Abstract
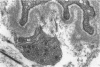
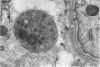
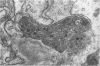
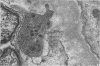
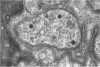
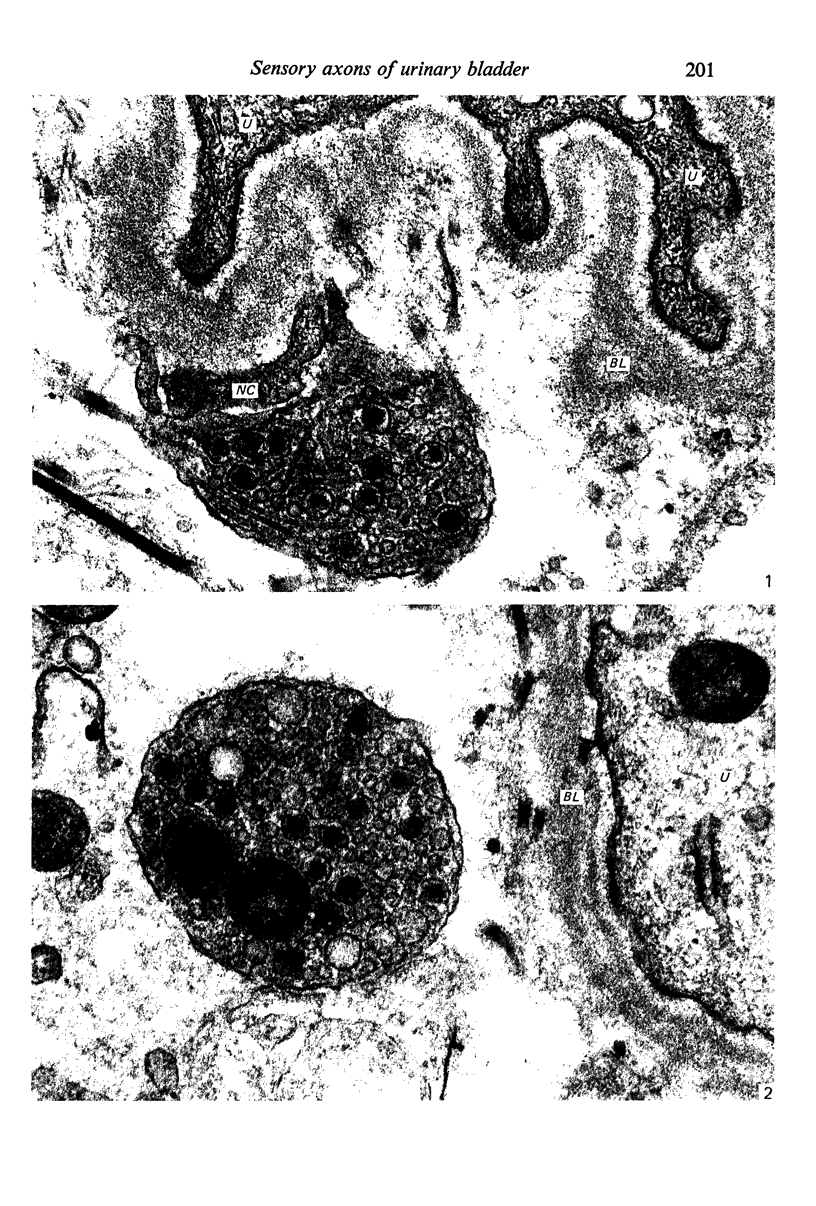
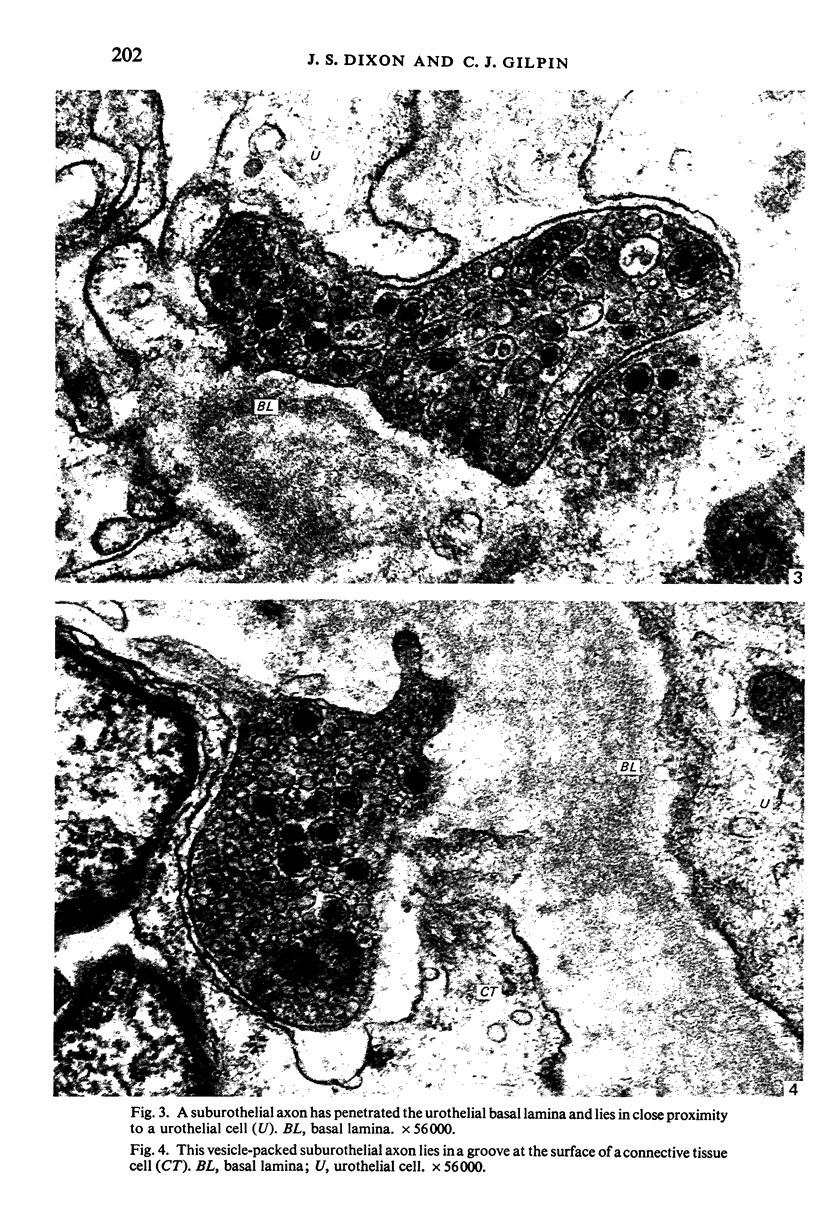
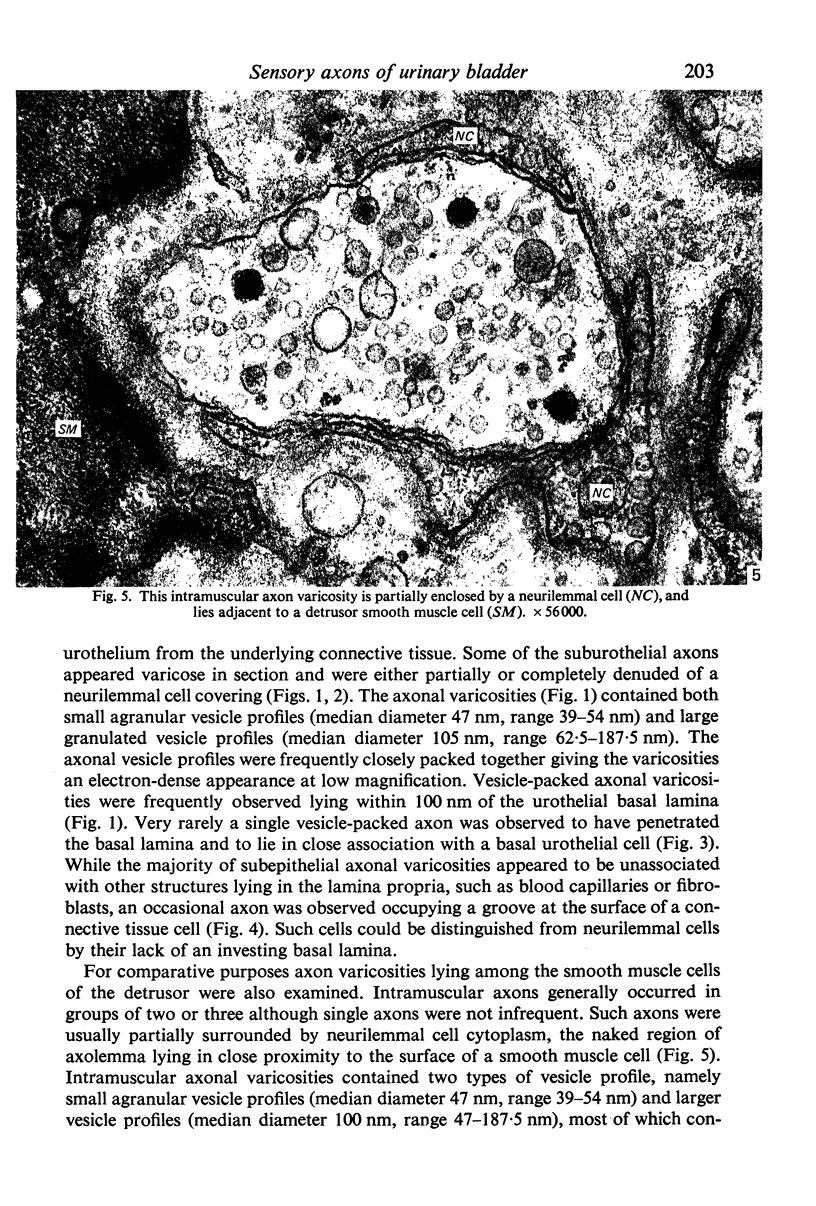
The mucosa of the human urinary bladder possesses an extensive plexus of suburothelial nerve fibres which are believed to be sensory in nature. Many of these presumptive sensory nerves occur as single axons whose vesicle-packed varicose regions are totally devoid of neurilemmal cell covering and occasionally penetrate the urothelial basal lamina. The axonal vesicles are of two types, small agranular vesicles (median diameter 47 nm, range 39-54 nm) and large granulated vesicles (median diameter 105 nm, range 62.5-187.5 nm). When compared statistically with intramuscular axon varicosities the suburothelial varicosities are shown to possess a significantly greater packing density of axonal vesicles and to contain a significantly greater proportion of large granulated vesicles. The latter finding may reflect the presence of substance P, a neuropeptide known to occur in primary sensory nerves.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm P., Alumets J., Brodin E., Håkanson R., Nilsson G., Sjöberg N. O., Sundler F. Peptidergic (substance P) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm P. Cholinergic innervation of the human urethra and urinary bladder: a histochemical study and review of methodology. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978;43 (Suppl 2):56–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb03220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Cowan W., Daniel V. P. Structural bases for neural and myogenic control of human detrusor muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;61(11):1247–1273. doi: 10.1139/y83-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek A., Alm P., Andersson K. E., Persson C. G. Adrenergic and Cholinergic Nerves of the Human Urethra and Urinary Bladder. A histochemical study. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Mar;99(3):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosling J. The structure of the bladder and urethra in relation to function. Urol Clin North Am. 1979 Feb;6(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Bucsics A., Lembeck F. Distribution of capsaicin-sensitive nerve fibres containing immunoreactive substance P in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 31;31(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Kellerth J. O., Nilsson G., Pernow B. Experimental immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of substance P in cat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 19;100(2):235–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson O., Lundberg J. M. Ultrastructural localization of VIP-like immunoreactivity in large dense-core vesicles of 'cholinergic-type' nerve terminals in cat exocrine glands. Neuroscience. 1981;6(5):847–862. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klück P. The autonomic innervation of the human urinary bladder, bladder neck and urethra: a histochemical study. Anat Rec. 1980 Nov;198(3):439–447. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091980306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell J., Benson G. S., Wood J. G. Autonomic innervation of the urogenital system: adrenergic and cholinergic elements. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):679–694. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley T. L., el-Badawi A., McDonald D. F., Schenk E. A. Innervation of the human urinary bladder. Surg Forum. 1966;17:505–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyo M. M. Innervation of the bladder and urethra. J Anat. 1969 Jul;105(Pt 1):210–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Meli A. The effect of capsaicin pretreatment on the cystometrograms of urethane anesthetized rats. J Urol. 1985 Apr;133(4):700–703. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)49164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Williams R. G., Schultzberg M., Dockray G. J. Sensory substance P-innervation of the urinary bladder: possible site of action of capsaicin in causing urine retention in rats. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]