiber type distribution and architecture of the cat diaphragm. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Nov;55(5):1386–1392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.5.1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström M., Kidman S., Larsén K. H., Angquist K. A. Z- and M-band appearance in different histochemically defined types of human skeletal muscle fibers. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jan;30(1):1–11. doi: 10.1177/30.1.7054271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallimann T., Eppenberger H. M. Localization and function of M-line-bound creatine kinase. M-band model and creatine phosphate shuttle. Cell Muscle Motil. 1985;6:239–285. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4723-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin H. Differences in histochemical attributes between diaphragm and hindleg muscles of the rat. Anat Rec. 1972 Jul;173(3):333–339. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091730308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]