Abstract
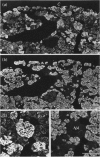
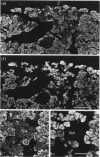
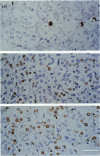
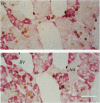
The adrenal medulla of mammals has a heterogeneous population of cells. In adults most are epithelial cells containing a particular type of cytoplasmic granule. Based on a variety of cytochemical and ultrastructural studies it is now accepted that 2 different adrenal medullary chromaffin cell types can be distinguished, i.e. noradrenaline (NA) and adrenaline (A) synthesising and storing cells. Other cell types present in the adrenal medulla include neuronal elements comprising either cell bodies or nerve fibres entering from outside the gland (extrinsic innervation). It is assumed that adrenal medullary cells have a limited life span, i.e. they are replaced after a certain period. Data on this replacement process are scarce. Recently, we initiated an investigation into this question using cytochemical procedures that enable the detection of DNA duplication to measure mitotic activity in individual cells. Female Sprague-Dawley rats aged 22-36 wk received a single i.p. injection of BrdU or BrdU was administered continuously via an implanted mini-osmotic pump. Cell nuclei that had incorporated BrdU were demonstrated using an indirect immunoperoxidase staining technique. At 1 h after a single injection, 0.46 +/- 0.07% of the adrenal medullary (chromaffin) cells were labelled. This increased to 0.77 +/- 0.08% after 12 h with no further increase during the next 7-8 d. With continuous infusion of BrdU the fraction of labelled cells increased gradually to about 40% after 73 d (the longest period studied). These results show that in adult rats adrenal medullary cells are able to divide, although at a slow rate (renewal rate of about 1%/day).
Full text
PDF


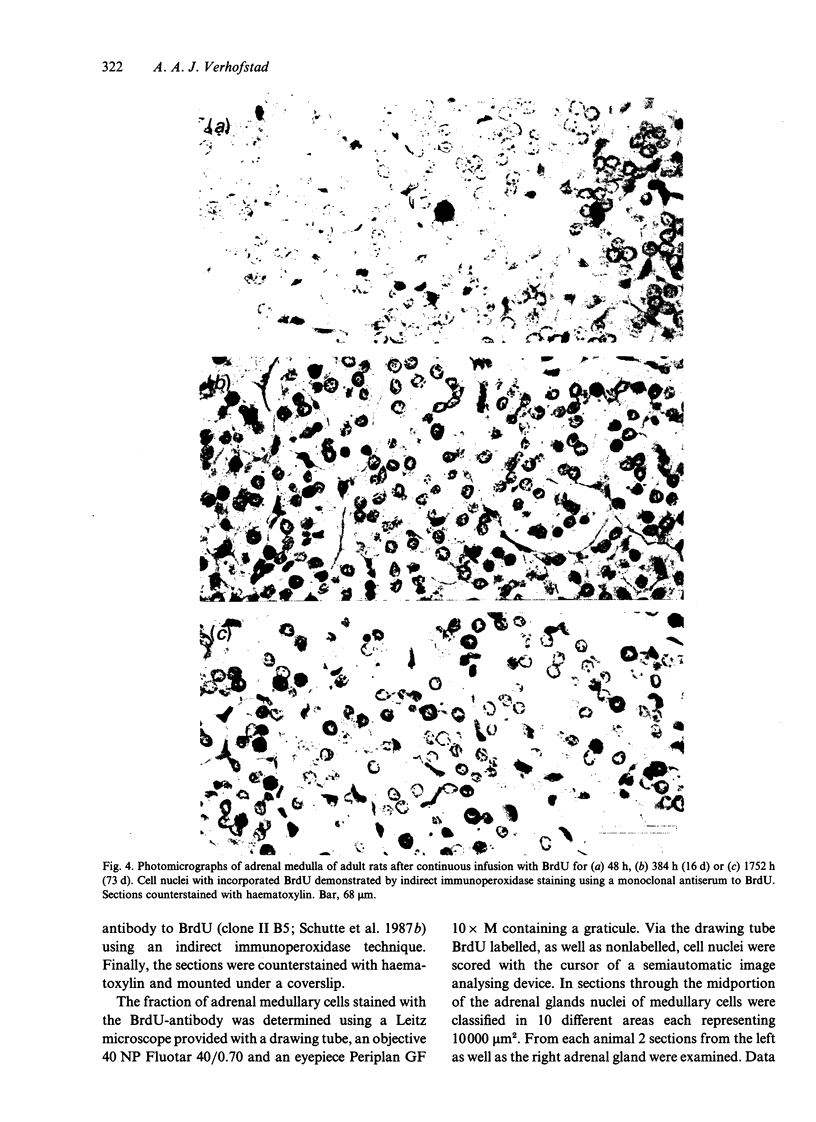




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alison M. R., Sarraf C. E. Apoptosis: a gene-directed programme of cell death. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1992 Jan;26(1):25–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H. The activity of l(-)-dopa decarboxylase. J Physiol. 1942 Nov 30;101(3):337–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1942.sp003988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E. (ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE RAT ADRENAL MEDULLA. I. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION OF CHROMAFFIN CELLS IN THE NORMAL ADRENAL MEDULLA.) J Anat. 1965 Apr;99:231–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E., PYPER A. S., HOPWOOD D. A METHOD FOR DIFFERENTIATING BETWEEN NORADRENALINE- AND ADRENALINE-STORING CELLS IN THE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1240–1242. doi: 10.1038/2011240b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Hopwood D. The mechanism of the differential staining reaction for adrenaline-and noreadrenaline-storing granules in tissues fixed in glutaraldehyde. J Anat. 1966 Apr;100(Pt 2):227–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E. The natural history of the chromaffin cell--twenty-five years on the beginning. Arch Histol Cytol. 1989;52 (Suppl):331–341. doi: 10.1679/aohc.52.suppl_331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Tomlinson A. The development and maturation of adrenal medullary chromaffin cells of the rat in vivo: a descriptive and quantitative study. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):419–438. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERANKO O. Fluorescing islets, adrenaline and noradrenaline in the adrenal medulla of some common laboratory animals. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1955;33(3):278–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G., Leif R. C., Ingram D. J., Castro A. The use of antibody specific for bromodeoxyuridine for the immunofluorescent determination of DNA replication in single cells and chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90612-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: A new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7123245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARP N. A., HOKFELT B. Evidence of adrenaline and noradrenaline in separate adrenal medullary cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Dec 31;30(1):55–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Levison D. A. Review: assessment of cell proliferation in histological material. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Mar;43(3):184–192. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Woods A. L. Immunohistochemical markers of cellular proliferation: achievements, problems and prospects. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1990 Nov;23(6):505–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1990.tb01343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Koike M., Matsutani M., Hoshino T. Effects of fixation time and enzymatic digestion on immunohistochemical demonstration of bromodeoxyuridine in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 May;36(5):511–514. doi: 10.1177/36.5.3282006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Joh T. H. Immunohistochemical localization of three catecholamine synthesizing enzymes: aspects on methodology. Histochemie. 1973;33(3):231–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00274236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurecka W., Lassmann H., Hörandner H. The proliferation of adrenal medullary cells in newborn and adult mice. A light and electron microscopic autoradiographic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 May 29;189(2):305–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00209279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Ohashi T., Uchida T., Nakao K., Imura H., Yanaihara N., Verhofstad A. A. Co-storage of adrenaline and noradrenaline with Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 and Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 in chromaffin cells of hamster adrenal medulla. Arch Histol Jpn. 1984 Aug;47(3):319–336. doi: 10.1679/aohc.47.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P. CLASSIFICATION OF CELL POPULATIONS ON THE BASIS OF THEIR PROLIFERATIVE BEHAVIOR. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 May;14:119–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P., WALKER B. E. Renewal of cell populations. Physiol Rev. 1956 Apr;36(2):255–276. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Sisson J. C., Shapiro B., Verhofstad A. A. Immunohistochemical localization of epinephrine, norepinephrine, catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes, and chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells and tumors. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hamberger B., Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Granberg P. O., Efendić S., Terenius L., Goldstein M., Luft R. Enkephalin- and somatostatin-like immunoreactivities in human adrenal medulla and pheochromocytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4079–4083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MESSIER B., LEBLOND C. P. Cell proliferation and migration as revealed by radioautography after injection of thymidine-H3 into male rats and mice. Am J Anat. 1960 May;106:247–285. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001060305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvaldi G., Mencacci P., Viola-Magni M. P. Mitoses in the adrenal medullary cells. Experientia. 1968 May 15;24(5):475–476. doi: 10.1007/BF02144402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvaldi G., Viola-Magni M. P. DNA turnover in adrenal medullary cells of different strains of rats and its enhancement after intermittent exposure to cold. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1972 Mar;5(2):103–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1972.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monkhouse W. S., Fussell I. A fraction of labelled mitoses study on adrenal chromaffin tissue in the newborn mouse and the effect of hydrocortisone. J Anat. 1988 Apr;157:105–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Schäfer E. A. The Physiological Effects of Extracts of the Suprarenal Capsules. J Physiol. 1895 Jul 18;18(3):230–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1895.sp000564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the Physiological Society, March 10, 1894. No. I. J Physiol. 1894 Apr 17;16(3-4):i–viii. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1894.sp000503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B., Reynders M. M., Bosman F. T., Blijham G. H. Effect of tissue fixation on anti-bromodeoxyuridine immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Nov;35(11):1343–1345. doi: 10.1177/35.11.3116075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B., Reynders M. M., Bosman F. T., Blijham G. H. Studies with anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibodies: II. Simultaneous immunocytochemical detection of antigen expression and DNA synthesis by in vivo labeling of mouse intestinal mucosa. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Mar;35(3):371–374. doi: 10.1177/35.3.3546484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., DeLellis R. A., Nunnemacher G., Wolfe H. J. Acute stimulation of chromaffin cell proliferation in the adult rat adrenal medulla. Lab Invest. 1988 Jun;58(6):733–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., McClain R. M., Childers H., Downing J. Neurogenic signals regulate chromaffin cell proliferation and mediate the mitogenic effect of reserpine in the adult rat adrenal medulla. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):374–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Ruzicka L. A., Donahue S. R., DeLellis R. A. Chromaffin cell proliferation in the adult rat adrenal medulla. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Ruzicka L. A., Donahue S. R., DeLellis R. A. Pharmacological stimulation of chromaffin cell proliferation in the adult adrenal medulla. Arch Histol Cytol. 1989;52 (Suppl):209–216. doi: 10.1679/aohc.52.suppl_209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. IV. Innervation of the rat adrenal medulla from birth to old age. A descriptive and quantitative morphometric and biochemical study of the innervation of chromaffin cells and adrenal medullary neurons in Wistar rats. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:209–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Durbin J., Coupland R. E. A quantitative analysis of rat adrenal chromaffin tissue: morphometric analysis at tissue and cellular level correlated with catecholamine content. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Colenbrander B. Immunohistochemical and biochemical analysis of the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells in the adrenal medulla of the rat and pig. Arch Histol Cytol. 1989;52 (Suppl):351–360. doi: 10.1679/aohc.52.suppl_351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Parker T. R., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00214536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Jonsson G. Immunohistochemical and neurochemical evidence for the presence of serotonin in the adrenal medulla of the rat. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1443–1453. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Lensen W. F. On the occurrence of lymphatic vessels in the adrenal gland of the white rat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1973;84(4):475–483. doi: 10.1159/000143955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viola-Magni M. P. A radioautographic study with H3-thymidine on adrenal medulla nuclei of rats intermittently exposed to cold. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jan;28(1):9–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Hazum E., Chang K. J. Opiate-like materials in the adrenal medulla: evidence for storage and secretion with catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):1101–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Wilson S. P. The adrenal chromaffin cell as a model to study the co-secretion of enkephalins and catecholamines. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Jan;7(1):41–58. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. Growth and Mitosis in the Mouse Suprarenal. J Anat. 1933 Apr;67(Pt 3):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman J. H., Jonker R. R., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van Dierendonck J. H. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jan;41(1):7–12. doi: 10.1177/41.1.7678025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. C., Woods A. L., Levison D. A. The assessment of cellular proliferation by immunohistochemistry: a review of currently available methods and their applications. Histochem J. 1992 Mar;24(3):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01047461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]