Abstract
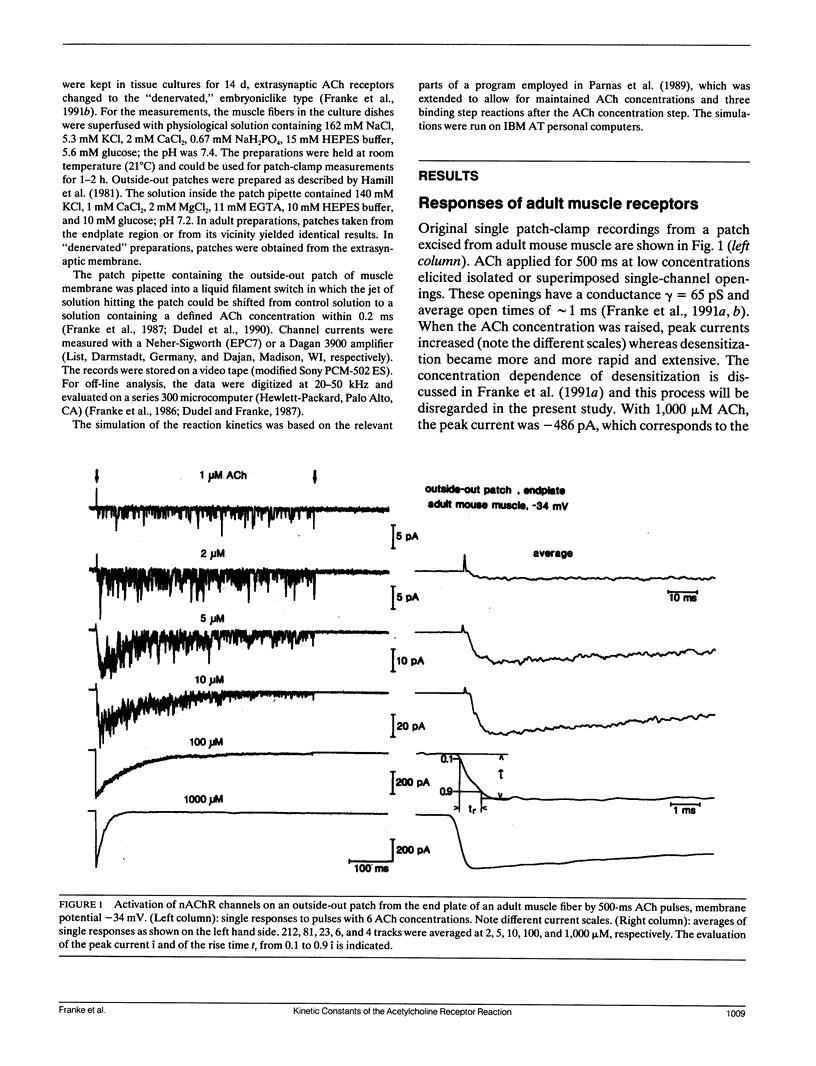
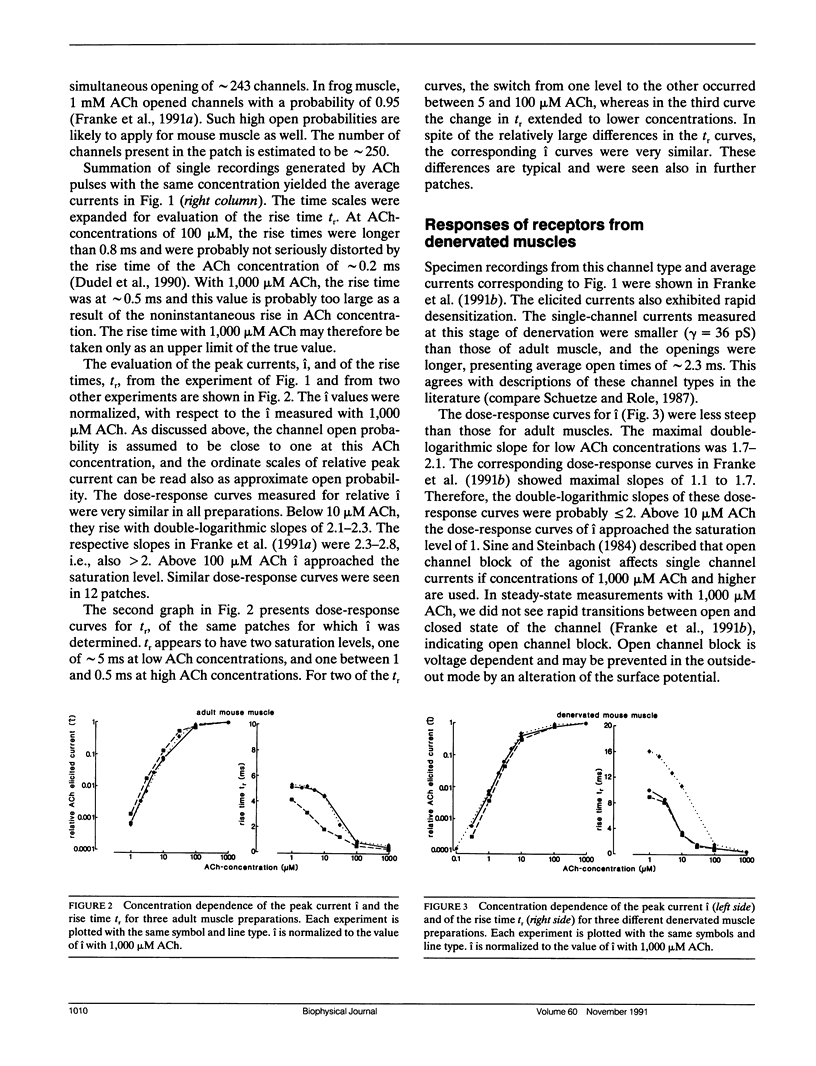
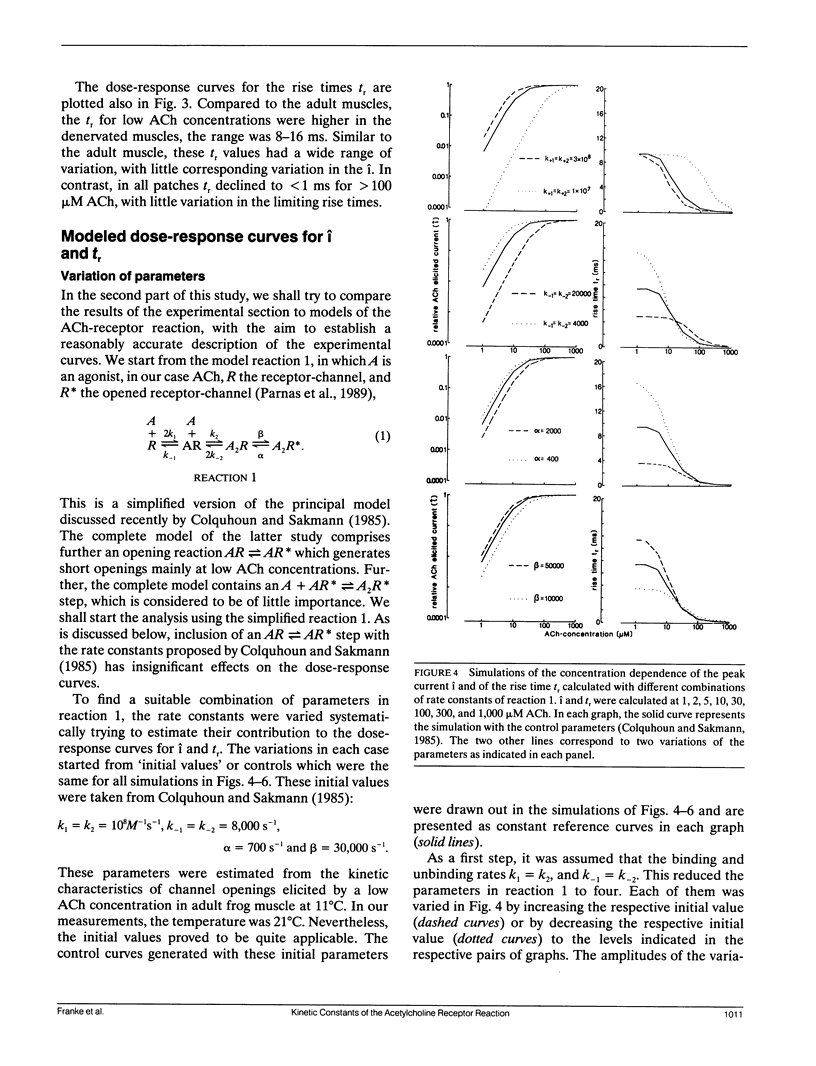
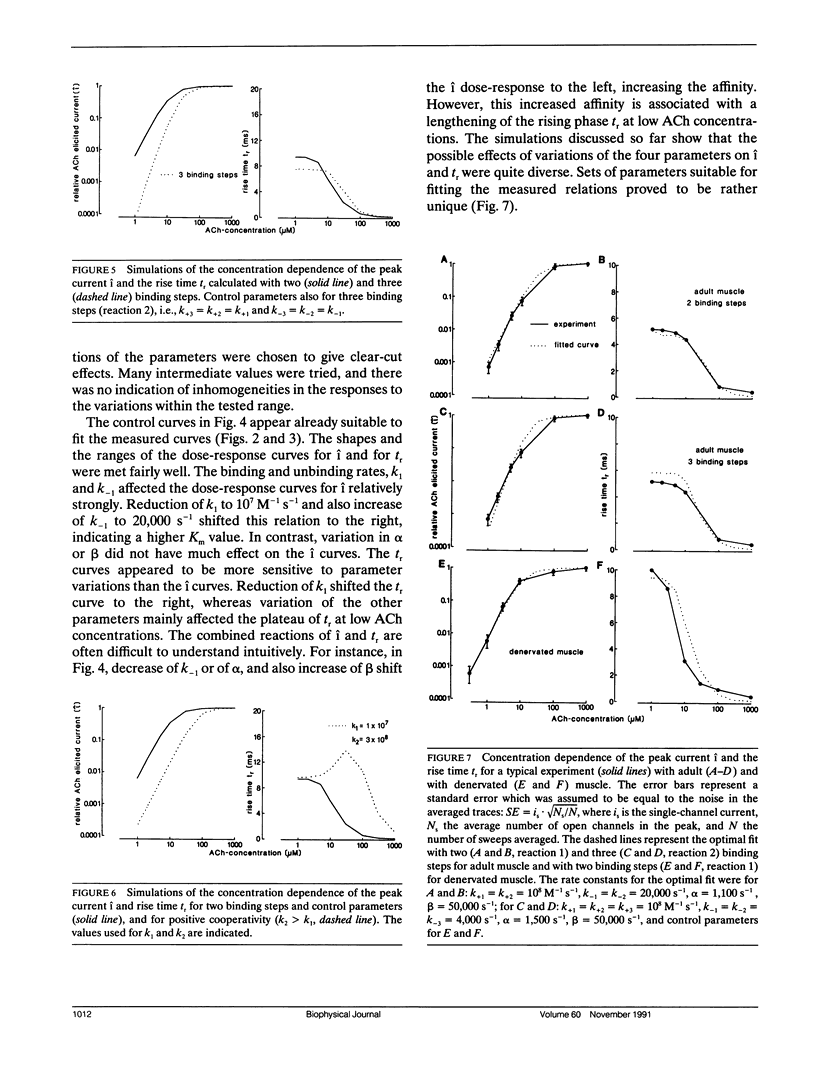
Outside-out patches of enzymatically dissociated adult and denervated mouse muscle fibers were superfused repetitively by pulses of acetylcholine (ACh) containing solution. Up to 300 channels opened simultaneously 300 microseconds after the beginning of a 1,000 microM ACh pulse corresponding to a peak current i of almost -1 nA. Single responses to ACh were averaged and the concentration dependence of i and of the rise time tr from 0.1 i to 0.9 i was measured. In adult receptors, i increased proportional to the second to third power of ACh concentration, whereas in embryonic-type receptors it was proportional to the first to the second power. tr increased from approximately 0.3 ms at 1,000 microM ACh to a plateau value of approximately 5 ms for adult and of approximately 10 ms for embryoniclike receptors at concentrations less than 10 microM ACh. The concentration dependence of i and tr was simulated using the standard model of ACh binding with different combinations of rate constants and two and three binding sites for ACh. The calculated curves were compared to the measurements and a set of well fitting rate constants was determined for adult and embryoniclike receptors. Three binding sites for ACh were necessary to fit the dose response for i for adult receptors. A method for deriving rate constants in a model of ACh-receptor interaction is described that avoids analysis of open-closed kinetics of single channels, which in rapid systems, as the ones studied here, are at the limit of the frequency response of the current measurement.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Single-channel currents from acetylcholine receptors in embryonic chick muscle. Kinetic and conductance properties of gaps within bursts. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):187–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84147-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Interaction at end-plate receptors between different choline derivatives. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):369–381. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Leibowitz M. D. Acetylcholine receptor kinetics. A description from single-channel currents at snake neuromuscular junctions. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84515-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. An analysis of the dose-response relationship at voltage-clamped frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:421–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K., Sterz R. Determination of dose-response curves by quantitative ionophoresis at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H. Rapid activation, desensitization, and resensitization of synaptic channels of crayfish muscle after glutamate pulses. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):533–545. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82569-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C. Single glutamate-gated synaptic channels at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. II. Dependence of channel open time on glutamate concentration. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Mar;408(3):307–314. doi: 10.1007/BF02181474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Dudel J. Liquid filament switch for ultra-fast exchanges of solutions at excised patches of synaptic membrane of crayfish muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 15;77(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90586-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The mode of action of nicotine and curari, determined by the form of the contraction curve and the method of temperature coefficients. J Physiol. 1909 Dec 23;39(5):361–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1909.sp001344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Lecar H., Askanas V., Engel W. K. Single cholinergic receptor channel currents in cultured human muscle. J Neurosci. 1982 Oct;2(10):1465–1473. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-10-01465.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo F., Schuetze S. M. Kinetic differences between embryonic- and adult-type acetylcholine receptors in rat myotubes. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:267–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Kinetic parameters for acetylcholine interaction in intact neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Knight D. E. A method for making solution changes in the sub-millisecond range at the tip of a patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):589–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00580996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Flashner M., Spira M. E. Sequential model to describe the nicotinic synaptic current. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):875–884. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82886-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Methfessel C., Mishina M., Takahashi T., Takai T., Kurasaki M., Fukuda K., Numa S. Role of acetylcholine receptor subunits in gating of the channel. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):538–543. doi: 10.1038/318538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze S. M., Role L. W. Developmental regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:403–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Claudio T., Sigworth F. J. Activation of Torpedo acetylcholine receptors expressed in mouse fibroblasts. Single channel current kinetics reveal distinct agonist binding affinities. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):395–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by high concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:325–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by low concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:129–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


