Abstract
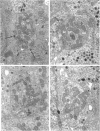
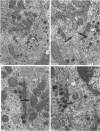
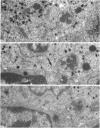
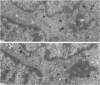
This study on the innervation of rabbit intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies (NEB) was undertaken to obtain more information about the detailed ultrastructure of morphologically afferent and efferent intracorpuscular NEB nerve endings, the extent to which they are in cytoplasmic continuity with one another, and the structure of the synaptic junctions they form with the NEB corpuscular cells. As in earlier studies, NEB exhibit intracorpuscular nerve endings containing predominantly either mitochondria (morphologically afferent) or synaptic vesicles (morphologically efferent). Both types of nerve endings form synaptic junctions with the NEB corpuscular cells, arranged so that a NEB corpuscular cell is the presynaptic element and the nerve ending the postsynaptic element. This arrangement implies that NEB can transmit nerve impulses to the central nervous system, thus arguing in favour of their hypothetical neuroreceptor function. Moreover, on serial sections, the morphologically afferent and efferent intracorpuscular nerve endings are often found in cytoplasmic continuity. Hence, transduction of stimuli in the NEB implies concomitant efferent modulation of the NEB corpuscular cells. In conclusion, intrapulmonary NEB apparently function as neuroreceptors that are locally modulated by axon reflexes.
Full text
PDF

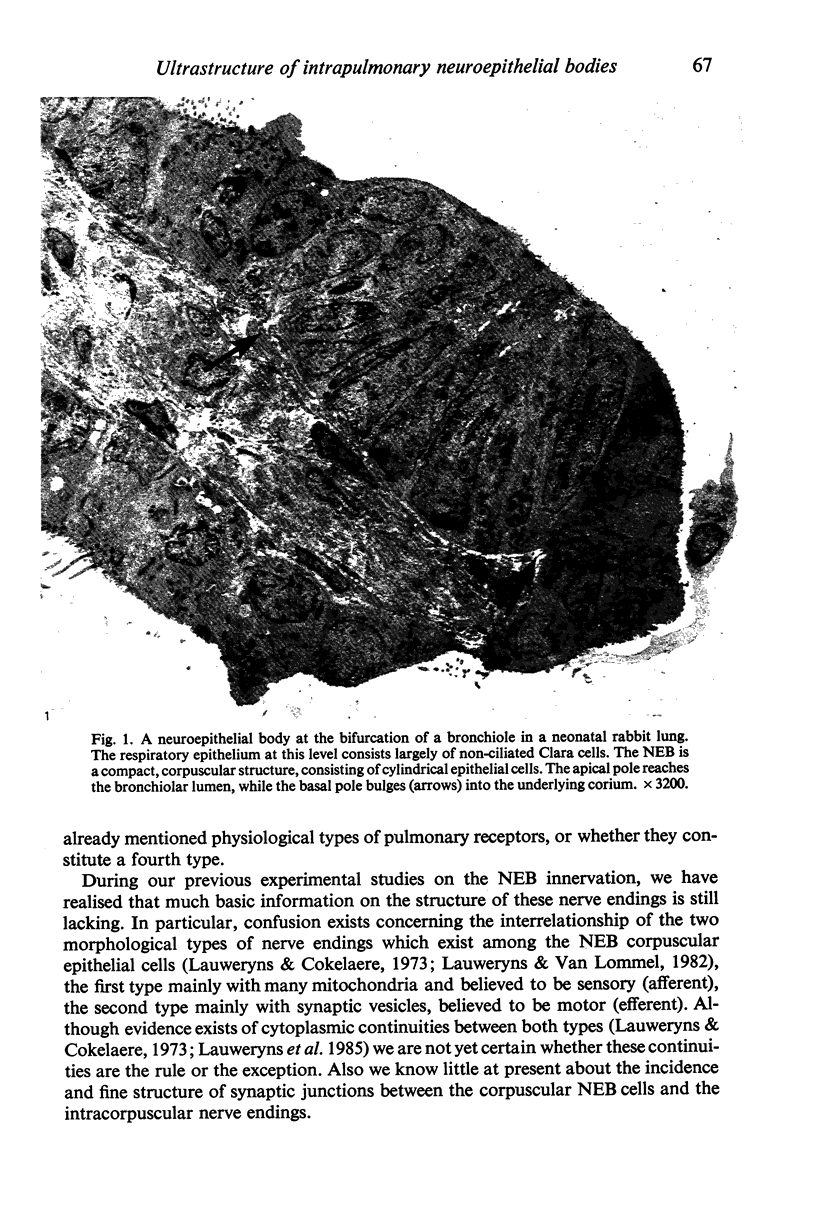

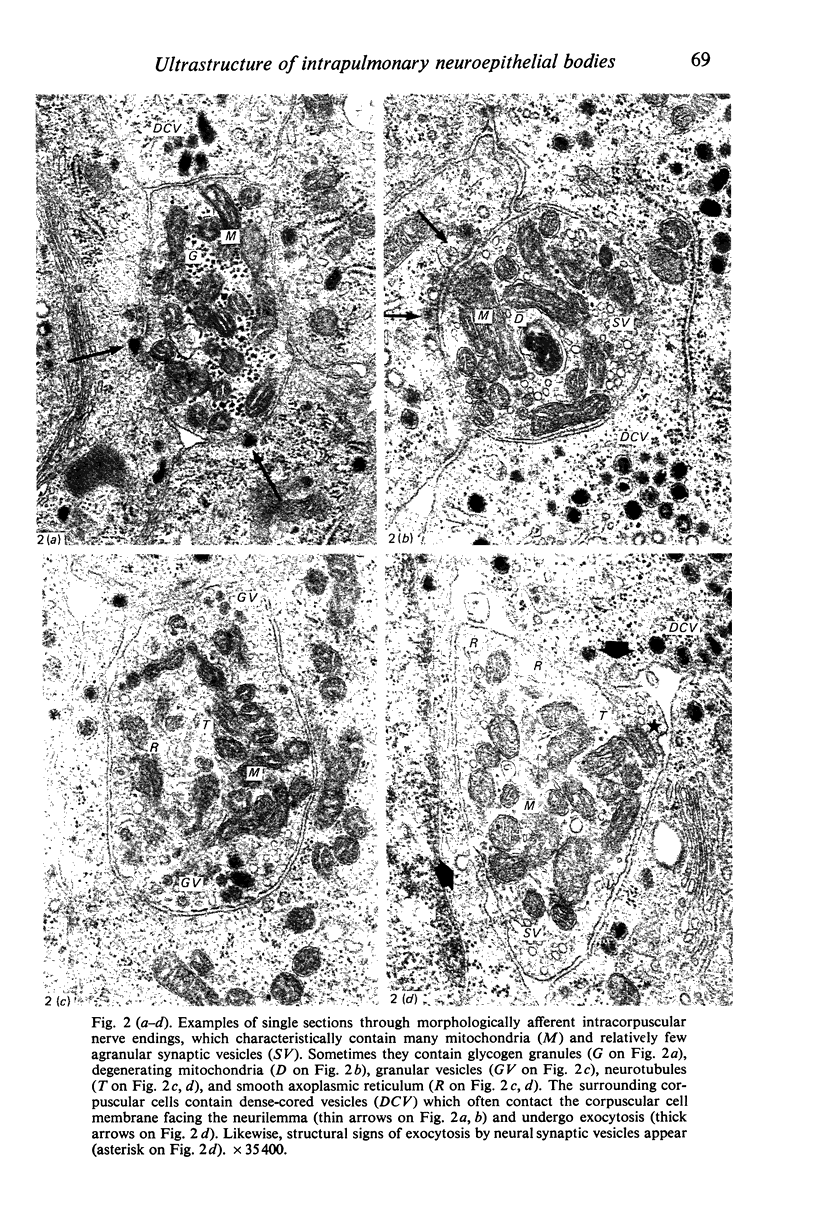
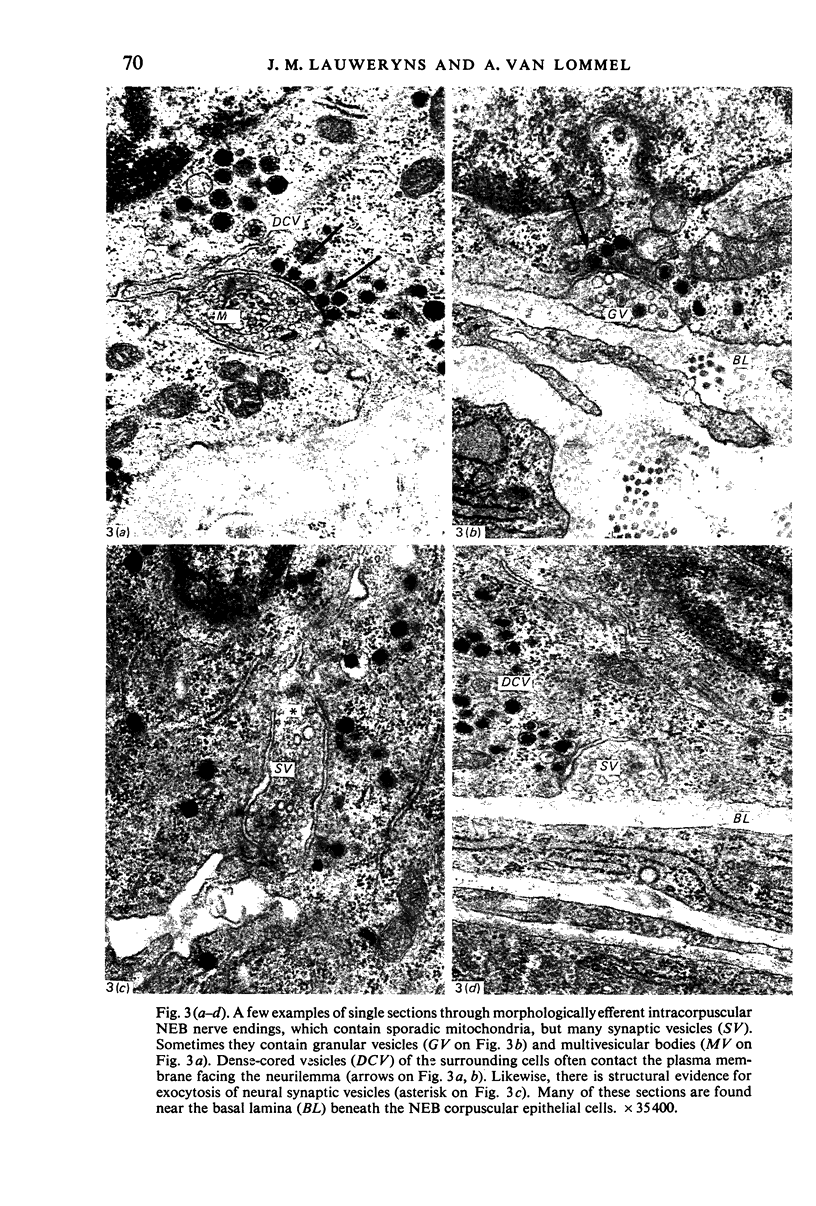

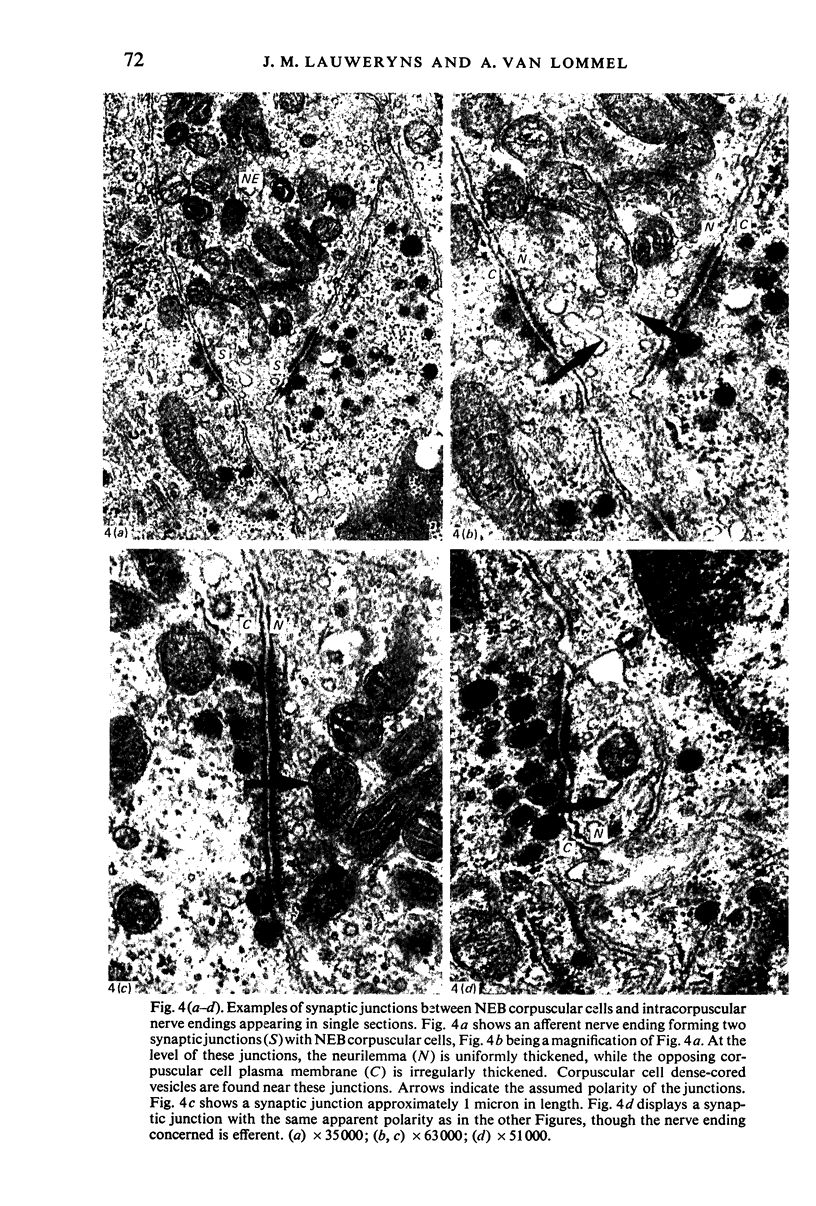
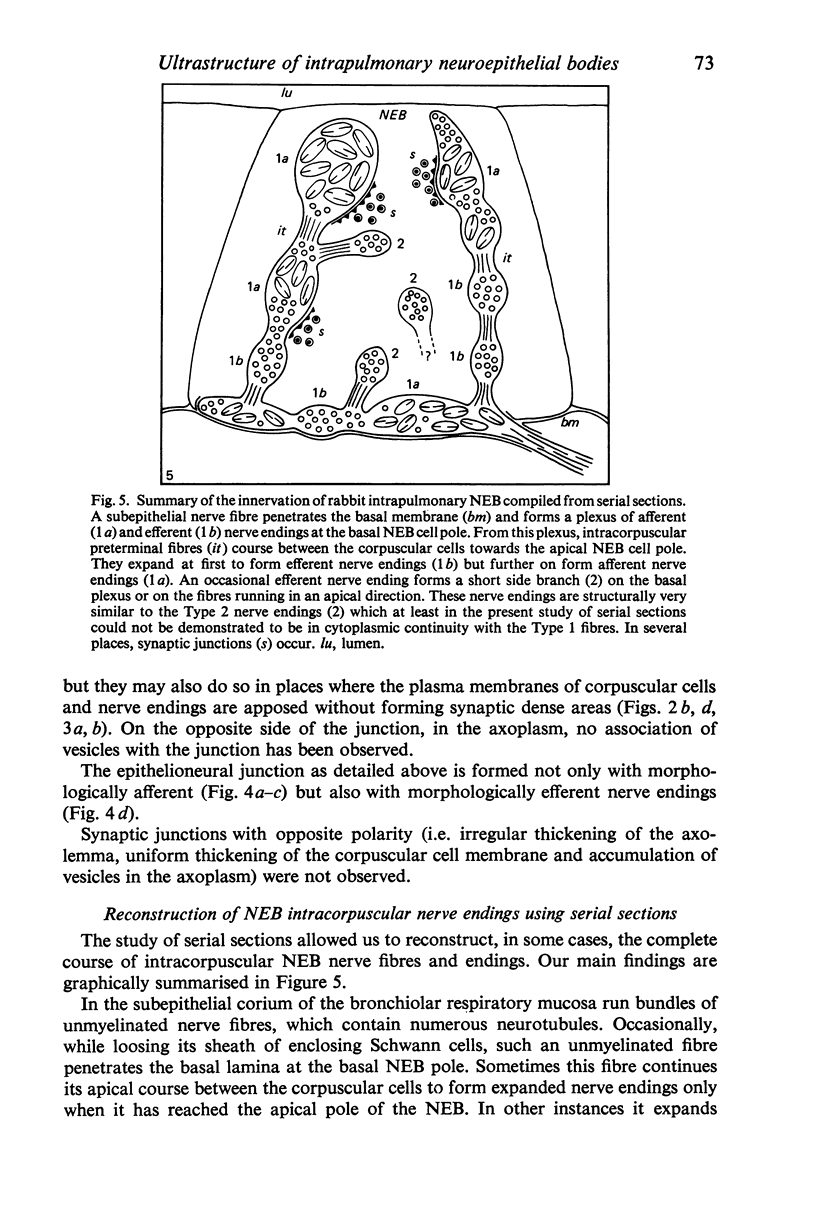
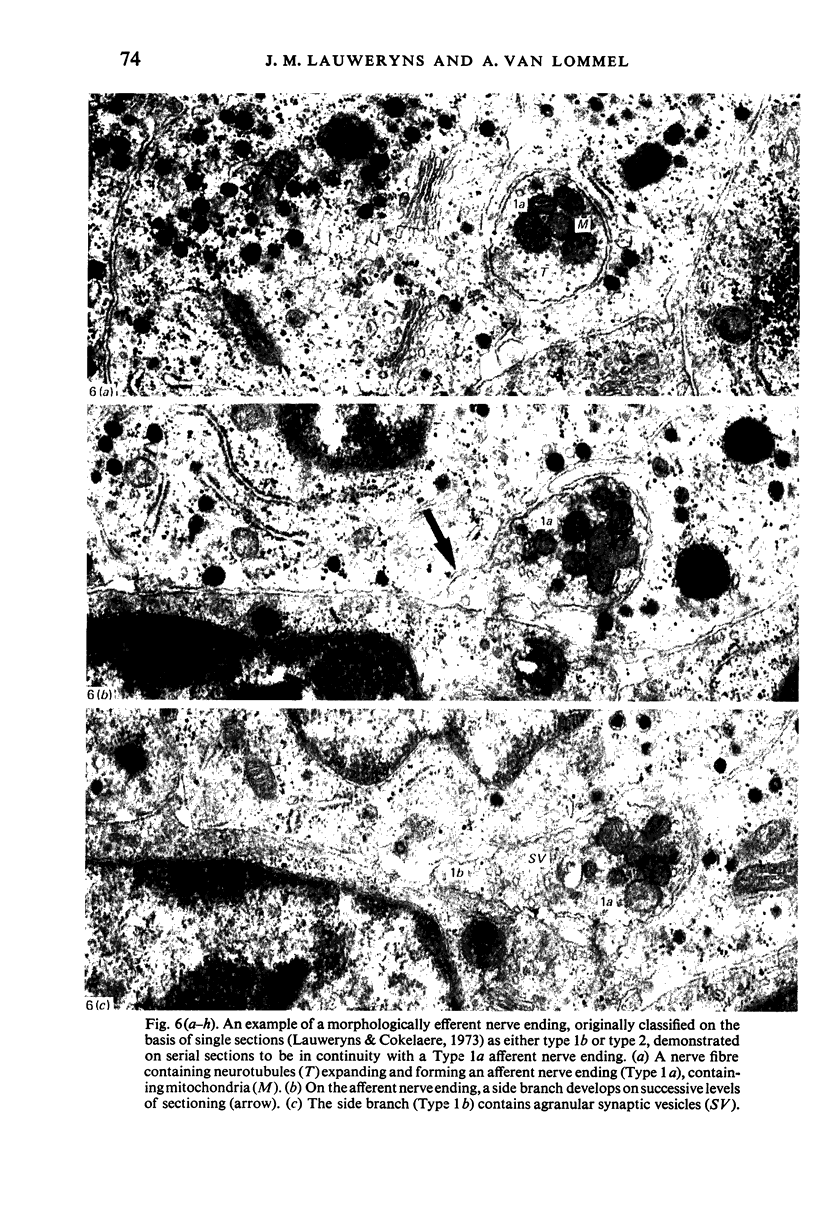
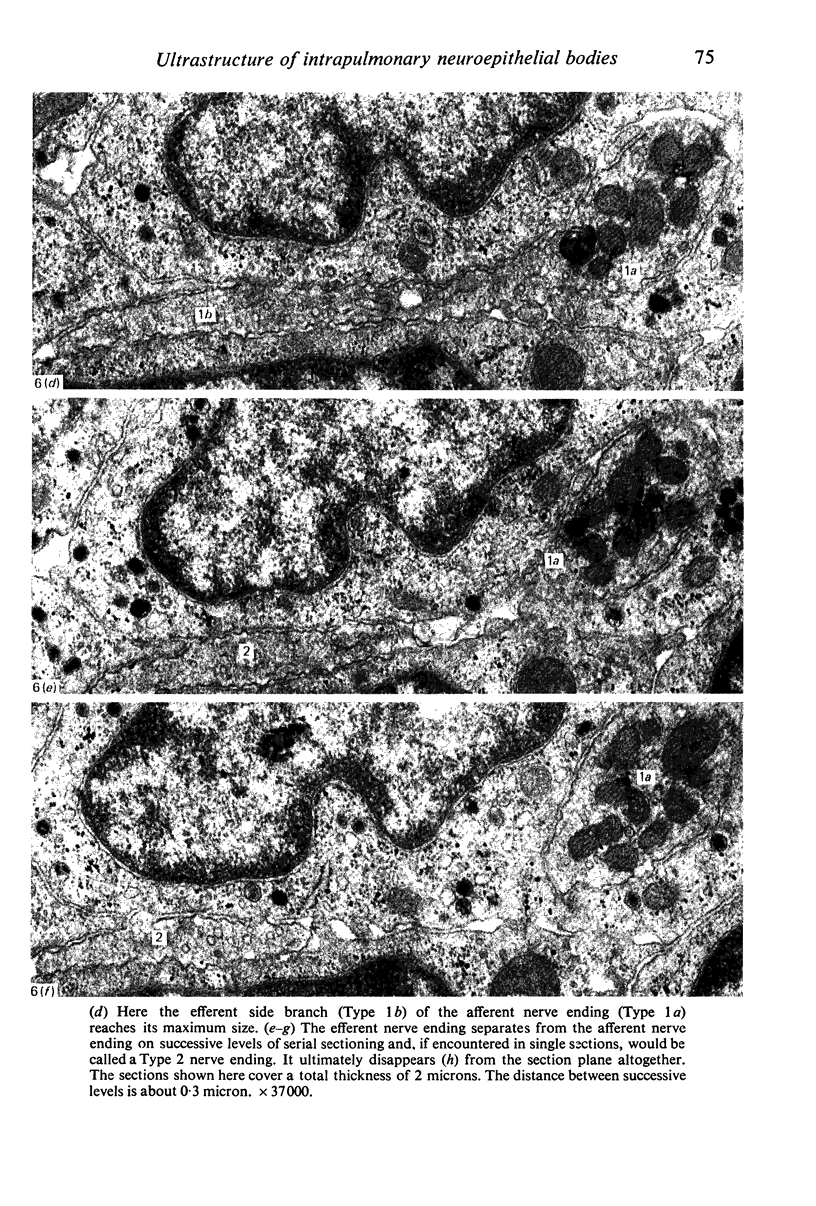
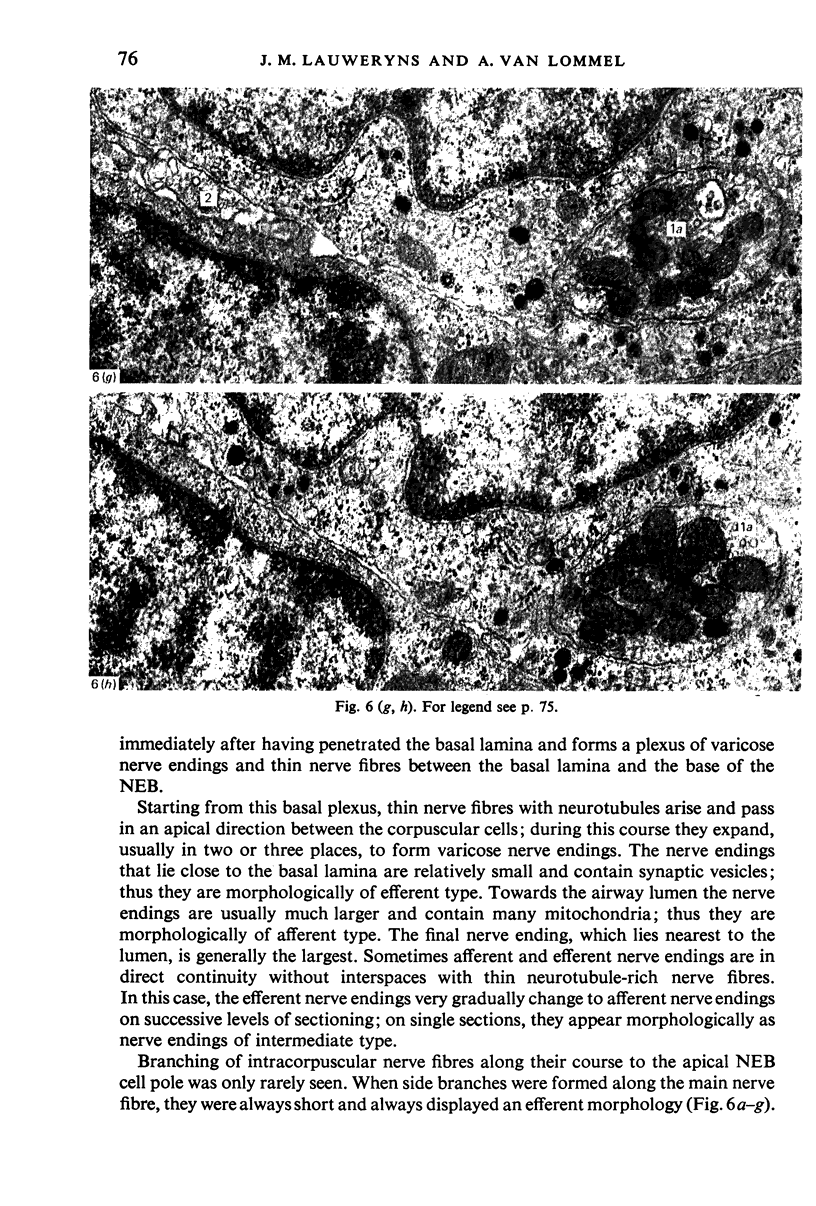







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basbaum C. B., Heuser J. E. Morphological studies of stimulated adrenergic axon varicosities in the mouse vas deferens. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):310–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker K. L., Monaghan K. G., Silva O. L. Immunocytochemical localization of calcitonin in Kulchitsky cells of human lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Apr;104(4):196–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Pallot D. Serial reconstruction with the electron microscope of carotid body tissue. The type I cell nerve supply. Experientia. 1972 Jan 15;28(1):33–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01928247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. The ultrastructure of autonomic cholinergic nerves and junctions. Prog Brain Res. 1979;49:3–21. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64618-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabba V. H., Sorokin S. P., Hoyt R. F., Jr Development of neuroepithelial bodies in intact and cultured lungs of fetal rats. Am J Anat. 1985 May;173(1):1–27. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001730102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Connell L. A., Lawson S. N. Somatic and visceral primary afferents in the lower thoracic dorsal root ganglia of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 20;228(3):422–431. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleridge J. C., Coleridge H. M. Afferent vagal C fibre innervation of the lungs and airways and its functional significance. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;99:1–110. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleridge J. C., Coleridge H. M. Lower respiratory tract afferents stimulated by inhaled irritants. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):S51–S54. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.S5.S51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutz E., Chan W., Sonstegard K. S. Identification of neuro-epithelial bodies in rabbit fetal lungs by scanning electron microscopy: a correlative light, transmission and scanning electron microscopic study. Anat Rec. 1978 Nov;192(3):459–466. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091920311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutz E., Chan W., Track N. S. Bombesin, calcitonin and leu-enkephalin immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of human lung. Experientia. 1981 Jul 15;37(7):765–767. doi: 10.1007/BF01967969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Lundberg J. M. Evidence for a spinal afferent innervation of the guinea pig lower respiratory tract as studied by the horseradish peroxidase technique. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Mar 23;45(2):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. M., Jeffery P. K., Widdicombe J. G. Experimental degeneration of intra-epithelia nerve fibres in cat airways. J Anat. 1979 Mar;128(Pt 2):259–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. M., Jeffrey P. K., Widdicombe J. G. The epithelial innervation of the lower respiratory tract of the cat. J Anat. 1978 May;126(Pt 1):123–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer A. M., De Mey J., Will J. A. Localization of somatostatin-, bombesin-, and serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the lung of the fetal rhesus monkey. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(3):621–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00219240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyzaguirre C., Zapata P. Perspectives in carotid body research. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):931–957. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidone S. J., Stensaas L. J., Zapata P. Sensory nerve endings containing "synaptic" vesicles: an electron-microscope autoradiographic study. J Neurobiol. 1975 Jul;6(4):423–427. doi: 10.1002/neu.480060407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B., Bull T. B., Guz A. Innervation of alveolar walls in the human lung: an electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1980 Dec;131(Pt 4):683–692. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith S. The afferent fibres of the sympathetic nervous system. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1979;28(2):613–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goniakowska-Witalińska L. Neuroepithelial bodies in the lung of the tree frog, Hyla arborea L. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;217(2):435–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00233593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosney J. R., Sissons M. C., O'Malley J. A. Quantitative study of endocrine cells immunoreactive for calcitonin in the normal adult human lung. Thorax. 1985 Nov;40(11):866–869. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.11.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Linnoila R. I. Pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies, neuroendocrine cells, and pulmonary tumors. Hum Pathol. 1982 Dec;13(12):1064–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONJIN R. Experimental degeneration of the vagus, and its relation to the nerve supply of the lung of the mouse, with special reference to the crossing innervation of the lung by the vagi. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Nov;106(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/cne.901060102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONJIN R. On the nerve supply of the lung of the mouse, with special reference to the structure of the peripheral vegetative nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Oct;105(3):587–625. doi: 10.1002/cne.901050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand A. R. Adrenergic and cholinergic nerve terminals in the rat parotid gland. Electron microscopic observations on permanganate-fixed glands. Anat Rec. 1972 Jun;173(2):131–139. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091730202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartschuh W., Weihe E. Fine structural analysis of the synaptic junction of Merkel cell-axon-complexes. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Aug;75(2):159–165. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12522555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S. Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):315–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyes A. D., Barber P., Jagessar H. Location in the nodose ganglion of the perikarya of neurons whose axons distribute in the epithelium of the rat trachea. J Anat. 1982 Mar;134(Pt 2):265–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyes A. D., Barber P. Morphology and response to vagus nerve section of the intra-epithelial axons of the rat trachea. A quantitative ultrastructural study. J Anat. 1981 May;132(Pt 3):331–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt R. F., Jr, Feldman H., Sorokin S. P. Neuroepithelial bodies (NEB) and solitary endocrine cells in the hamster lung. Exp Lung Res. 1982 Nov;3(3-4):299–311. doi: 10.3109/01902148209069659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung K. S. Fine structure of tracheo-bronchial epithelial nerves of the cat. Anat Rec. 1976 May;185(1):85–91. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091850108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung K. S., Hertweck M. S., Hardy J. D., Loosli C. G. Electron microscopic observations of nerve endings in the alveolar walls of mouse lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Aug;108(2):328–333. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.2.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung K. S., Hertweck M. S., Hardy J. D., Loosli C. G. Innervation of pulmonary alveoli of the mouse lung: an electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1972 Dec;135(4):477–495. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001350404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery P., Reid L. Intra-epithelial nerves in normal rat airways: a quantitative electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1973 Jan;114(Pt 1):35–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith I. M., Wiley L. A., Will J. A. Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells: decreased serotonin fluorescence and stable argyrophil-cell numbers in acute hypoxia. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;214(1):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00235157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith I. M., Wiley L. A., Will J. A. Standardization of formaldehyde-induced fluorescence and its measurement to quantify serotonin emission in pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. Histochemistry. 1982;75(2):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00496015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith I. M., Will J. A. Hypoxia and the neonatal rabbit lung: neuroendocrine cell numbers, 5-HT fluorescence intensity, and the relationship to arterial thickness. Thorax. 1981 Oct;36(10):767–773. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.10.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. The involvement of mast cells in vasodilatation due to axon reflexes in injured skin. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Jul;57(3):311–317. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoche H., Wiesner-Menzel L., Addicks K. Ultrastructure of baroreceptors in the carotid sinus of the rabbit. Acta Anat (Basel) 1980;106(1):63–83. doi: 10.1159/000145170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S. Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. 2. Ultrastructure of the synapses on the chief cell. Arch Histol Jpn. 1971 Dec;33(5):397–420. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.33.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H. Innervation of the carotid body of the adult rat. A serial ultrathin section analysis. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Oct 1;173(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00219262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauhs J. M. Morphology of presumptive slowly adapting receptors in dog trachea. Anat Rec. 1984 Sep;210(1):73–85. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen A. Ultrastructural organisation of intraepithelial nerves in the human airway tract. Thorax. 1985 Jul;40(7):488–492. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.7.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere J., Theunynck P. Serotonin producing neuroepithelial bodies in rabbit respiratory mucosa. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):410–413. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M., Deleersynder M., Liebens M. Intrapulmonary neuro-epithelial bodies in newborn rabbits. Influence of hypoxia, hyperoxia, hypercapnia, nicotine, reserpine, L-DOPA and 5-HTP. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Sep 5;182(4):425–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00219827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M. Hypoxia-sensitive neuro-epithelial bodies. Intrapulmonary secretory neuroreceptors, modulated by the CNS. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Dec 21;145(4):521–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00306722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M., Lerut T., Theunynck P. Cross-circulation studies on the influence of hypoxia and hypoxaemia on neuro-epithelial bodies in young rabbits. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Oct 30;193(3):373–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00225336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M., Theunynck P. Neuro-epithelial bodies in the respiratory mucosa of various mammals. A light optical, histochemical and ultrastructural investigation. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;135(4):569–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00583438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Goddeeris P. Neuroepithelial bodies in the human child and adult lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):469–476. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Liebens M. Microspectrography of formaldehyde and fluorescamine-induced fluorescence in rabbit pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies: demonstration of a new, probably polypeptide intracytoplasmic substance. Experientia. 1977 Nov 15;33(11):1510–1511. doi: 10.1007/BF01918840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Peuskens J. C. Neuro-epithelial bodies (neuroreceptor or secretory organs?) in human infant bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium. Anat Rec. 1972 Mar;172(3):471–481. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091720301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Van Lommel A. T., Dom R. J. Innervation of rabbit intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies. Quantitative and qualitative ultrastructural study after vagotomy. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Jan;67(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Van Lommel A. Morphometric analysis of hypoxia-induced synaptic activity in intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(1):201–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00217094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Van Lommel A. The intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies after vagotomy: demonstration of their sensory neuroreceptor-like innervation. Experientia. 1983 Oct 15;39(10):1123–1124. doi: 10.1007/BF01943141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., de Bock V., Guelinckx P., Decramer M. Effects of unilateral hypoxia on neuroepithelial bodies in rabbit lungs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Dec;55(6):1665–1668. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.6.1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., de Bock V., Verhofstad A. A., Steinbusch H. W. Immunohistochemical localization of serotonin in intrapulmonary neuro-epithelial bodies. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(1):215–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00217095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindh B., Dalsgaard C. J., Elfvin L. G., Hökfelt T., Cuello A. C. Evidence of substance P immunoreactive neurons in dorsal root ganglia and vagal ganglia projecting to the guinea pig pylorus. Brain Res. 1983 Jun 20;269(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Uchida T., Nakajima T., Ozawa H. Presence of reciprocal synapses in the rabbit carotid body. Arch Histol Jpn. 1980 Aug;43(3):275–279. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.43.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M., Mitchell R. A. The neural pathway involved in "efferent inhibition" of chemoreceptors in the cat carotid body. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Sep 20;201(3):457–476. doi: 10.1002/cne.902010310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Nerves in rat intra-acinar alveoli: an electron microscopic study. Respir Physiol. 1971 Mar;11(3):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(71)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migally N. The innervation of the mouse adrenal cortex. Anat Rec. 1979 May;194(1):105–111. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091940107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M., Pack R. J., Howe A. Nerve endings in rat carotid body. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;157(2):255–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00222070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnell J. F. Sensory components in the terminal innervation of the ovine cardiac conduction system. Am J Anat. 1982 Apr;163(4):337–350. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001630406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pack R. J., Al-Ugaily L. H., Widdicombe J. G. The innervation of the trachea and extrapulmonary bronchi of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;238(1):61–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00215145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Thoracic receptors connected with sensation. Br Med Bull. 1977 May;33(2):169–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallot D. J., Blakeman N. Quantitative ultrastructural studies of the cat carotid body. II. The type I cell nerve endings. Acta Anat (Basel) 1982;113(2):151–158. doi: 10.1159/000145550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P: its distribution, pharmacological actions and possible physiological role in sensory neurons. Clin Physiol. 1981 Jun;1(3):235–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1981.tb00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. C., Haller C. J. Innervation and cytochemistry of the neuroepithelial bodies in the ciliated epithelium of the toad lung (Bufo marinus). Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Dec 29;195(3):395–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00233885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G. Information arising from the tracheobronchial tree of mammals. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):531–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarikas S. N., Hoyt R. F., Jr, Sorokin S. P. Ontogeny of small-granule APUD cells in hamster lung: a morphological study. Anat Rec. 1985 Nov;213(3):396–409. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092130306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalzi H. A., Price H. M. The arrangement and sensory innervation of the intrafusal fibers in the feline muscle spindle. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Aug;36(3):375–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuermann D. W., De Groodt-Lasseel M. H., Stilman C., Meisters M. L. A correlative light-, fluorescence- and electron-microscopic study of neuroepithelial bodies in the lung of the red-eared turtle, Pseudemys scripta elegans. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(2):249–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00213767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. Pancreatic polypeptide: a unique model for vagal control of endocrine systems. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Oct;9(1):99–111. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Davis B. J. Morphological and functional aspects of pancreatic islet innervation. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Oct;9(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstegard K. S., Mailman R. B., Cheek J. M., Tomlin T. E., DiAugustine R. P. Morphological and cytochemical characterization of neuroepithelial bodies in fetal rabbit lung. I. Studies of isolated neuroepithelial bodies. Exp Lung Res. 1982 Nov;3(3-4):349–377. doi: 10.3109/01902148209069663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin S. P., Hoyt R. F., Jr, Grant M. M. Development of neuroepithelial bodies in fetal rabbit lungs. I. Appearance and functional maturation as demonstrated by high-resolution light microscopy and formaldehyde-induced fluorescence. Exp Lung Res. 1982 Nov;3(3-4):237–259. doi: 10.3109/01902148209069656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H. An ultrastructural study of the inner core of the Pacinian corpuscle. J Neurocytol. 1973 Jun;2(2):217–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01474721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach W., Radke R. Zur Innervation der Langerhansschen Inseln. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Pankreas von Laboratoriumstieren. Endokrinologie. 1982 Jun;79(2):210–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman M. T., Gray M. E. Ontogeny of neuroendocrine cells in human fetal lung. I. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1984 Oct;51(4):449–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman M. T., Kasselberg A. G., Orth D. N., Gray M. E. Ontogeny of neuroendocrine cells in human fetal lung. II. An immunohistochemical study. Lab Invest. 1985 Jan;52(1):52–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi R., Ishikawa O. The effect of N-nitrosobis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine on pulmonary neuroepithelial cells in Syrian golden hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):326–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. Pulmonary argyrophil cells at high altitude. J Pathol. 1977 Jul;122(3):137–144. doi: 10.1002/path.1711220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenchard D. Do axon reflexes exist within the lung? Med Hypotheses. 1983 Dec;12(4):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(83)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verna A. Ulstrastructure of the carotid body in the mammals. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;60:271–330. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasano K., Yamamoto T. A scanning and transmission electron-microscopic study on neuro-epithelial bodies in the neonatal mouse lung. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;216(3):481–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00238645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasano K., Yamamoto T. Monoamine-containing granulated cells in the frog lung. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Oct 17;193(2):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00209034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Solcia E., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the lung. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):769–770. doi: 10.1038/273769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G. Pulmonary and respiratory tract receptors. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:41–57. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G. Studies on afferent airway innervation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jun;115(6 Pt 2):99–105. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.S.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm D. S., Munger B. L. Fetal development of primate chemosensory corpuscles. II. Synaptic relationships in early gestation. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Sep 1;219(1):36–50. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von D5auring M., Andres K. H., Iravani J. The fine structure of the pulmonary stretch receptor in the rat. Kidney Int. 1974 May;5(5):215–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00525771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]