Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
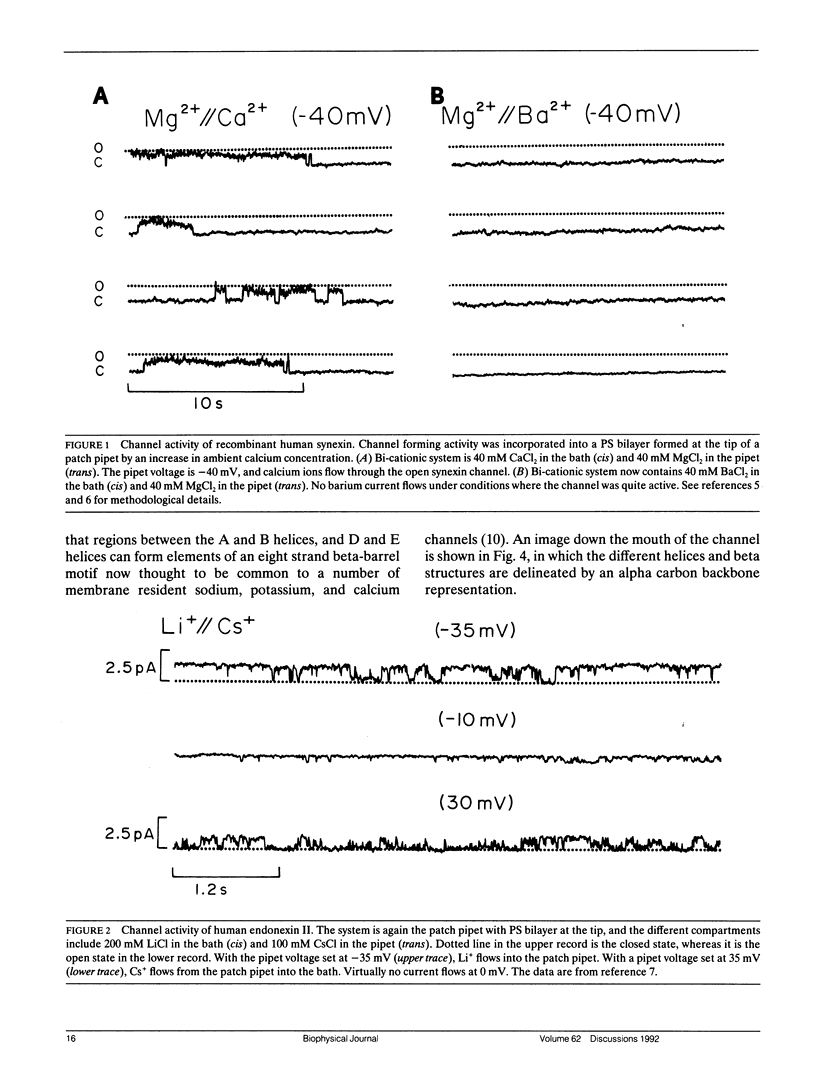
- Burns A. L., Magendzo K., Shirvan A., Srivastava M., Rojas E., Alijani M. R., Pollard H. B. Calcium channel activity of purified human synexin and structure of the human synexin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3798–3802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Römisch J., Paques E. P. The crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V, an anticoagulant protein that binds to calcium and membranes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
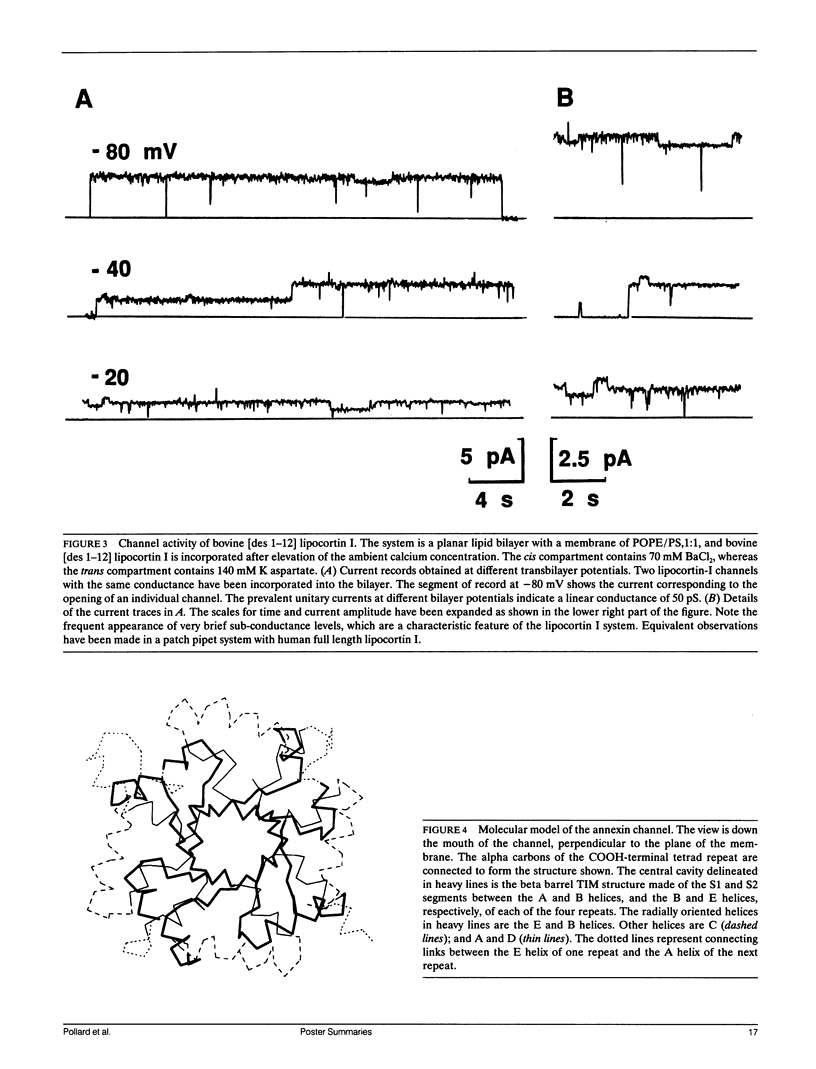
- Pollard H. B., Burns A. L., Rojas E. Synexin (annexin VII): a cytosolic calcium-binding protein which promotes membrane fusion and forms calcium channels in artificial bilayer and natural membranes. J Membr Biol. 1990 Aug;117(2):101–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01868677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E., Burns A. L. Synexin and chromaffin granule membrane fusion. A novel "hydrophobic bridge" hypothesis for the driving and directing of the fusion process. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:524–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E. Ca2+-activated synexin forms highly selective, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E., Pastor R. W., Rojas E. M., Guy H. R., Burns A. L. Synexin: molecular mechanism of calcium-dependent membrane fusion and voltage-dependent calcium-channel activity. Evidence in support of the "hydrophobic bridge hypothesis" for exocytotic membrane fusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:328–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Pollard H. B., Haigler H. T., Parra C., Burns A. L. Calcium-activated endonexin II forms calcium channels across acidic phospholipid bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21207–21215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Pollard H. B. Membrane capacity measurements suggest a calcium-dependent insertion of synexin into phosphatidylserine bilayers. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


