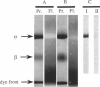
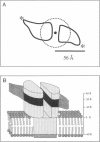
Abstract
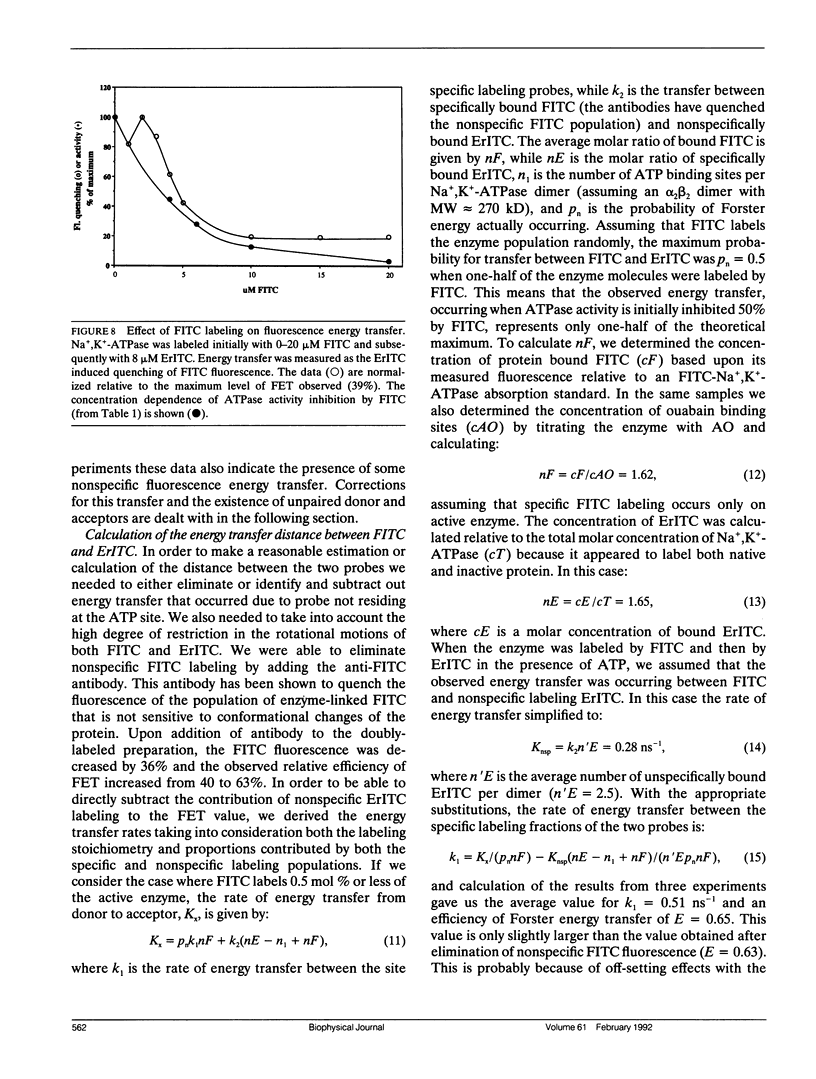
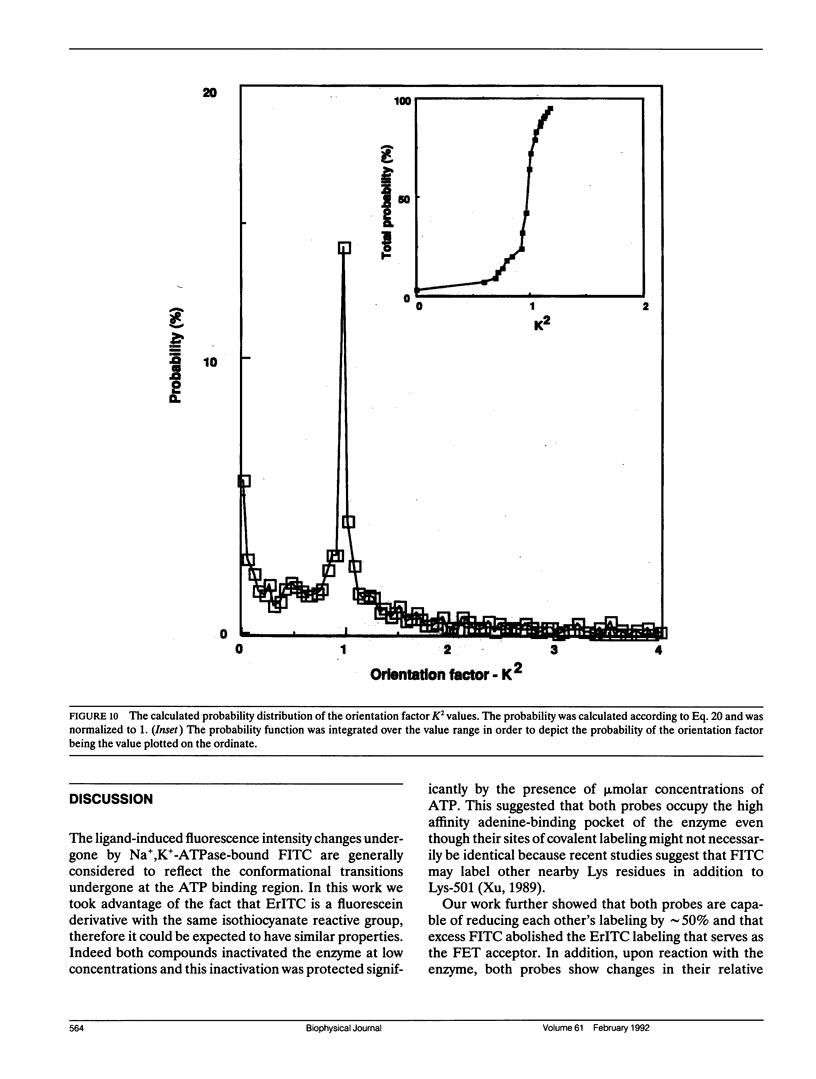
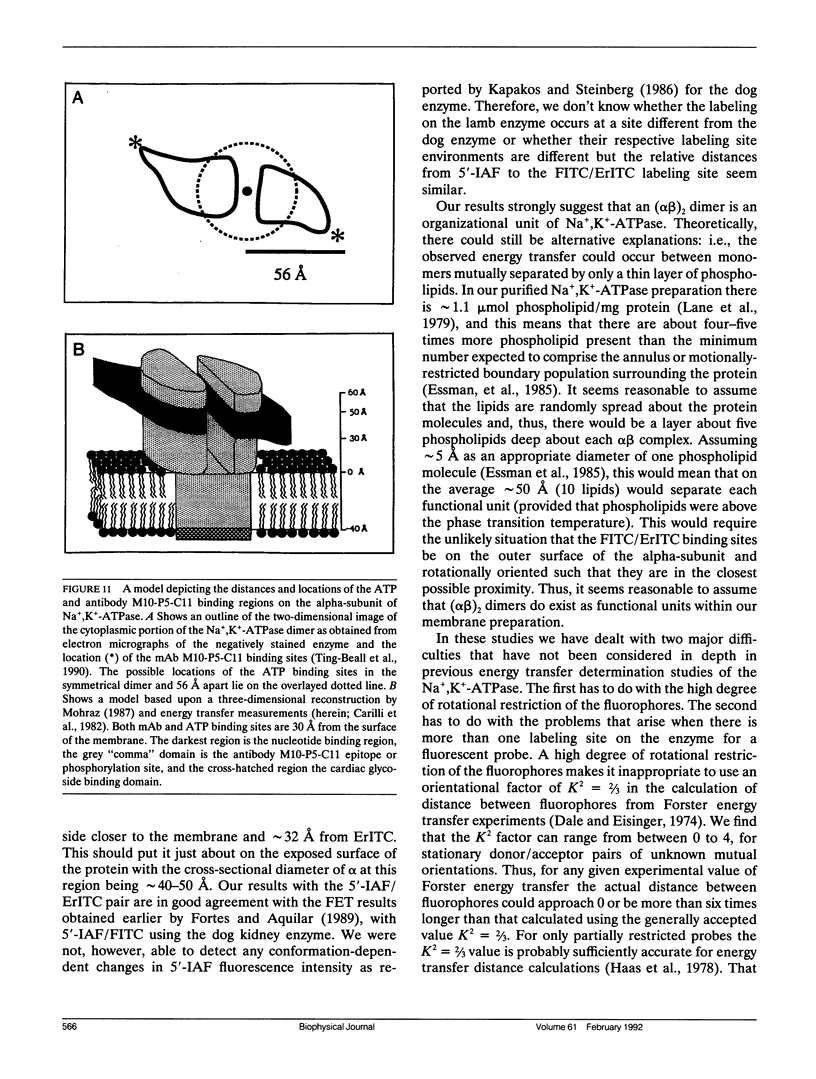
The oligomeric nature of the purified lamb kidney Na+,K(+)-ATPase was investigated by measuring the fluorescence energy transfer between catalytic (alpha) subunits following sequential labeling with fluorescein 5'-isothiocyanate (FITC) and erythrosin 5'-isothiocyanate (ErITC). Although these two probes had different spectral responses upon reaction with the enzyme, our studies suggest that a sizeable proportion of their binding occurs at the same ATP protectable, active site domain of alpha. Fluorescence energy transfer (FET) from donor (FITC) to acceptor (ErITC) revealed an apparent 56 A distance between the putative ATP binding sites of alpha subunits, which is consistent with (alpha beta)2 dimers rather than randomly spaced alpha beta heteromonomers. In this work, methods were introduced to eliminate the contribution of nonspecific probe labeling to FET values and to determine the most probable orientation factor (K2) for these rigidly bound fluorophores. FET measurements between anthroylouabain/ErITC, 5'-iodoacetamide fluorescein (5'IAF)/ErITC, and TNP-ATP/FITC, donor/acceptor pairs were also made. Interestingly, none of these distances were affected by ligand-dependent changes in enzyme conformation. These results and those from electron microscopy imaging (Ting-Beall et al. 1990. FEBS Lett. 265:121) suggest a model in which ATP binding sites of (alpha beta)2 dimers are 56 A apart, and reside 30 A from the intracellular surface of the membrane contiguous with the phosphorylation domain.
Full text
PDF


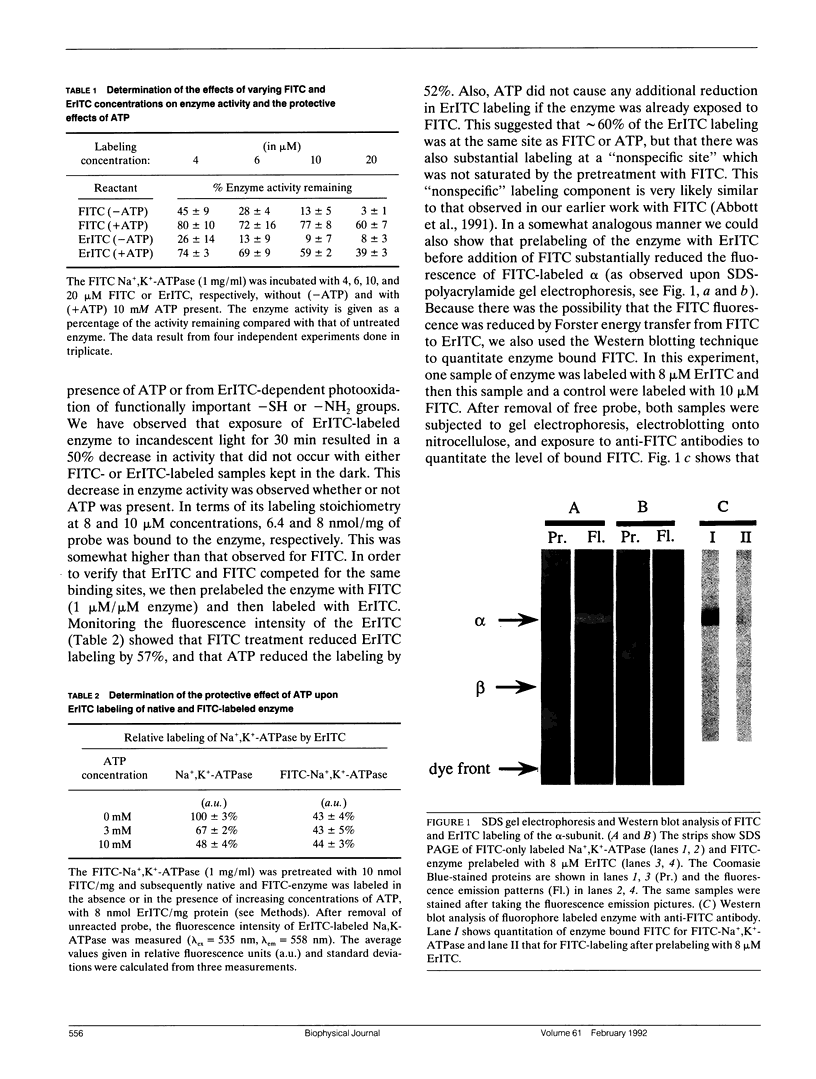
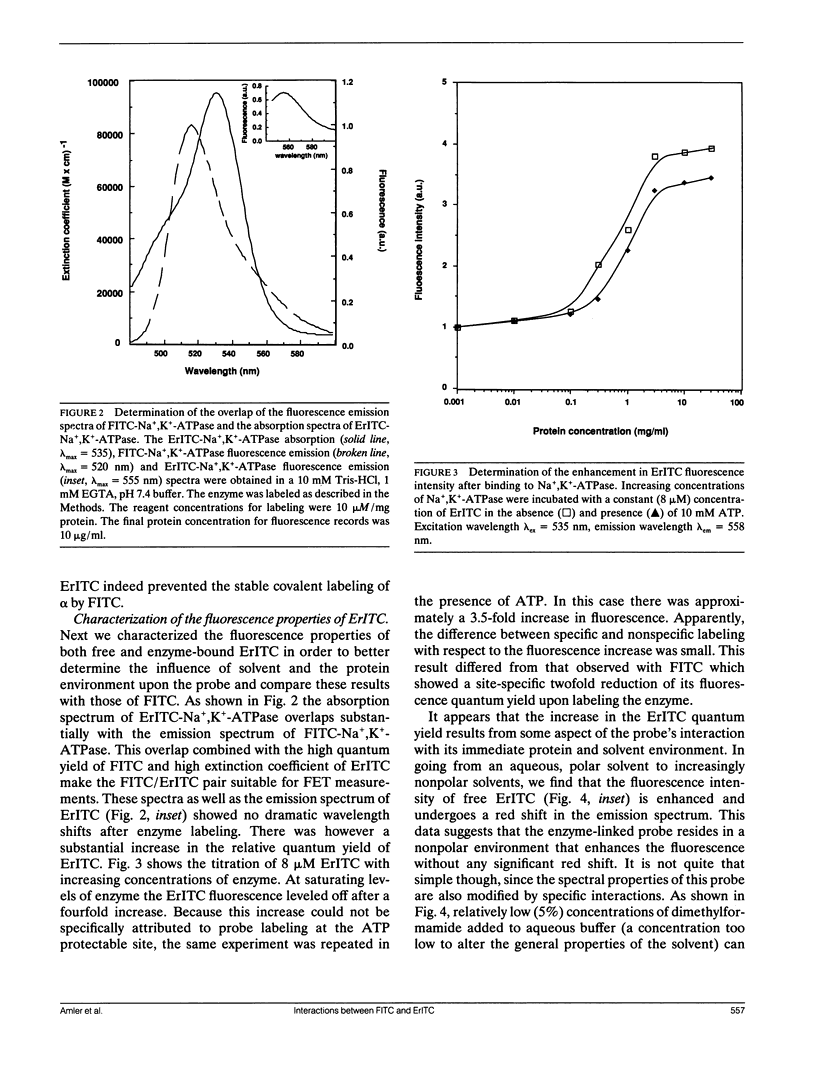




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott A. J., Amler E., Ball W. J., Jr Immunochemical and spectroscopic characterization of two fluorescein 5'-isothiocyanate labeling sites on Na+,K(+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1692–1701. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball W. J., Jr Uncoupling of ATP binding to Na+,K+-ATPase from its stimulation of ouabain binding: studies of the inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase by a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7155–7162. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall H. C., Hastings D. F., Ting-Beall H. P. Digital image analysis of two-dimensional Na,K-ATPase crystals: dissimilarity between pump units. J Microsc. 1989 Apr;154(Pt 1):71–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1989.tb00569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmachu W., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum studied by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3904–3914. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherus J. R., Jacobsen L., Jørgensen P. L. Soluble and enzymatically stable (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from mammalian kidney consisting predominantly of protomer alpha beta-units. Preparation, assay and reconstitution of active Na+, K+ transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 10;731(2):290–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carilli C. T., Farley R. A., Perlman D. M., Cantley L. C. The active site structure of Na+- and K+-stimulated ATPase. Location of a specific fluorescein isothiocyanate reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5601–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavieres J. D. Association of biochemical functions with specific subunit arrangements in purified Na, K-ATPase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268A:175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. E., Eisinger J. Intramolecular energy transfer and molecular conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):271–273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of lipid-protein interactions in (Na+,K+)-ATPase membranes from rectal glands of Squalus acanthias. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1386–1393. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley R. A., Tran C. M., Carilli C. T., Hawke D., Shively J. E. The amino acid sequence of a fluorescein-labeled peptide from the active site of (Na,K)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9532–9535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortes P. A. A fluorometric method for the determination of functional (Na,K)-ATPase and cardiac glycoside receptors. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 1;158(2):454–462. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90575-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortes P. A., Aguilar R. Distances between 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein and the ATP and ouabain sites of (Na,K)-ATPase determined by fluorescence energy transfer. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268A:197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. L., Ball W. J., Jr Determination of monoclonal antibody-induced alterations in Na+/K+-ATPase conformations using fluorescein-labeled enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 16;995(1):42–53. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingold M. P., Rigaud J. L., Champeil P. Fluorescence energy transfer between ATPase monomers in sarcoplasmic reticulum reconstituted vesicles. Biochimie. 1981 Nov-Dec;63(11-12):923–925. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Katchalski-Katzir E., Steinberg I. Z. Effect of the orientation of donor and acceptor on the probability of energy transfer involving electronic transitions of mixed polarization. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5064–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Mimura K., Matsui H., Takagi T. Minimum enzyme unit for Na+/K+-ATPase is the alpha beta-protomer. Determination by low-angle laser light scattering photometry coupled with high-performance gel chromatography for substantially simultaneous measurement of ATPase activity and molecular weight. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 7;983(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert H., Skriver E., Kavéus U., Maunsbach A. B. Coexistence of different forms of Na,K-ATPase in two-dimensional membrane crystals. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80978-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Nørby J. G. Thallium binding to native and radiation-inactivated Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 3;985(3):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Fortes P. A. Fluorescence studies of the sodium and potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase labeled with fluorescein mercuric acetate and anthroylouabain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):459–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Andersen J. P. Structural basis for E1-E2 conformational transitions in Na,K-pump and Ca-pump proteins. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(2):95–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Mechanism of the Na+, K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):27–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapakos J. G., Steinberg M. 5-Iodoacetamidofluorescein-labeled (Na,K)-ATPase. Steady-state fluorescence during turnover. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2090–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J. Characterization of conformational changes in (Na,K) ATPase labeled with fluorescein at the active site. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1980 Aug;12(3-4):111–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00744678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H., Maliwal B. P. Time-resolved fluorescence anisotropies of diphenylhexatriene and perylene in solvents and lipid bilayers obtained from multifrequency phase-modulation fluorometry. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):376–383. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Laczko G., Cherek H., Gratton E., Limkeman M. Analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics from variable-frequency phase shift and modulation data. Biophys J. 1984 Oct;46(4):463–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84043-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. K., Potter J. D., Collins J. H. Large-scale purification of Na,K-ATPase and its protein subunits from lamb kidney medulla. Prep Biochem. 1979;9(2):157–170. doi: 10.1080/00327487908061681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Fortes P. A. Spatial relationship and conformational changes between the cardiac glycoside site and beta-subunit oligosaccharides in sodium plus potassium activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8133–8141. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough A. A., Geering K., Farley R. A. The sodium pump needs its beta subunit. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1598–1605. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2156741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Krstenansky J. L., Owen T. J., Eftink M. R., Hagaman K. A. Effect of micelle diameter on tryptophan dynamics in an amphipathic helical peptide in phosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8403–8410. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E. G., Fortes P. A. Characterization of 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrocyclohexadienylidine)adenosine 5'-triphosphate as a fluorescent probe of the ATP site of sodium and potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. Determination of nucleotide binding stoichiometry and ion-induced changes in affinity for ATP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2346–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohraz M., Simpson M. V., Smith P. R. The three-dimensional structure of the Na,K-ATPase from electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):1–8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørby J. G., Jensen J. A model for the stepwise radiation inactivation of the alpha 2-dimer of Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19548–19558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi P., Ellory J. C. Radiation inactivation of (Na,K)-ATPase, an enzyme showing multiple radiation-sensitive domains. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14895–14907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachence J. M., Edelman I. S., Schoenborn B. P. Low-angle neutron scattering analysis of Na/K-ATPase in detergent solution. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):702–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papp S., Pikula S., Martonosi A. Fluorescence energy transfer as an indicator of Ca2+-ATPase interactions in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):205–220. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83326-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedemonte C. H., Kaplan J. H. Chemical modification as an approach to elucidation of sodium pump structure-function relations. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C1–23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Allen J. C., Harigaya S. Possible involvement of cardiac Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase in the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Jul;168(1):31–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver E., Maunsbach A. B., Jørgensen P. L. Formation of two-dimensional crystals in pure membrane-bound Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M., Karlish S. J. Studies on conformational changes in Na,K-ATPase labeled with 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2726–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Tosa H., Suzuki K., Kamo Y. Microenvironment of two different extrinsic fluorescence probes in Na+,K+-ATPase changes out of phase during sequential appearance of reaction intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12943–12947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting-Beall H. P., Beall H. C., Hastings D. F., Friedman M. L., Ball W. J., Jr Identification of monoclonal antibody binding domains of Na+,K(+)-ATPase by immunoelectron microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80899-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Inesi G. Structural effects of substrate utilization on the adenosinetriphosphatase chains of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3254–3259. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu K. Y. Any of several lysines can react with 5'-isothiocyanatofluorescein to inactivate sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5764–5772. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampighi G., Kyte J., Freytag W. Structural organization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in purified membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1851–1864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]