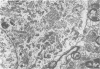Abstract
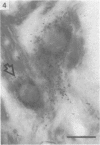
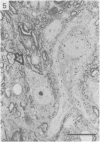
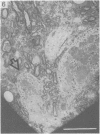
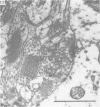
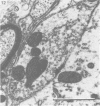
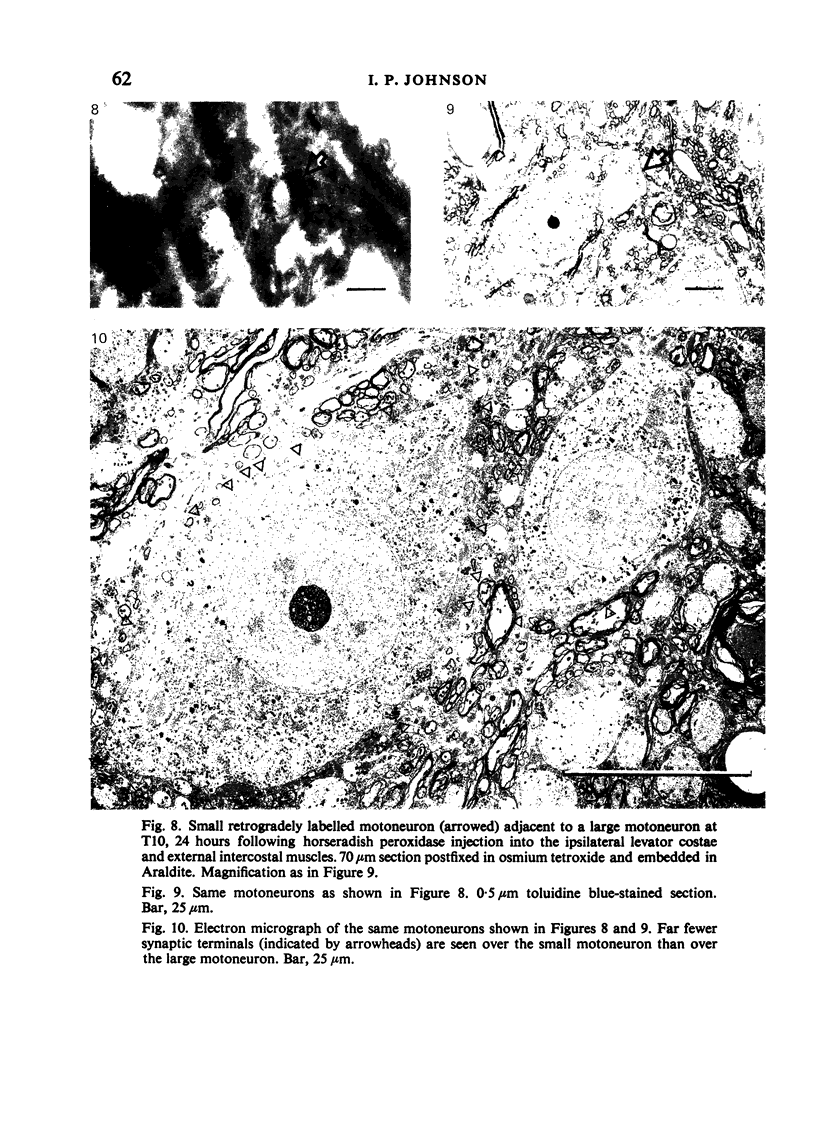
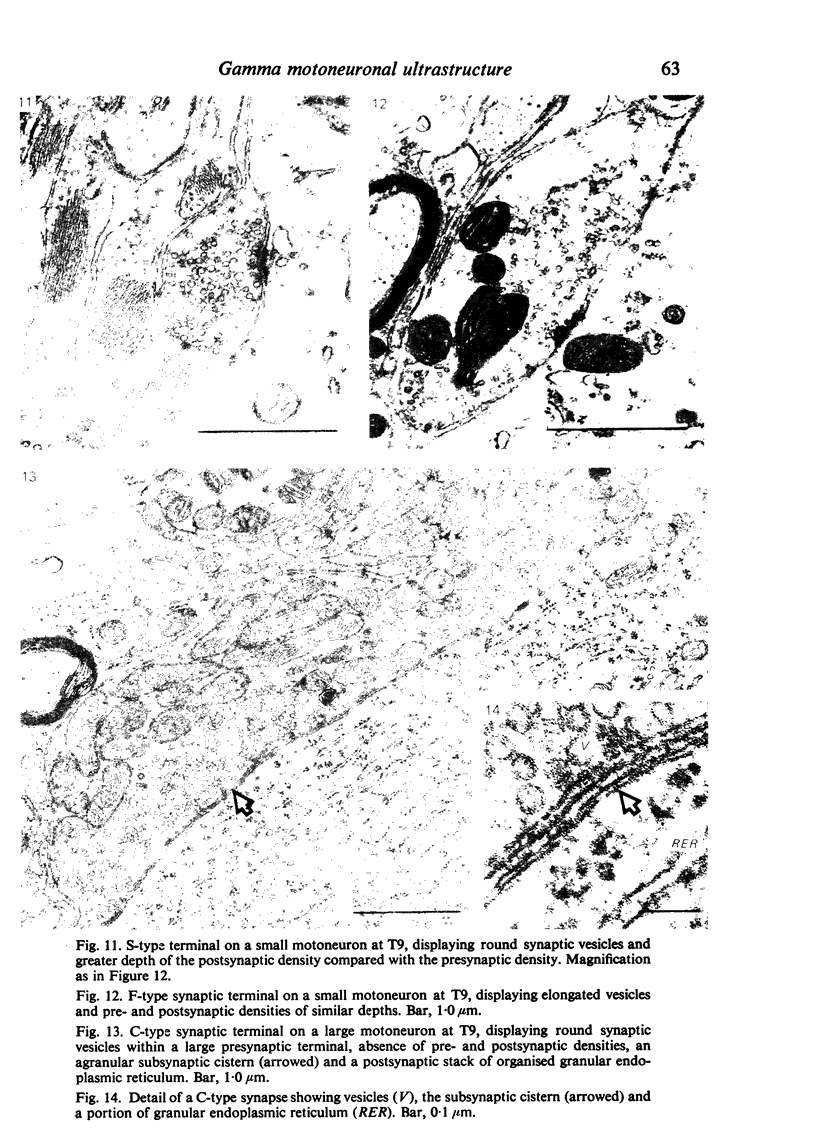
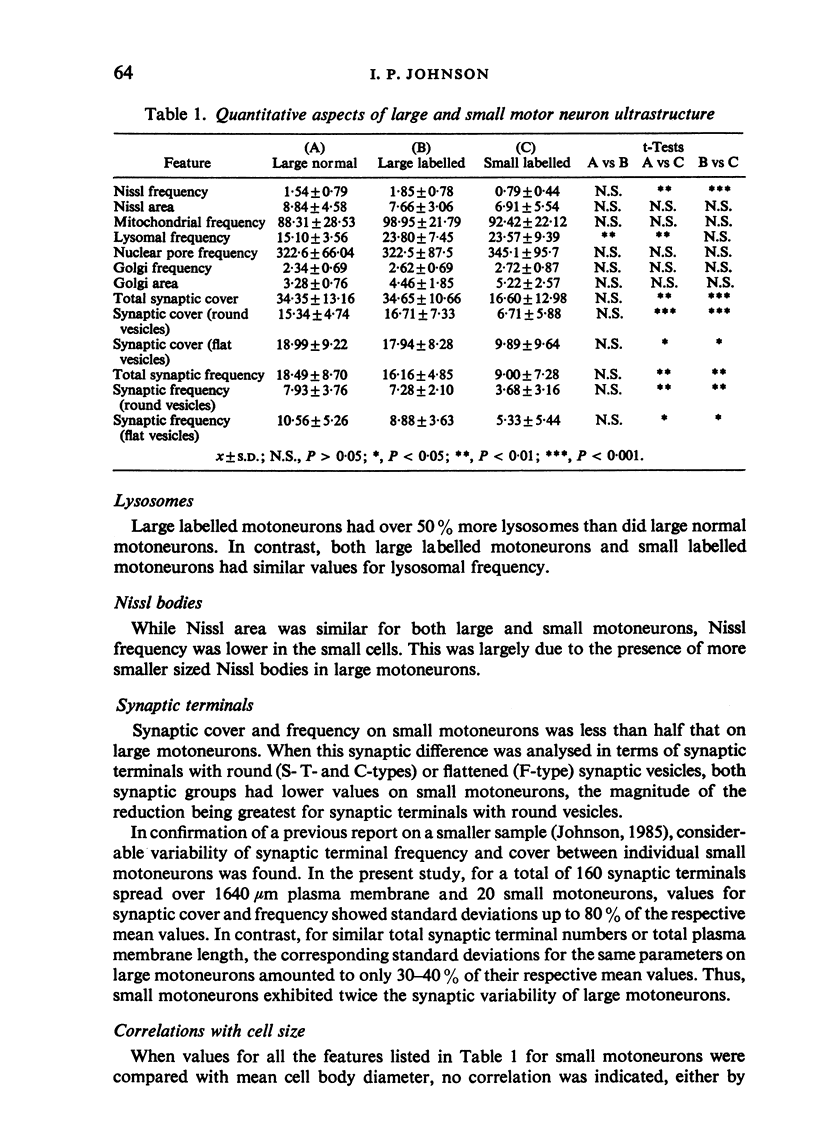
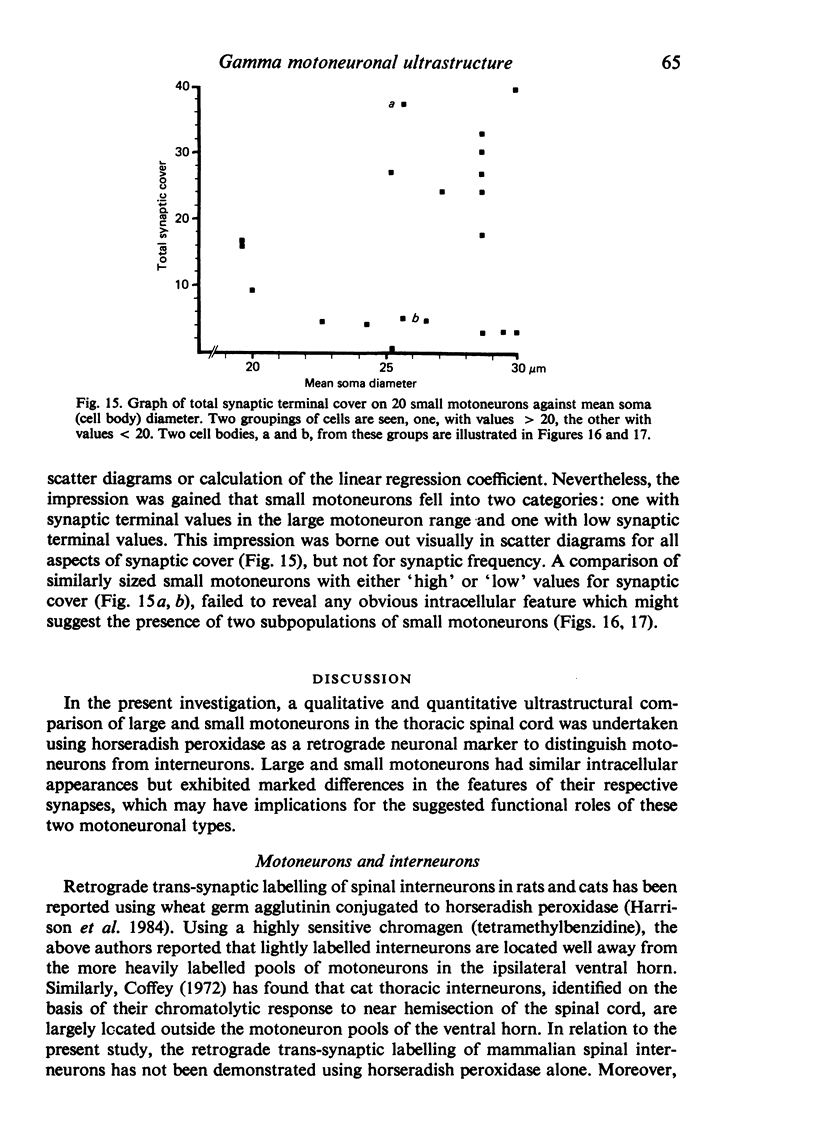
The cell bodies of motoneurons supplying both the levator costae and external intercostal muscles were identified after retrograde labelling with horseradish peroxidase. A quantitative ultrastructural comparison of cell bodies of large (greater than 40 microns) and small (less than 30 microns) diameter revealed that the intracellular appearance of large and small motoneurons was similar. However, small motoneurons had less than half the synaptic terminal frequency or cover of large motoneurons. Furthermore, only synapses of the S- and F-type were seen on small motoneurons, while S- T- F- and C-type terminals were consistently seen on large motoneurons. The variation between individual small motoneurons for various aspects of their synaptic features was more than twice that found for large motoneurons. No correlation between small motoneuronal ultrastructure and cell body diameter was found, although scatter diagrams of synaptic terminal cover against cell body size indicated the presence of two groups of small motoneurons: one with relatively high values for synaptic cover and the other with relatively low values. On the basis of the similarity of their cell body diameters to those of electrophysiologically identified alpha and gamma motoneurons, it is concluded that the large and small motoneurons examined in the present study are alpha and gamma motoneurons respectively. The synaptic difference found between alpha and gamma motoneurons is discussed in relation to both their different functional properties and the different natures of their respective peripheral targets.
Full text
PDF


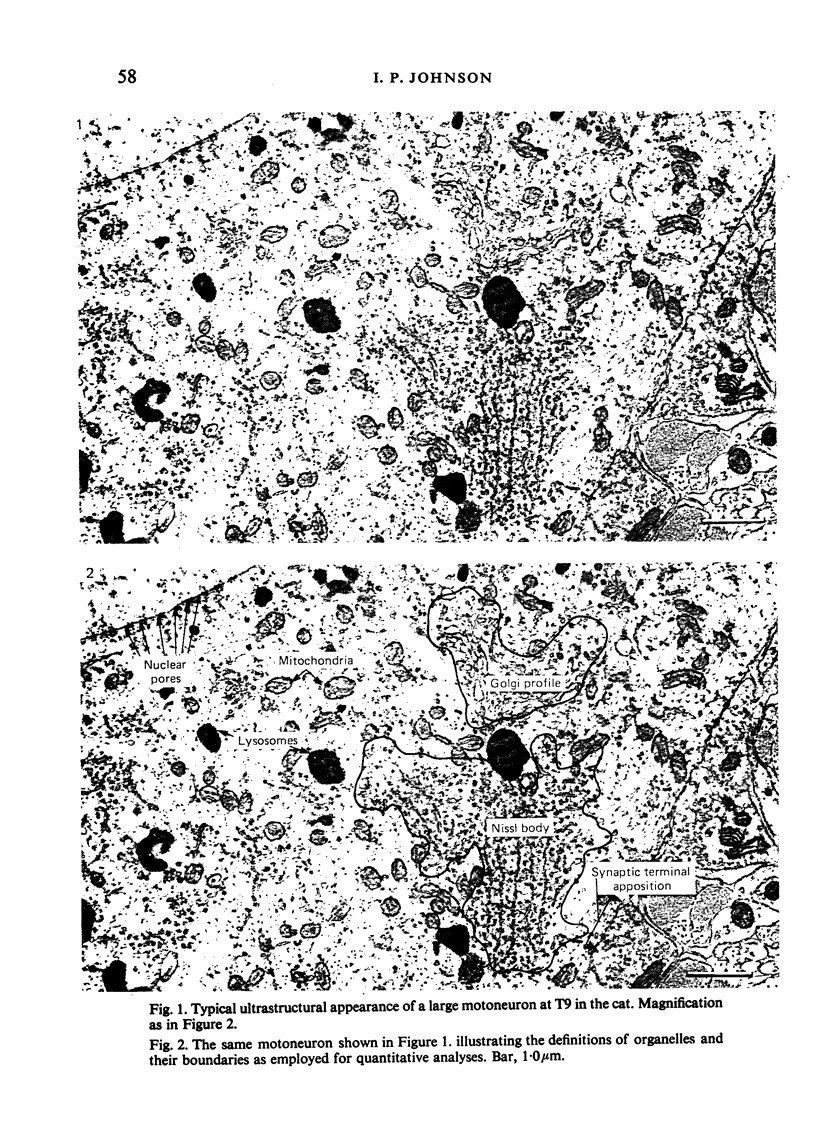
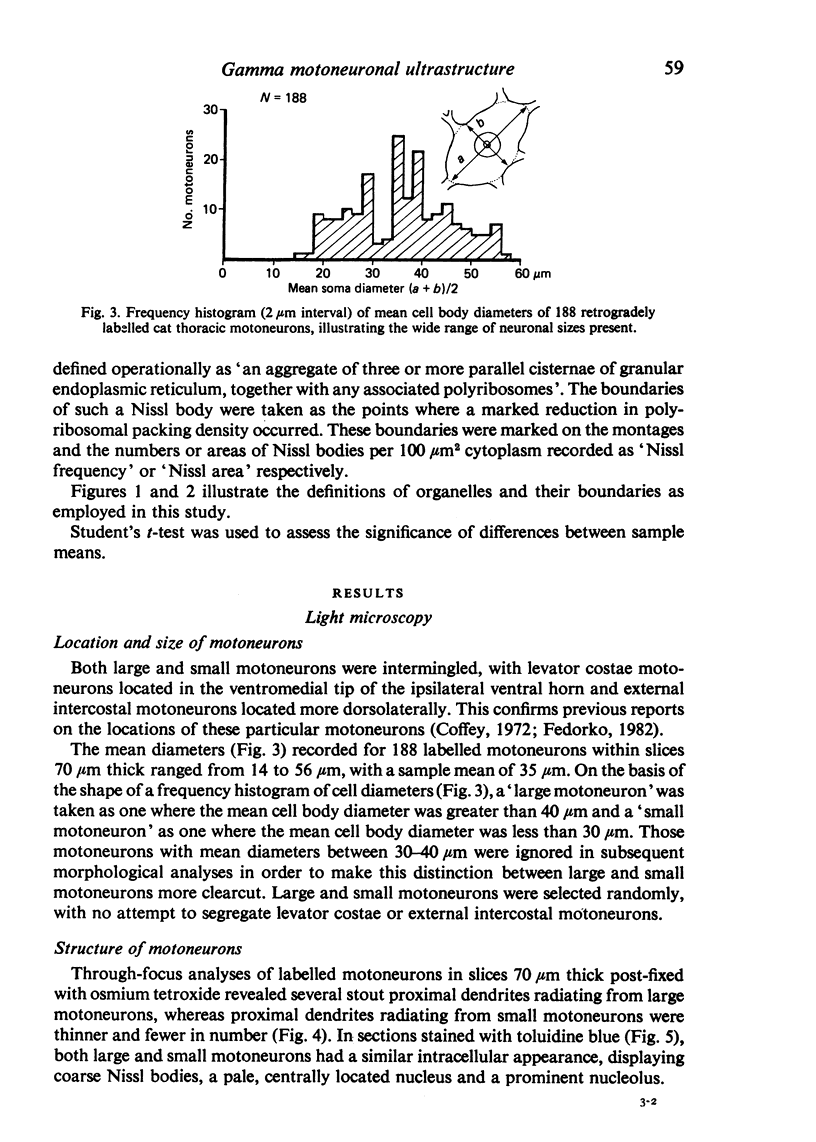
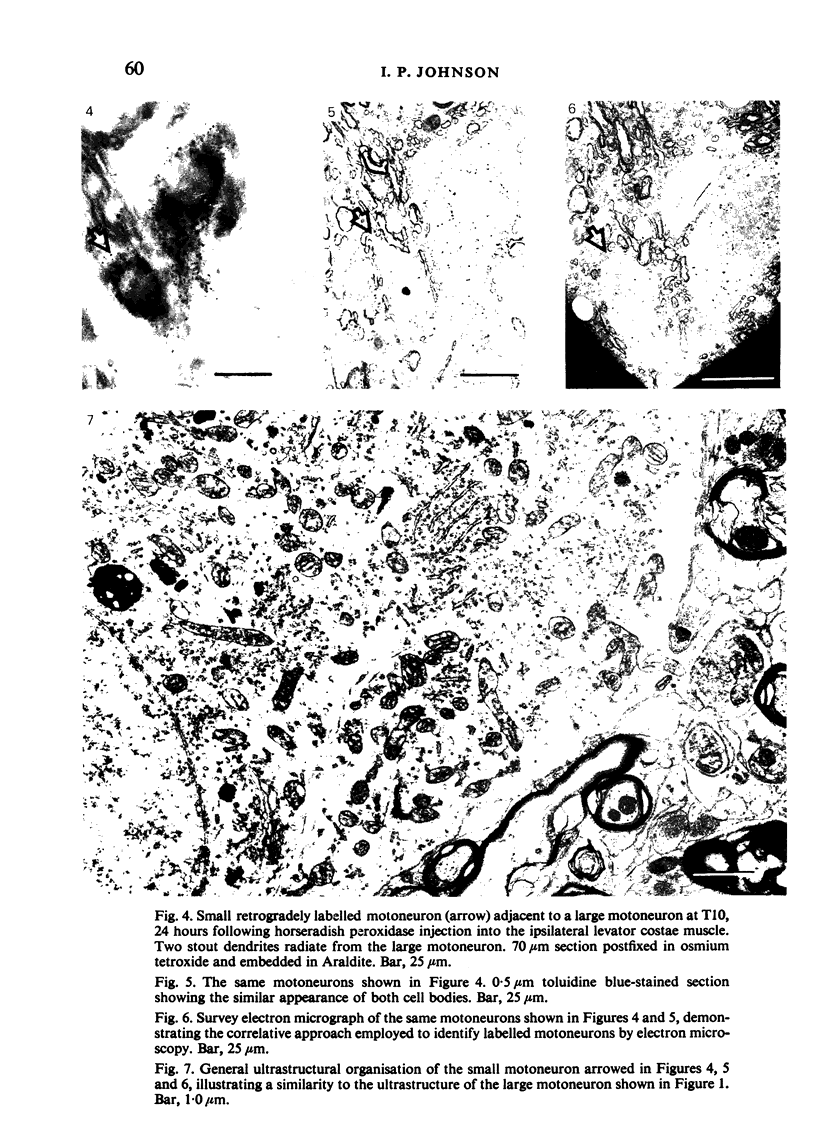

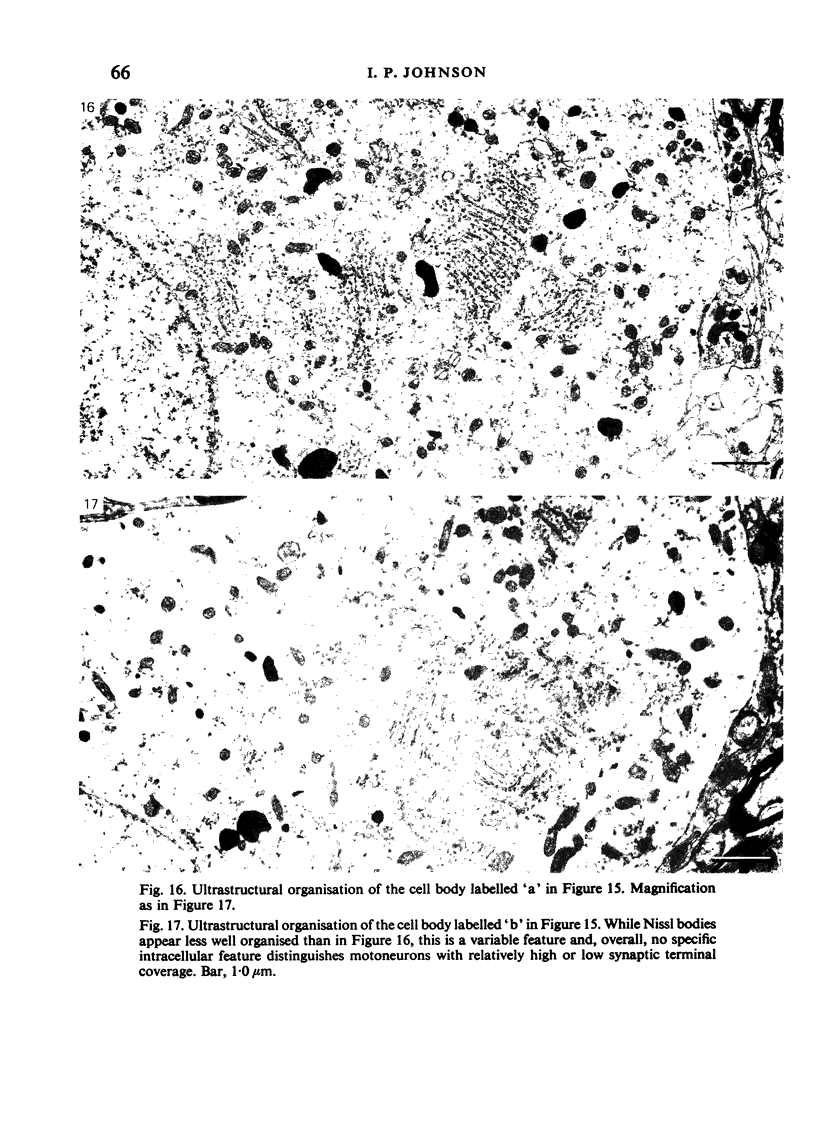






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., SEARS T. A. THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND INNERVATION OF FAST AND SLOW MOTOR UNITS IN THE INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:114–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Actions on gamma-motoneurones elicited by electrical stimulation of group III muscle afferent fibres in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:275–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinzinger K., Kreutzberg G. Displacement of synaptic terminals from regenerating motoneurons by microglial cells. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;85(2):145–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00325030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D., Brightman M. W. Cytochemistry of undamaged neurons transporting exogenous protein in vivo. J Comp Neurol. 1979 May 1;185(1):31–73. doi: 10.1002/cne.901850104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. Direct observations on the contacts made between Ia afferent fibres and alpha-motoneurones in the cat's lumbosacral spinal cord. J Physiol. 1981;313:121–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan R. N., Trevino D. L., Willis W. D. Evidence for a common location of alpha and gamma motoneurons. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 10;38(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90602-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Strick P. L., Kanda K., Kim C. C., Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):667–680. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa J. F., Engel W. K. Histochemistry of motor neurons and interneurons in the cat lumbar spinal cord. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):559–568. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. H. Qualitative and quantitative study of synaptic displacement in chromatolyzed spinal motoneurons of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Feb 15;177(4):635–664. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradi S. Ultrastructure and distribution of neuronal and glial elements on the motoneuron surface in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the adult cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;332:5–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull R. E. Rôle of axonal transport in maintaining central synaptic connections. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Nov 28;24(1):97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00236020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Proportion of muscles spindles supplied by skeletofusimotor axons (beta-axons) in peroneus brevis muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1390–1394. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., SOMJEN G., CARPENTER D. O. FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL SIZE IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:560–580. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Katz R., Storai B., Zytnicki D. Labelling of interneurones by retrograde transsynaptic transport of horseradish peroxidase from motoneurones in rats and cats. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Mar 9;45(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., HUNT C. C., QUILLIAM J. P. Function of medullated small-nerve fibers in mammalian ventral roots; efferent muscle spindle innervation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Jan;14(1):29–54. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerbäck P. A. An ultrastructural study of cat lumbosacral gamma-motoneurons after retrograde labelling with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 15;240(3):256–264. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG-HANSEN R. ANATOMICAL DEMONSTRATION OF GAMMA MOTONEURONS IN THE CAT'S SPINAL CORD. Exp Neurol. 1965 Sep;13:71–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(65)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B., Novikoff P. M. Cytochemical contributions to differentiating GERL from the Golgi apparatus. Histochem J. 1977 Sep;9(5):525–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01002901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. H., Sears T. A. Modification of "C" synapses following partial central deafferentation of thoracic motoneurones. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 21;145(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90802-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. H., Sears T. A. Trophism between C-type axon terminals and thoracic motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:373–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANES G. J. THE MOTOR POOLS OF THE SPINAL CORD. Prog Brain Res. 1964;11:93–119. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanovicz D. K., Hanker J. S. Wafer embedding: specimen selction in electron microscopic cytochemistry with osmiophilic polymers. Histochem J. 1977 May;9(3):317–327. doi: 10.1007/BF01004768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHADE J. P., VAN HARREVELD A. Volume distribution of moto- and interneurons in the peroneus-tibialis neuron pool of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Dec;117:387–398. doi: 10.1002/cne.901170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. EFFERENT DISCHARGES IN ALPHA AND FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:295–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE FIBRE CALIBRE SPECTRA OF SENSORY AND MOTOR FIBRES IN THE INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:150–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAGUE J. M. Motor and propriospinal cells in the thoracic and lumbar ventral horn of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Aug;95(1):103–123. doi: 10.1002/cne.900950107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strick P. L., Burke R. E., Kanda K., Kim C. C., Walmsley B. Differences between alpha and gamma motoneurons labeled with horseradish peroxidase by retrograde transport. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 3;113(3):582–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Cullheim S. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal gamma -motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):585–596. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbury D. R. A comparison of the structures of alpha and gamma-spinal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:79–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]