Abstract
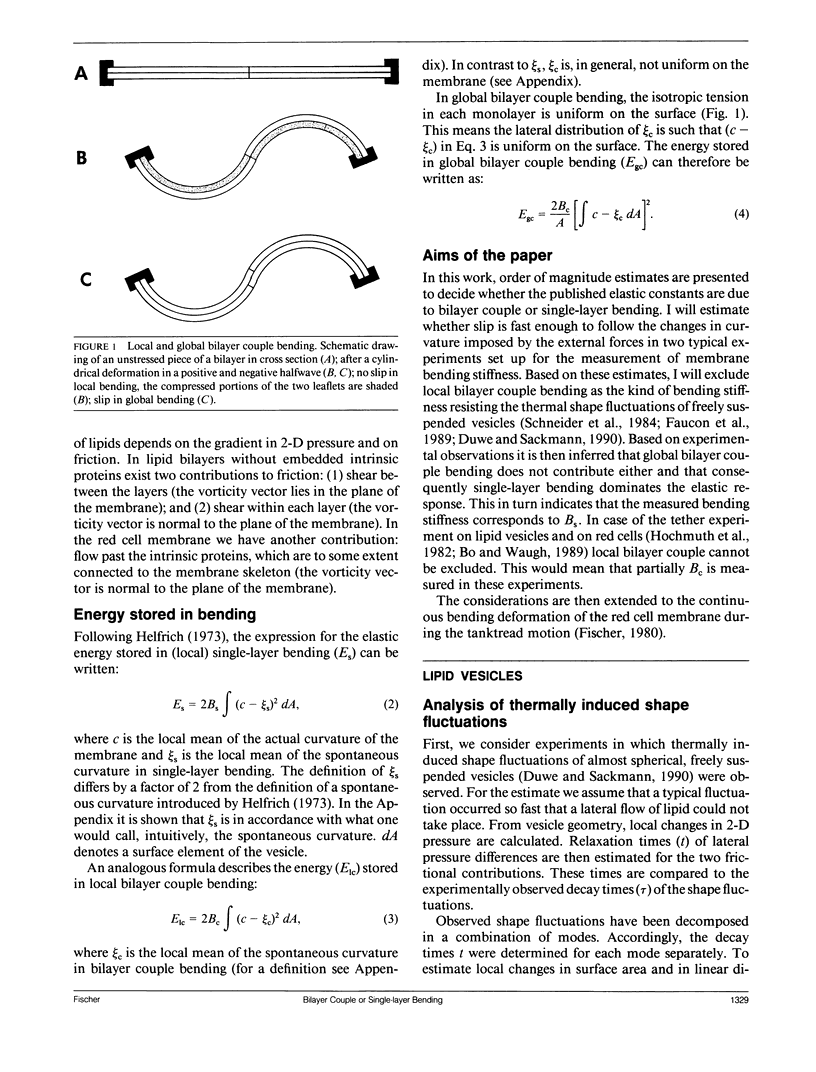
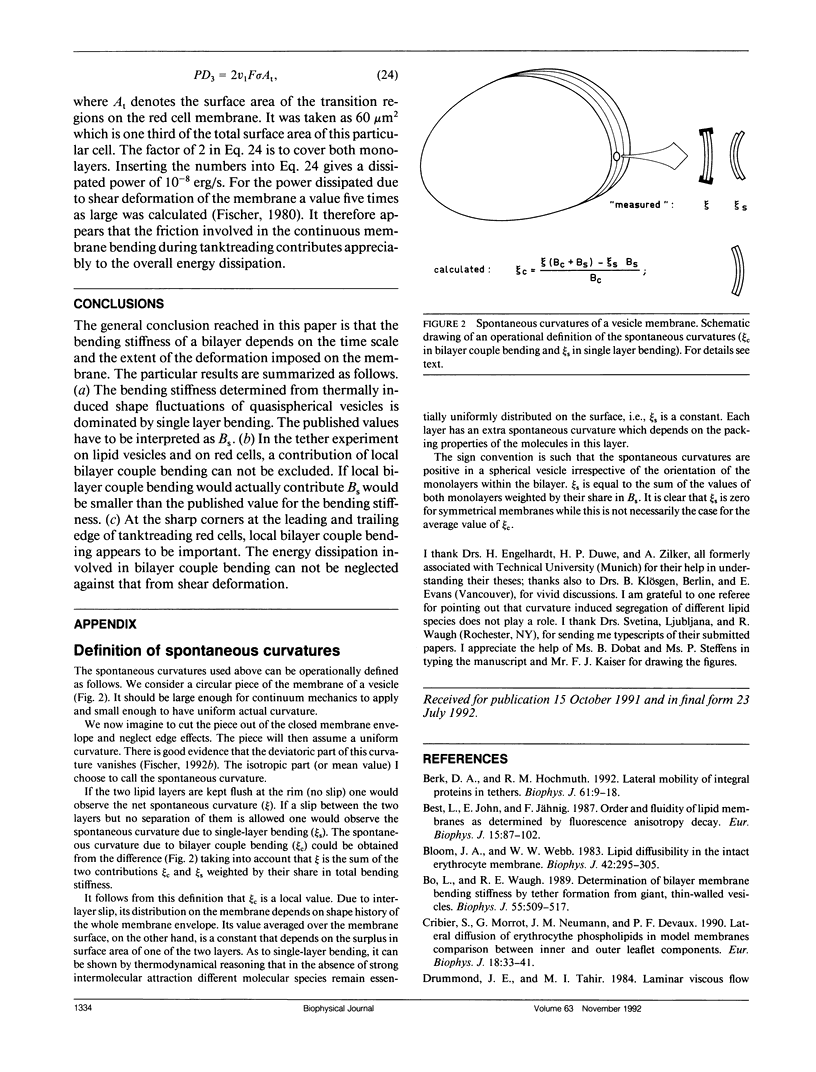
To describe the resistance of a bilayer to changes in curvature two mechanisms are distinguished which are termed bilayer couple bending and single-layer bending. In bilayer couple bending, the resistance arises from the 2-D isotropic elasticity of the two layers and their fixed distance. Single-layer bending covers the intrinsic bending stiffness of each monolayer. The two mechanisms are not independent. Even so, the distinction is useful since bilayer couple bending can relax by a slip between the layers from the local to the global fashion. Therefore, the bending stiffness of a bilayer depends on the time scale and on the extent of the deformation imposed on the membrane. Based on experimental data, it is shown by order of magnitude estimates that (a) the bending stiffness determined from thermally induced shape fluctuations of almost spherical vesicles is dominated by single-layer bending; (b) in the tether experiment on lipid vesicles and on red cells, a contribution of local bilayer couple bending can not be excluded; and (c) at the sharp corners at the leading and the trailing edge of tanktreading red cells, local bilayer couple bending appears to be important.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk D. A., Hochmuth R. M. Lateral mobility of integral proteins in red blood cell tethers. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81811-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. A., Webb W. W. Lipid diffusibility in the intact erythrocyte membrane. Biophys J. 1983 Jun;42(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84397-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo L., Waugh R. E. Determination of bilayer membrane bending stiffness by tether formation from giant, thin-walled vesicles. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82844-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribier S., Morrot G., Neumann J. M., Devaux P. F. Lateral diffusion of erythrocyte phospholipids in model membranes comparison between inner and outer leaflet components. Eur Biophys J. 1990;18(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00185418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending resistance and chemically induced moments in membrane bilayers. Biophys J. 1974 Dec;14(12):923–931. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85959-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 2. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Nov;3(4):331–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E, Rawicz W. Entropy-driven tension and bending elasticity in condensed-fluid membranes. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Apr 23;64(17):2094–2097. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. M. On the energy dissipation in a tank-treading human red blood cell. Biophys J. 1980 Nov;32(2):863–868. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85022-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich W. Elastic properties of lipid bilayers: theory and possible experiments. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Nov-Dec;28(11):693–703. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Wiles H. C., Evans E. A., McCown J. T. Extensional flow of erythrocyte membrane from cell body to elastic tether. II. Experiment. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84493-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummrow M, Helfrich W. Deformation of giant lipid vesicles by electric fields. Phys Rev A. 1991 Dec 15;44(12):8356–8360. doi: 10.1103/physreva.44.8356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D., Nunn R. S. Elastic deformation and failure of lipid bilayer membranes containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):997–1009. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82444-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. B., Jenkins J. T., Webb W. W. Thermal fluctuations of large cylindrical phospholipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):891–899. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84235-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servuss R. M., Harbich W., Helfrich W. Measurement of the curvature-elastic modulus of egg lecithin bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 15;436(4):900–903. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Membrane skeletal dynamics: role in modulation of red cell deformability, mobility of transmembrane proteins, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Microviscosity parameters and protein mobility in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):133–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J., Waugh R. E. Bilayer membrane bending stiffness by tether formation from mixed PC-PS lipid vesicles. J Biomech Eng. 1990 Aug;112(3):235–240. doi: 10.1115/1.2891178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke B. T., Mikkelsen A., Elgsaeter A. The human erythrocyte membrane skeleton may be an ionic gel. I. Membrane mechanochemical properties. Eur Biophys J. 1986;13(4):203–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00260368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svetina S., Ottova-Leitmannová A., Glaser R. Membrane bending energy in relation to bilayer couples concept of red blood cell shape transformations. J Theor Biol. 1982 Jan 7;94(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E., Hochmuth R. M. Mechanical equilibrium of thick, hollow, liquid membrane cylinders. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83227-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E., Song J., Svetina S., Zeks B. Local and nonlocal curvature elasticity in bilayer membranes by tether formation from lecithin vesicles. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):974–982. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81904-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E. Surface viscosity measurements from large bilayer vesicle tether formation. II. Experiments. Biophys J. 1982 Apr;38(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84527-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


