Abstract
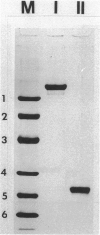
Sedimentation equilibrium and velocity studies were performed with turkey gizzard myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and telokin, a small protein apparently corresponding to the sequence of the COOH-terminal end of MLCK. The measurements carried out with MLCK give values for the monomer molecular weight (M(r)), sedimentation coefficient (S20 degrees,w), and virial coefficient (A2) of 108,000, 3.74 S, and -1.95 x 10(-4) mol.ml.g-2, respectively. In the case of telokin, M(r) = 18,500; S20 degrees, w = 1.63 S; and A2 = 5.81 x 10(-4)mol.ml.g-2. Combination of the results of the two kinds of experiment shows that MLCK is a rod-shaped molecule (a/b = 18.9) with a Stoke's radius of 69 A. Telokin is also elongated (a/b = 8.3) with a Stoke's radius of 29 A. MLCK apparently exhibits self-association, with 15% of the protein sedimenting as a dimer in the experiments.
Full text
PDF

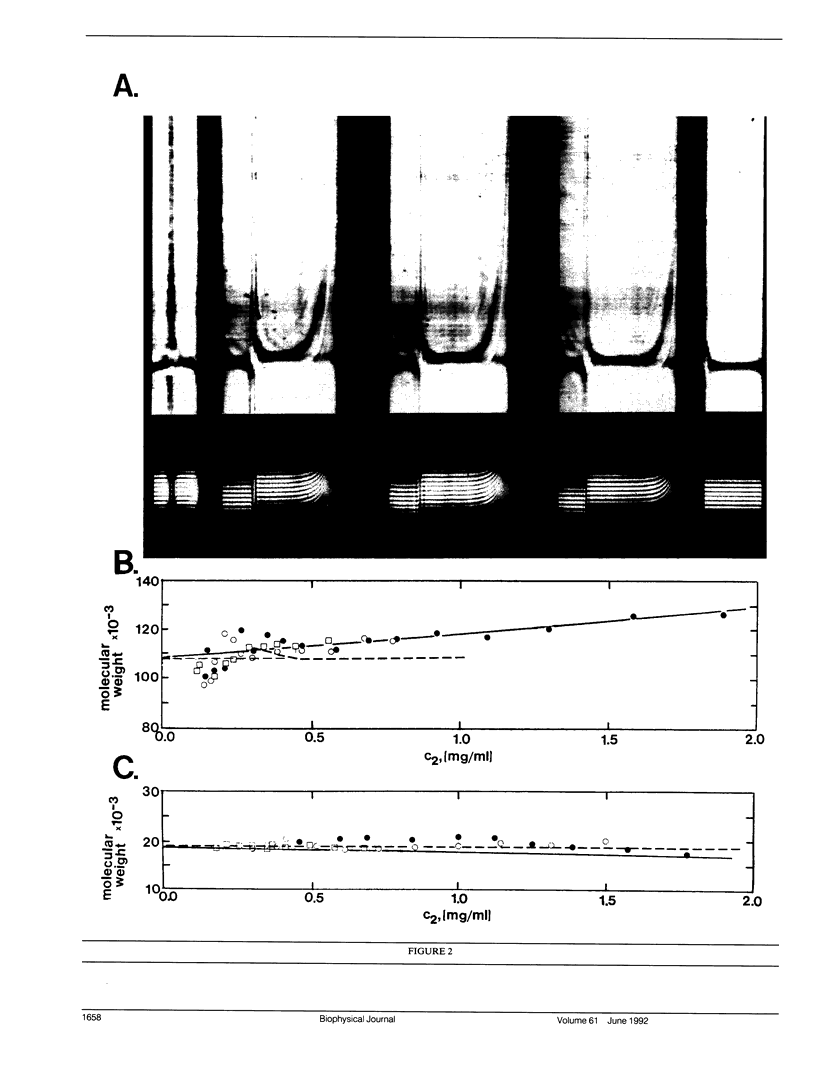

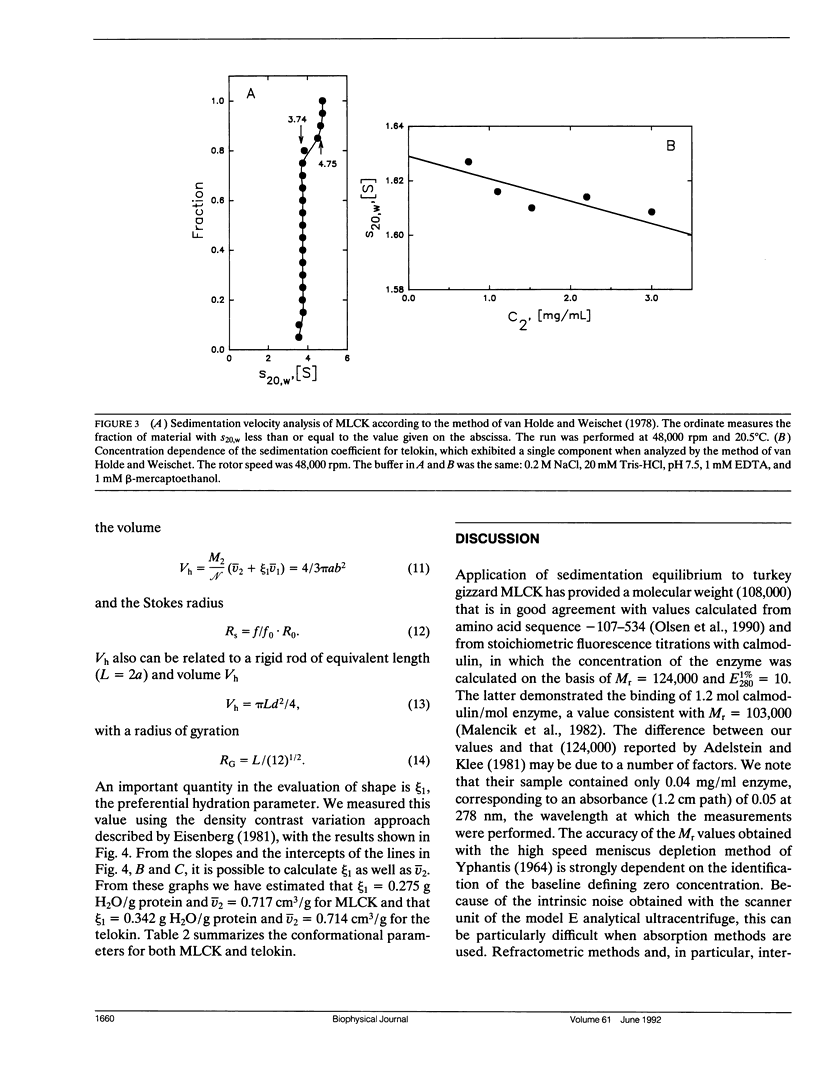


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Purification and characterization of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7501–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babul J., Stellwagen E. Measurement of protein concentration with interferences optics. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Aromatorio D., Sherry J. M., Hartshorne D. J. Composition of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 24;78(4):1263–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91429-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Felsenfeld G. Hydrodynamic studies of the interaction between nucleosome core particles and core histones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):537–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H. Forward scattering of light, X-rays and neutrons. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 May;14(2):141–172. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Siemankowski R. F. Regulation of smooth muscle actomyosin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:519–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Dabrowska R., Guerriero V., Jr, Hartshorne D. J. Identification in turkey gizzard of an acidic protein related to the C-terminal portion of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13971–13974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Dingwall C., Maier G., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of a karyophilic, histone-binding protein: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and expression of nuclear protein N1/N2 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3547–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R., Bohnert J. L., Shalitin Y. Functional interactions between smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase and calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4031–4039. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Ausio J., Byles C. E., Modrell B., Anderson S. R. Turkey gizzard caldesmon: molecular weight determination and calmodulin binding studies. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8227–8233. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Zhao Z. Z., Anderson S. R. Determination of dityrosine, phosphotyrosine, phosphothreonine, and phosphoserine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1990 Feb 1;184(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90693-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr G. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Shape and substructure of skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4316–4326. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. J., Pearson R. B., Needleman D. S., Hurwitz M. Y., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Regulatory and structural motifs of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. The molecular weights of vertebrate histones exploiting a modified sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoretic method. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7557–7560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J. Protein volumes and hydration effects. The calculations of partial specific volumes, neutron scattering matchpoints and 280-nm absorption coefficients for proteins and glycoproteins from amino acid sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):169–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Hudlicka O., Patchell V. B., Westwood S. A. Role of myosin light chain kinase in muscle contraction. Fed Proc. 1984 Dec;43(15):3015–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Studies of self-associating systems by equilibrium ultracentrifugation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 7;164(1):245–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano E., Maki M., Mori H., Hatanaka M., Marti T., Titani K., Kannagi R., Ooi T., Murachi T. Pig heart calpastatin: identification of repetitive domain structures and anomalous behavior in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1964–1972. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yphantis D. A., Roark D. E. Equilibrium centrifugation of nonideal systems. Molecular weight moments for removing the effects of nonideality. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):2925–2934. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z. Z., Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R. Protein-induced inactivation and phosphorylation of rabbit muscle phosphofructokinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2204–2216. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]