Abstract
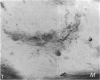
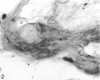
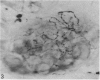
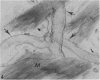
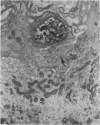
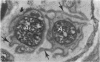
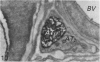
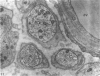
Substance P-like immunoreactive (SP-IR) nerves formed 2 types of relationships with nerve cells in the cardiac ganglia of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). The first type consisted of varicose SP-IR nerve fibres that ramified throughout the cardiac ganglia, forming a loose network with several nerve cell bodies. The second type consisted of several nerve cell bodies enwrapped by a dense pericellular (basket-like) investment of varicose SP-IR nerve fibres. Numerous SP-IR nerve fibres formed perivascular networks around the walls of the blood vessels within the cardiac ganglia and the muscle. The cardiac muscle cells were also innervated either by an isolated single varicose SP-IR nerve fibre or by complex networks. At the ultrastructural level, the substance P reaction product appeared to be associated with the microtubules and the outer mitochondrial membranes of labelled axons. Substance P reaction product was also localised on the membranes of small agranular vesicles of the labelled axon terminals. The SP-IR axons and axon terminals were closely related to the nerve cell bodies and they occurred either singly or in small groups. Most of the axons were enwrapped by a sheath from the adjacent Schwann cells which often exhibited pseudopodia-like processes. None of the axon terminals was observed to make synaptic contact with the cell bodies. However, a few axoaxonal contacts involving SP-IR and non-SP-IR axon terminals were present, the significance of which is not understood. Several axon terminals lay close to blood vessels, and may modulate the activity of these vessels.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bałuk P., Gabella G. Some intrinsic neurons of the guinea-pig heart contain substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 9;104(3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90587-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Franco-Cereceda A., Saria A., Lundberg J. M., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hökfelt T. Distribution and origin of substance P- and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive nerves in the guinea-pig heart. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;243(3):477–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00218054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren S., Moravec M., Moravec J. Catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes and neuropeptides in rat heart epicardial ganglia; an immunohistochemical study. Histochem J. 1990 Dec;22(12):667–676. doi: 10.1007/BF01047451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren S. Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in relation to the distribution of sympathetic nerve fibers in the heart conduction system. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1989 Mar;21(3):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(89)90743-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren S. The distribution of nerve fibers showing substance P-like immunoreactivity in the conduction system of the bovine heart: dense innervation in the atrioventricular bundle. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;179(5):485–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00319591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassall C. J., Burnstock G. Immunocytochemical localisation of neuropeptide Y and 5-hydroxytryptamine in a subpopulation of amine-handling intracardiac neurones that do not contain dopamine beta-hydroxylase in tissue culture. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 29;422(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90541-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassall C. J., Burnstock G. Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in cultured intrinsic neurones of the heart. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougland M. W., Hoover D. B. Detection of substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerve fibers in the heart of guinea-pigs but not rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Jul;8(3):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Rehfeld J., Elde R., Said S. Peptide neurons in the vagus, splanchnic and sciatic nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Dec;104(4):499–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papka R. E., Furness J. B., Della N. G., Costa M. Depletion by capsaicin of substance P-immunoreactivity and acetylcholinesterase activity from nerve fibres in the guinea-pig heart. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 18;27(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papka R. E., Urban L. Distribution, origin and sensitivity to capsaicin of primary afferent substance P-immunoreactive nerves in the heart. Acta Physiol Hung. 1987;69(3-4):459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechardt L., Aalto-Setälä K., Purjeranta M., Pelto-Huikko M., Kyösola K. Peptidergic innervation of human atrial myocardium: an electron microscopical and immunocytochemical study. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1986 Sep;17(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(86)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M., Forssmann W. G. Regulatory peptides (SP, NT, VIP, PHI, ENK) of autonomic nerves in the guinea pig heart. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1984;6(10-11):1867–1871. doi: 10.3109/10641968409046094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M., Weihe E., Carraway R. E., Leeman S. E., Forssmann W. G. Localization of neurotensin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea-pig heart: evidence derived by immunohistochemistry, radioimmunoassay and chromatography. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1785–1795. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M., Weihe E., Forssmann W. G. Substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the heart. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Dec;20(3):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Palay S. L. The fine structure of the later vestibular nucleus in the rat. II. Synaptic organization. Brain Res. 1970 Feb 17;18(1):93–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tay S. S., Williams T. H., Jew J. Y. Neurotensin immunoreactivity in the central nucleus of the rat amygdala: an ultrastructural approach. Peptides. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban L., Papka R. E. Origin of small primary afferent substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea-pig heart. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1985 Apr;12(4):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(85)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihe E., Reinecke M., Forssmann W. G. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the mammalian heart. Interrelation with neurotensin- and substance P-like immunoreactive nerves. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;236(3):527–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00217219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihe E., Reinecke M., Opherk D., Forssmann W. G. Peptidergic innervation (substance P) in the human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihe E., Reinecke M. Peptidergic innervation of the mammalian sinus nodes: vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neurotensin, substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 4;26(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Gulbenkian S., Merighi A., Kuhn D. M., Jahn R., Taylor K. M., Polak J. M. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural localisation of peptide-containing nerves and myocardial cells in the human atrial appendage. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Oct;254(1):155–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00220029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Gordon L., Banner N. R., Springall D. R., Rose M., Khagani A., Wallwork J., Yacoub M. H. Immunohistochemical demonstration of human cardiac innervation before and after transplantation. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):900–912. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., McGregor G. P., Bishop A. E., Bloom S. R. The distribution of substrate P-like immunoreactive nerves in the guinea-pig heart. Neuroscience. 1981;6(11):2193–2204. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]