Abstract
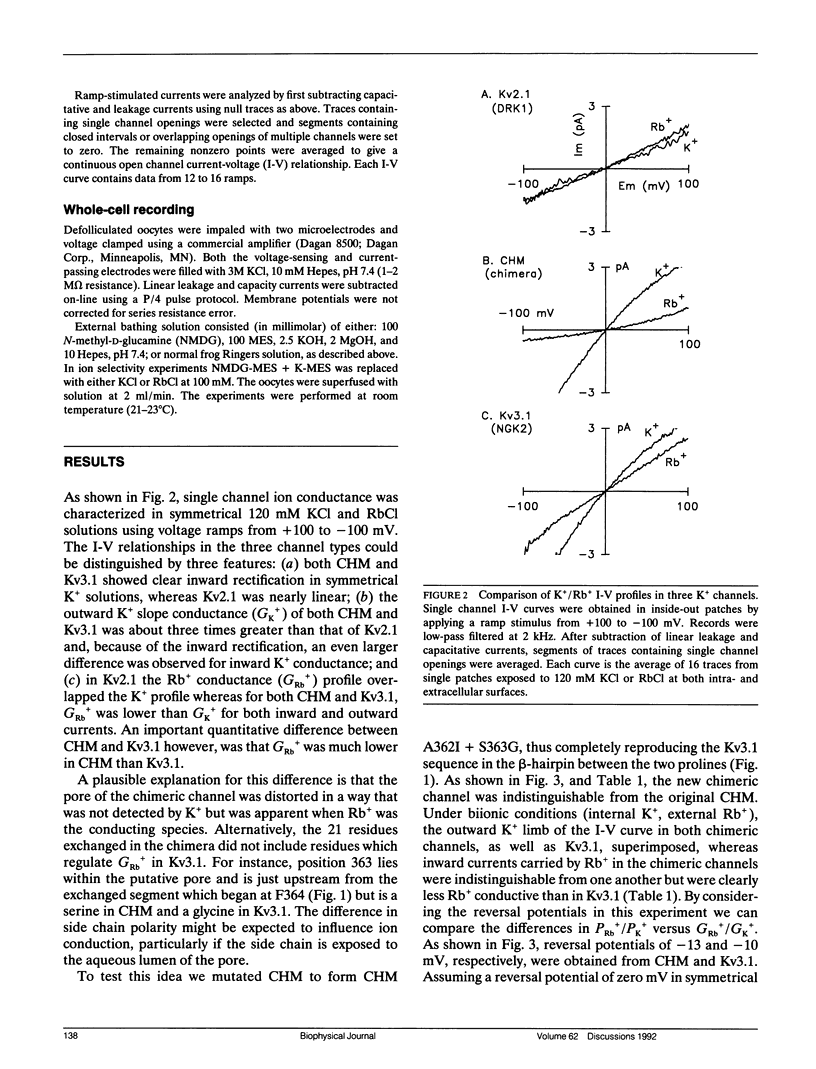
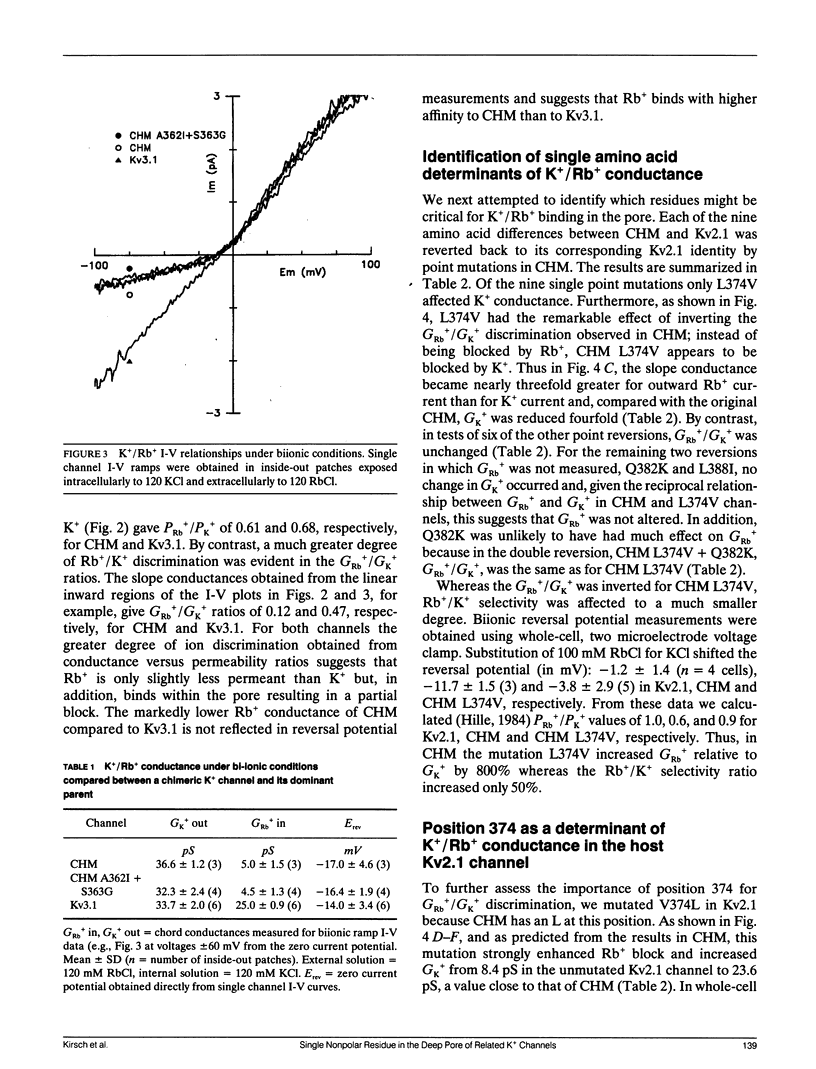
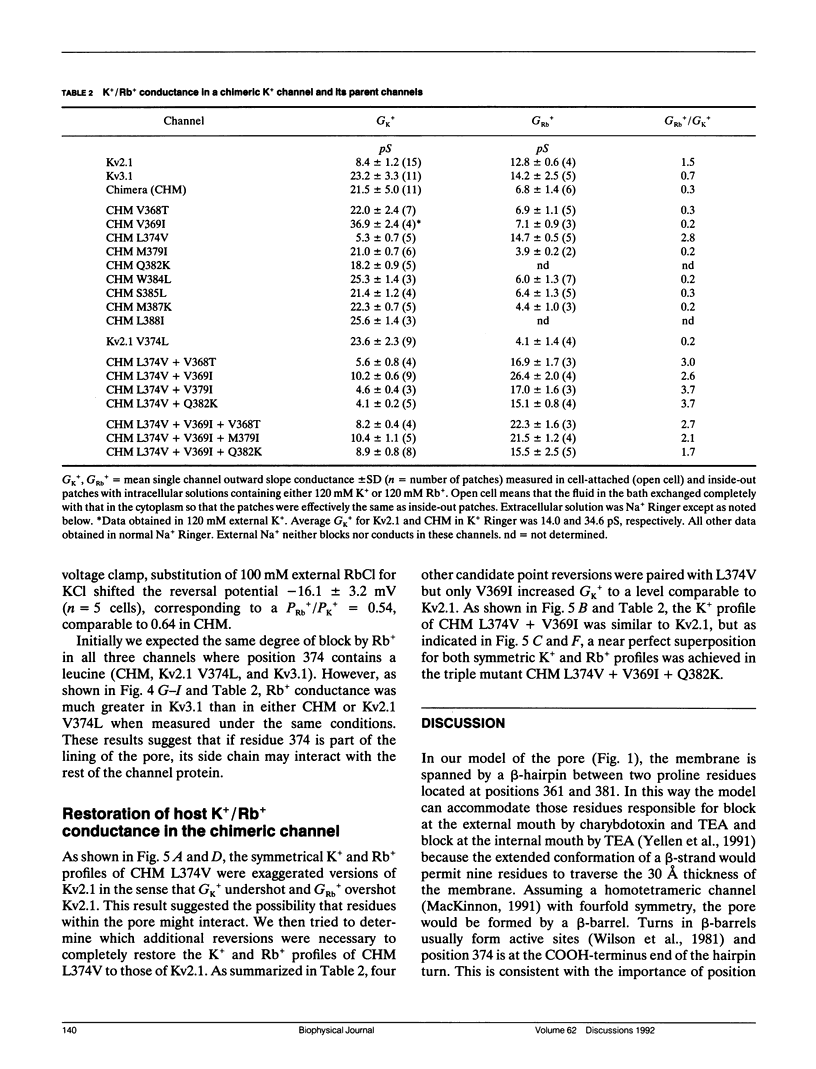
K+ and Rb+ conductances (GK+ and GRb+) were investigated in two delayed rectifier K+ channels (Kv2.1 and Kv3.1) cloned from rat brain and a chimera (CHM) of the two channels formed by replacing the putative pore region of Kv2.1 with that of Kv3.1. CHM displayed ion conduction properties which resembled Kv3.1. In CHM, GK+ was three times greater than that of Kv2.1 and GRb+/GK+ = 0.3 (compared with 1.5 and 0.7, respectively, in Kv2.1 and Kv3.1). A point mutation in CHM L374V, which restored 374 to its Kv2.1 identity, switched the K+/Rb+ conductance profiles so that GK+ was reduced fourfold, GRb+ was increased twofold, and GRb+/GK+ = 2.8. Quantitative restoration of the Kv2.1 K+/Rb+ profiles, however, required simultaneous point mutations at three nonadjacent residues suggesting the possibility of interactions between residues within the pore. The importance of leucine at position 374 was verified when reciprocal changes in K+/Rb+ conductances were produced by the mutation of V374L in Kv2.1 (GK+ was increased threefold, GRb+ was decreased threefold, and GRb+/GK+ = 0.2). We conclude that position 374 is responsible for differences in GK+ and GRb+ between Kv2.1 and Kv3.1 and, given its location near residues critical for block by internal tetraethylammonium, may be part of a cation binding site deep within the pore.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Gramicidin channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:531–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann A., Grupe A., Ackermann A., Pongs O. Structure of the voltage-dependent potassium channel is highly conserved from Drosophila to vertebrate central nervous systems. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2457–2463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. J., Winter G., Wilkinson A. J., Fersht A. R. The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):835–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Exchange of conduction pathways between two related K+ channels. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):942–944. doi: 10.1126/science.2000495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Rudy B. A-type potassium channels expressed from Shaker locus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5723–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R. H., Moorman J. R., VanDongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Silberberg H., Schuster G., Brown A. M. Toxin and kinetic profile of rat brain type III sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Feb;7(2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90087-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Multi-spanning membrane proteins: how accurate are the models? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Sep;13(9):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R. Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of a voltage-activated potassium channel. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):232–235. doi: 10.1038/350232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Heginbotham L., Abramson T. Mapping the receptor site for charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking potassium channel inhibitor. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):767–771. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90335-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mutant potassium channels with altered binding of charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking peptide inhibitor. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1382–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.2476850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. Changes in sodium channel gating produced by point mutations in a cytoplasmic linker. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):688–691. doi: 10.1126/science.2173138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. Ion transport in a model gramicidin channel. Structure and thermodynamics. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):961–981. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82311-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):837–839. doi: 10.1038/332837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):939–942. doi: 10.1126/science.2000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Imoto K., Kawamura T., Higashida H., Iwabe N., Miyata T., Numa S. Potassium channels from NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNAs. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81488-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yool A. J., Schwarz T. L. Alteration of ionic selectivity of a K+ channel by mutation of the H5 region. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):700–704. doi: 10.1038/349700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]