Abstract
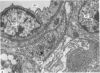
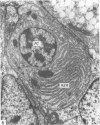
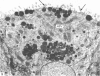
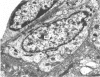
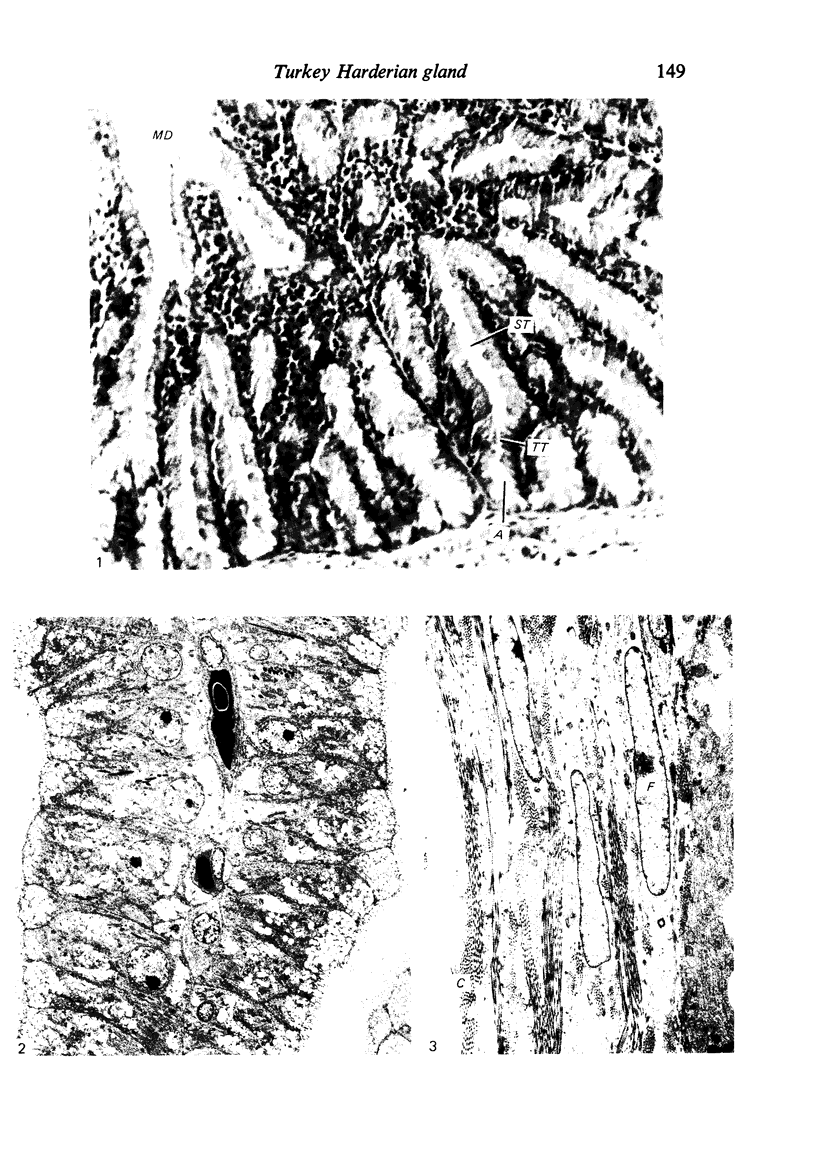
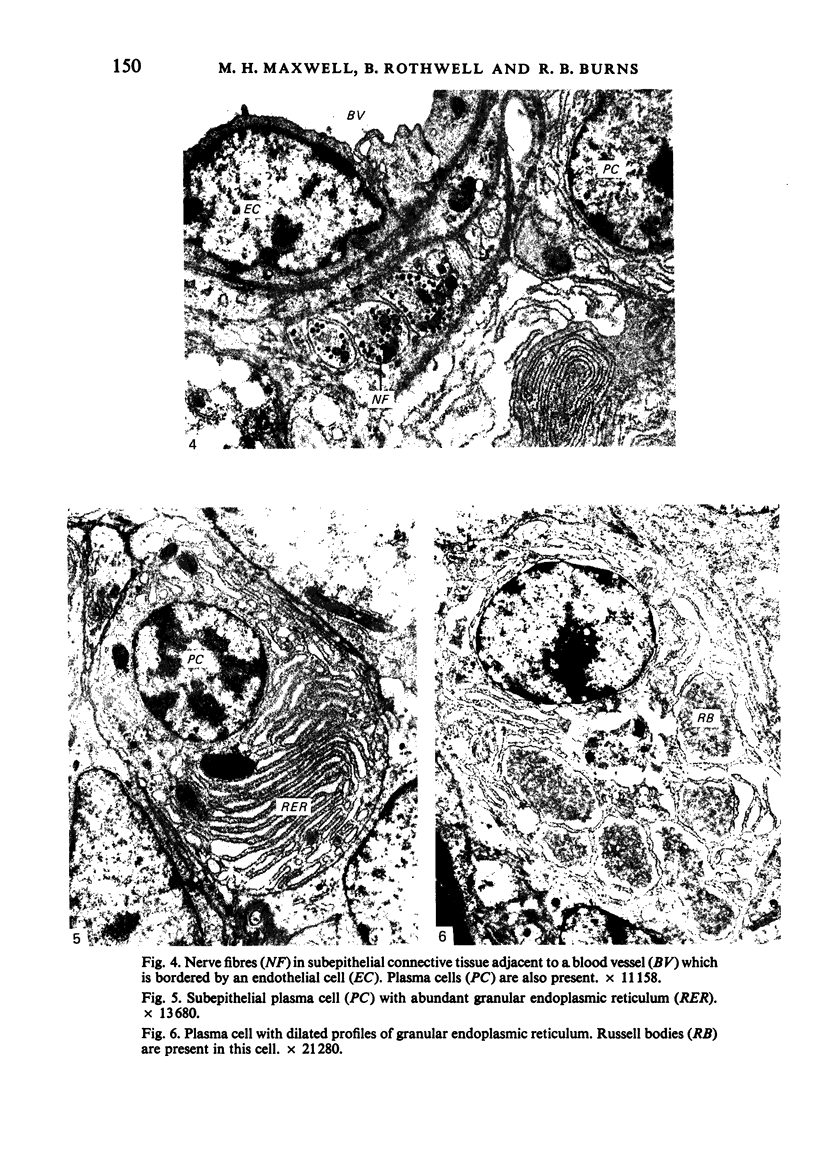
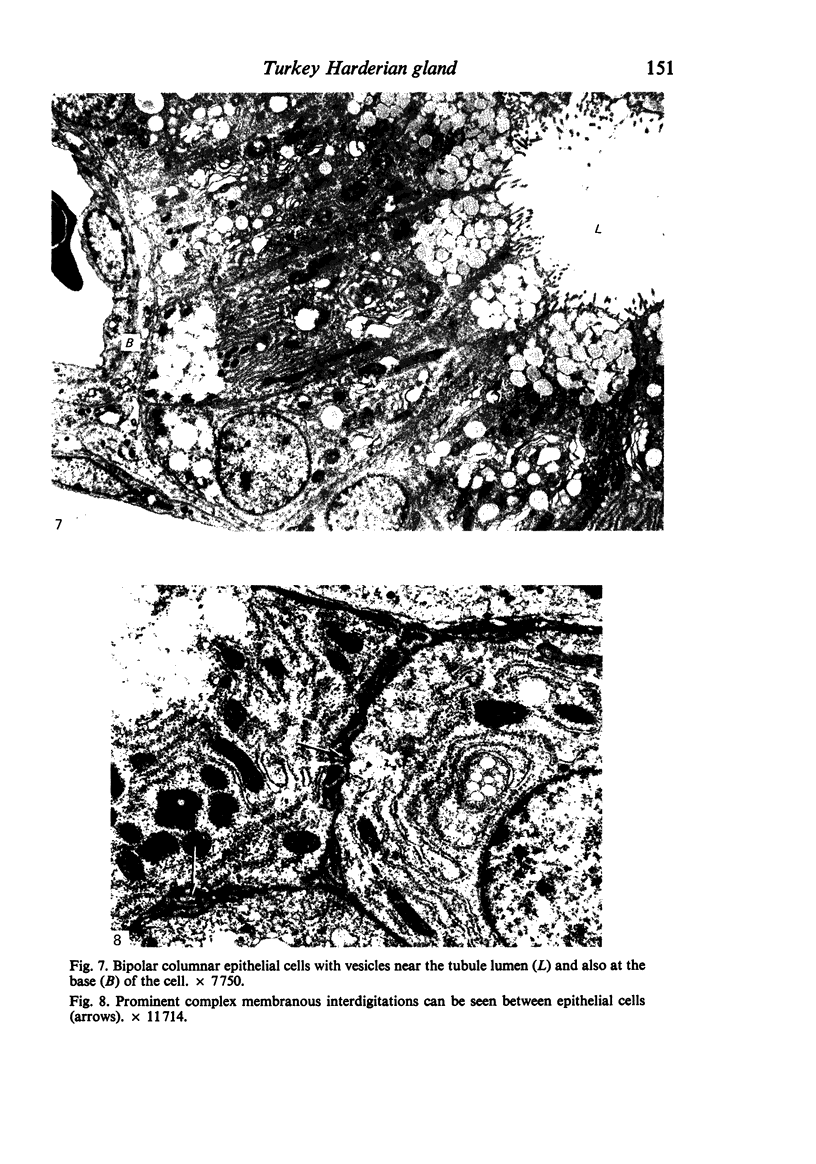
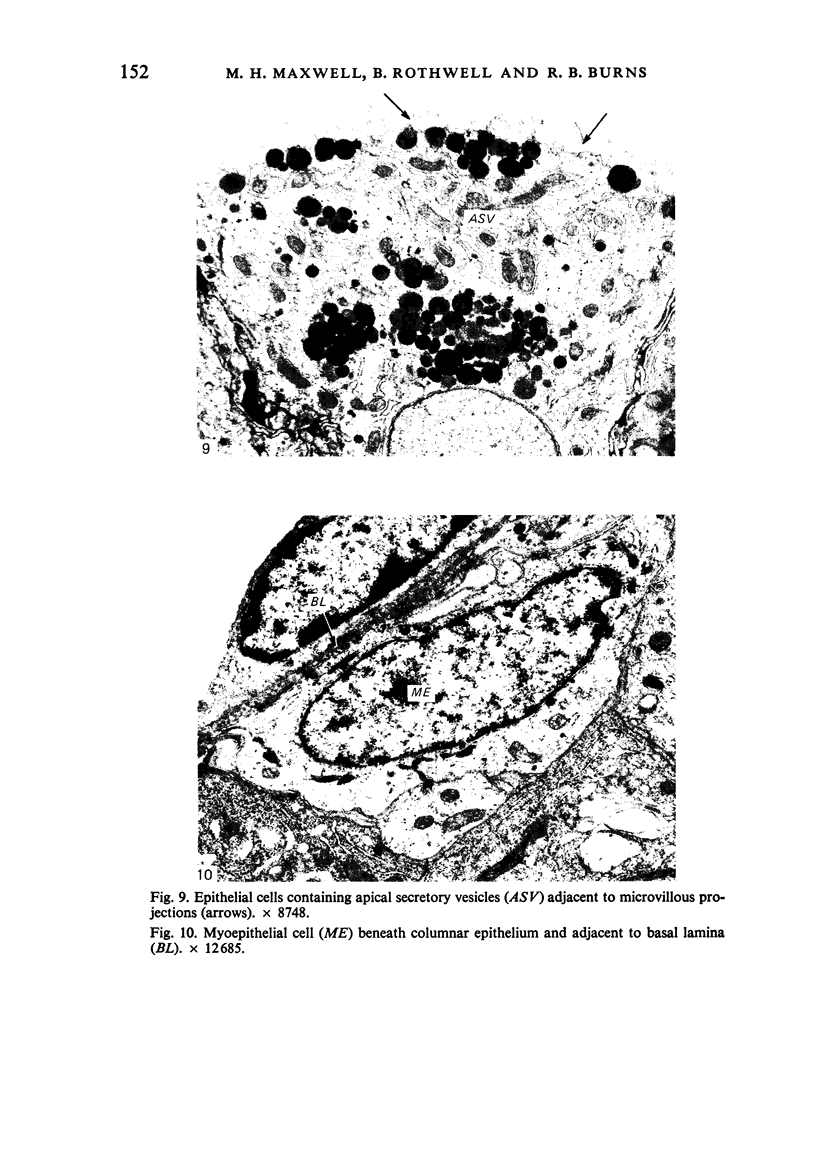
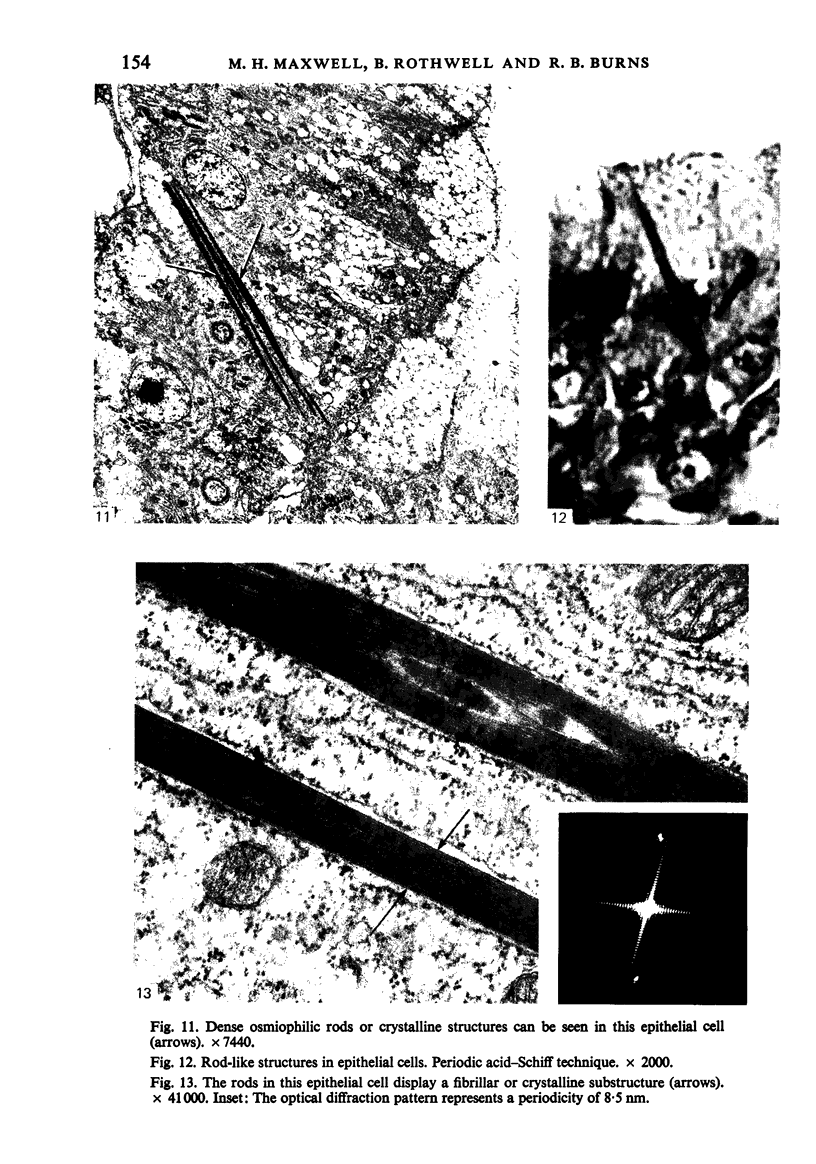
The ultrastructure of the turkey Harderian gland is described and the findings support previous histological descriptions of the gland. The gland is a compound tubulo-acinar structure composed of characteristic bipolar epithelial cells providing a predominantly merocrine secretion to the lumina. In the basal aspect of the cell, aggregations of non-secretory lipid-like droplets were evident and apically, the secretion was mucoid. The cells had abundant mitochondria, granular endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and a complex network of Golgi elements. In the subepithelial regions, myoepithelial cells and large numbers of plasma cells were seen. Within the granular endoplasmic reticulum cisternae of the epithelial cells, fibrillary or crystalline rods in some instances measuring up to 10 micron in length, with a 7.0 nm repeat pattern, were frequently seen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brobby G. W., Sr On the Harderian gland of the domestic duck (Anas platyrhynchus). Morphological and histochemical investigations. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;133(2):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00307144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. B., MacKenzie G. M. Cholinesterase activity in the Harderian gland of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Res Vet Sci. 1973 Mar;14(2):261–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. B., Maxwell M. H. The structure of the Harderian and lacrimal gland ducts of the turkey, fowl and duck. A light microscope study. J Anat. 1979 Mar;128(Pt 2):285–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. B. Plasma cells in the avian Harderian gland and the morphology of the gland in the rook. Can J Zool. 1975 Sep;53(9):1258–1269. doi: 10.1139/z75-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. B. Specific antibody production against a soluble antigen in the Harderian gland of the domestic fowl. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):371–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabough J. W., Norvell J. E. Pineal influence on the Harderian glands of female golden hamsters. Anat Rec. 1974 Jan;178(1):119–125. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091780110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourman J., Ballantyne B. Cholinesterase activity in the Harderian gland of Anas domesticus. Anat Rec. 1967 Sep;159(1):17–27. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091590104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel W., Beier H. M. Morphologie und Cytochemie der Harderschen Drüse von Anatiden. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Jul 31;141(2):255–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell M. H., Burns R. B. The ultrastructure of the epithelium of the ducts of the Harderian and lacrimal glands of the turkey, fowl and duck. J Anat. 1979 May;128(Pt 3):445–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell M. H. Safer substitutes for xylene and propylene oxide in histology, haematology, and electron microscopy. Med Lab Sci. 1978 Oct;35(4):401–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedorf H. R., Wolters B. Dvelopment of the Harderian gland in the chicken: light and electron microscopic investigations. Invest Cell Pathol. 1978 Jul-Sep;1(3):205–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell B. Perfusion fixation of the kidney of the domestic fowl. J Microsc. 1974 Jan;100(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1974.tb03917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell B., Wight P. A., Burns R. B., Mackenzie G. M. The Harderian glands of the domestic fowl. 3. Ultrastructure. J Anat. 1972 Jul;112(Pt 2):233–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T. The mammalian Harderian gland: morphology, biochemistry, function and phylogeny. Arch Histol Jpn. 1981 Sep;44(4):299–333. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.44.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm U. Lymphoid cells in the Harderian gland of birds. An electron microscopical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;205(1):85–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00234445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaker F. J. Light microscopic and ultrastructural features of the Harderian gland of the nine-banded armadillo. J Anat. 1981 Aug;133(Pt 1):49–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight P. A., Burns R. B., Rothwell B., Mackenzie G. M. The Harderian gland of the domestic fowl. I. Histology, with reference to the genesis of plasma cells and Russell bodies. J Anat. 1971 Nov;110(Pt 2):307–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight P. A., Mackenzie G. M. Mucosubstances in the Harderian gland of the domestic duck. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Jul;17(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight P. A., Mackenzie G. M., Rothwell B., Burns R. B. The Harderian glands of the domestic fowl. II. Histochemistry. J Anat. 1971 Dec;110(Pt 3):323–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zicca A., Cadoni A., Leprini A., Millo R., Lydyard P. M., Grossi C. E. Immunofluorescent and ultrastructural analysis of plasma cell degeneration in the chicken Harder's gland. Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Winter;6(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(82)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]