Abstract
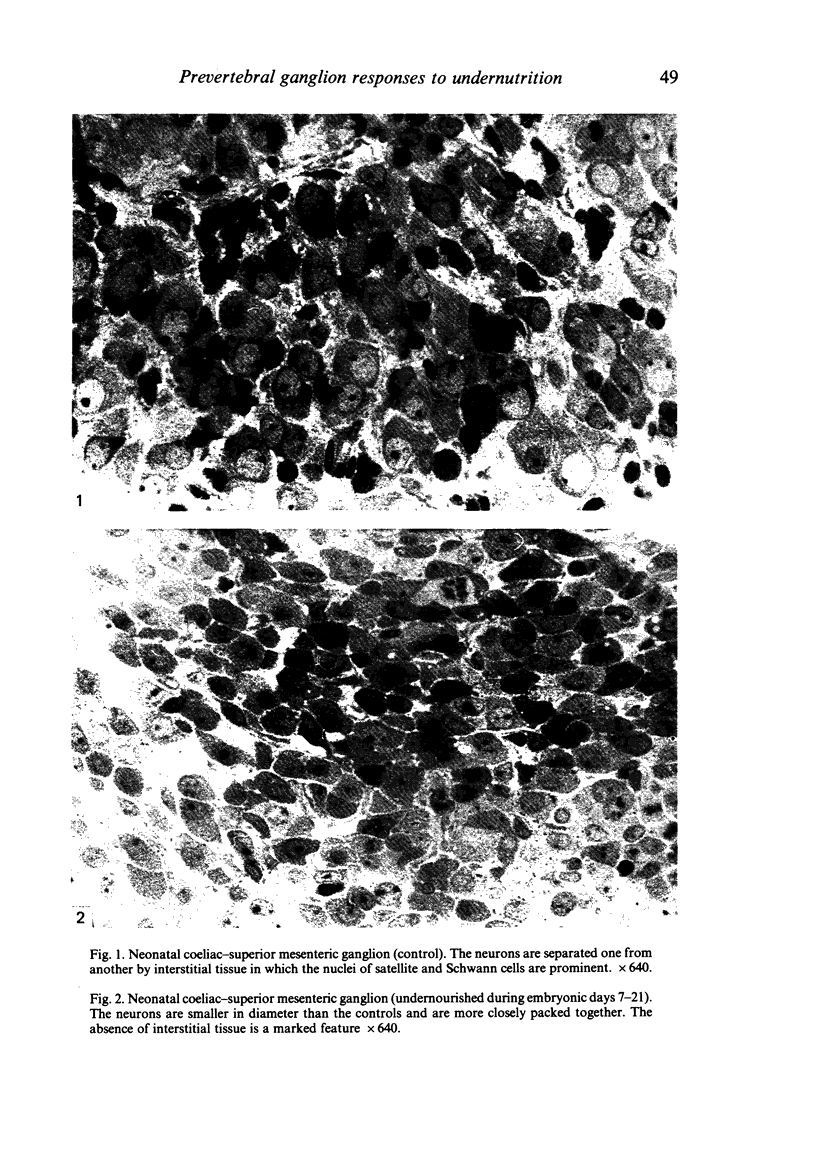
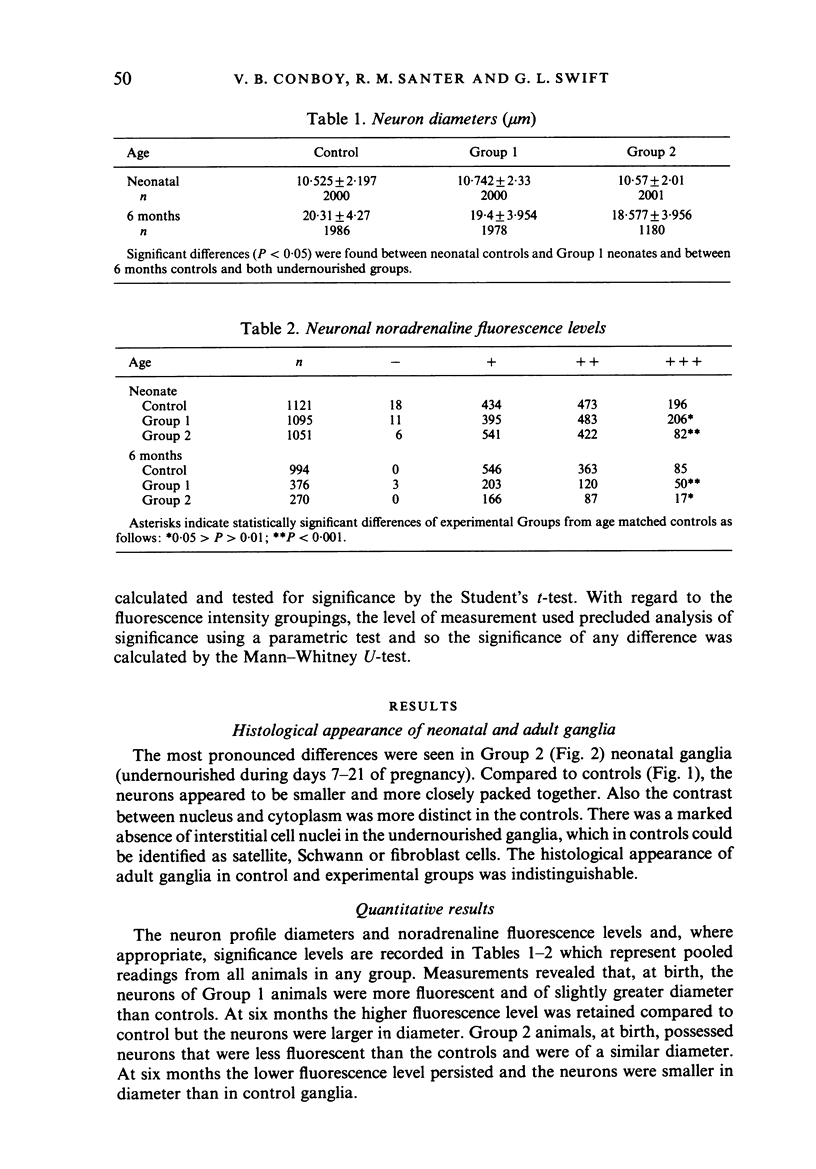
The effects of maternal undernutrition during the last seven and last fourteen days of pregnancy on neurons of the rat coeliac-superior mesenteric ganglion has been investigated in neonates and in adult animals. The parameters studied were neuron diameter and the level of neuronal noradrenaline fluorescence. The morphology was more permanently affected by fourteen than by seven days undernutrition as shown by the smaller neuron diameters persisting at six months. Both periods of undernutrition affected noradrenaline levels permanently: seven days undernutrition producing a rise and fourteen days producing a depression. These changes demonstrate the permanent effects of maternal undernutrition on the development and maturation of prevertebral sympathetic neurons.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohn M. C., Goldstein M., Black I. B. Role of glucocorticoids in expression of the adrenergic phenotype in rat embryonic adrenal gland. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90423-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Champlain J., Malmfors T., Olson L., Sachs C. Ontogenesis of peripheral adrenergic neurons in the rat: pre- and postnatal observations. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Oct;80(2):276–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Basso P., Keller E. A., Salica C., Orsingher O. A. Vascular reactivity in perinatally undernourished rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson S. E., Jones D. G. Some effects of undernutrition on synaptic development -- a quantitative ultrastructural study. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90960-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernholm M. On the appearance of monoamines in the sympathetic systems and the chromaffin tissue in the mouse embryo. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1972;135(3):350–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00519044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernholm M. On the development of the sympathetic chain and the adrenal medulla in the mouse. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1971;133(3):305–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00519305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaetani S., Mengheri E., Spadoni M. A., Rossi A., Toschi G. Effects of litter size on protein, choline acetyltransferase (cat), and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH) of a mouse sympathetic ganglion. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 14;86(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90639-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., De Champlain J., Glowinski J., Axelrod J. Uptake, storage and metabolism of norepinephrine in tissues of the developing rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Sep;157(3):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. A., Munaro N. I., Orsingher O. A. Perinatal undernutrition reduces alpha and beta adrenergic receptor binding in adult rat brain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1269–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.7058348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Teillet M. A. Experimental analysis of the migration and differentiation of neuroblasts of the autonomic nervous system and of neurectodermal mesenchymal derivatives, using a biological cell marking technique. Dev Biol. 1974 Nov;41(1):162–184. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J., Dubos R. Lasting biological effects of early environmental influences. 8. Effects of neonatal infection, perinatal malnutrition, and crowding on catecholamine metabolism of brain. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1031–1042. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marichich E. S., Molina V. A., Orsingher O. A. Persistent changes in central catecholaminergic system after recovery of perinatally undernourished rats. J Nutr. 1979 Jun;109(6):1045–1050. doi: 10.1093/jn/109.6.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owman C., Sjöberg N. O., Swedin G. Histochemical and chemical studies on pre- and postnatal development of the different systems of "short" and "long" adrenergic neurons in peripheral organs of the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;116(3):319–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00330631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read J. B., Burnstock G. Developement of the adrenergic innervation and chromaffin cells in the human fetal gut. Dev Biol. 1970 Jul;22(3):513–534. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. Development of the rat superior cervical ganglion: ganglion cell maturation. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):673–684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00673.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. Development of the rat superior cervical ganglion: ingrowth of preganglionic axons. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):685–696. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00685.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Díaz S., Nieto A. Effects of neonatal food deprivation on cortical spines and dendritic development of the rat. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. Effects of early undernutrition on dendritic spines of cortical pyramidal cells in the rat. Dev Neurosci. 1980;3(3):109–117. doi: 10.1159/000112384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker W. J., Wurtman R. J. Perinatal undernutrition: accumulation of catecholamines in rat brain. Science. 1971 Mar 12;171(3975):1017–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3975.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D. Rostrocaudal differences in dendritic growth and synaptogenesis in rat sympathetic chain ganglia. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Feb 8;244(2):245–253. doi: 10.1002/cne.902440210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka T. J., Cook M. P., Brodie R. E. Neonatal malnutrition: neurochemical, hormonal and behavioral manifestations. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 18;65(3):443–457. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. SOURCES OF NORADRENALINE IN THE 'IMMUNOSYMPATHECTOMIZED' RAT. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1315–1316. doi: 10.1038/2041315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamenhof S., Van Marthens E., Margolis F. L. DNA (cell number) and protein in neonatal brain: alteration by maternal dietary protein restriction. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):322–323. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]