Abstract
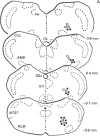
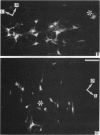
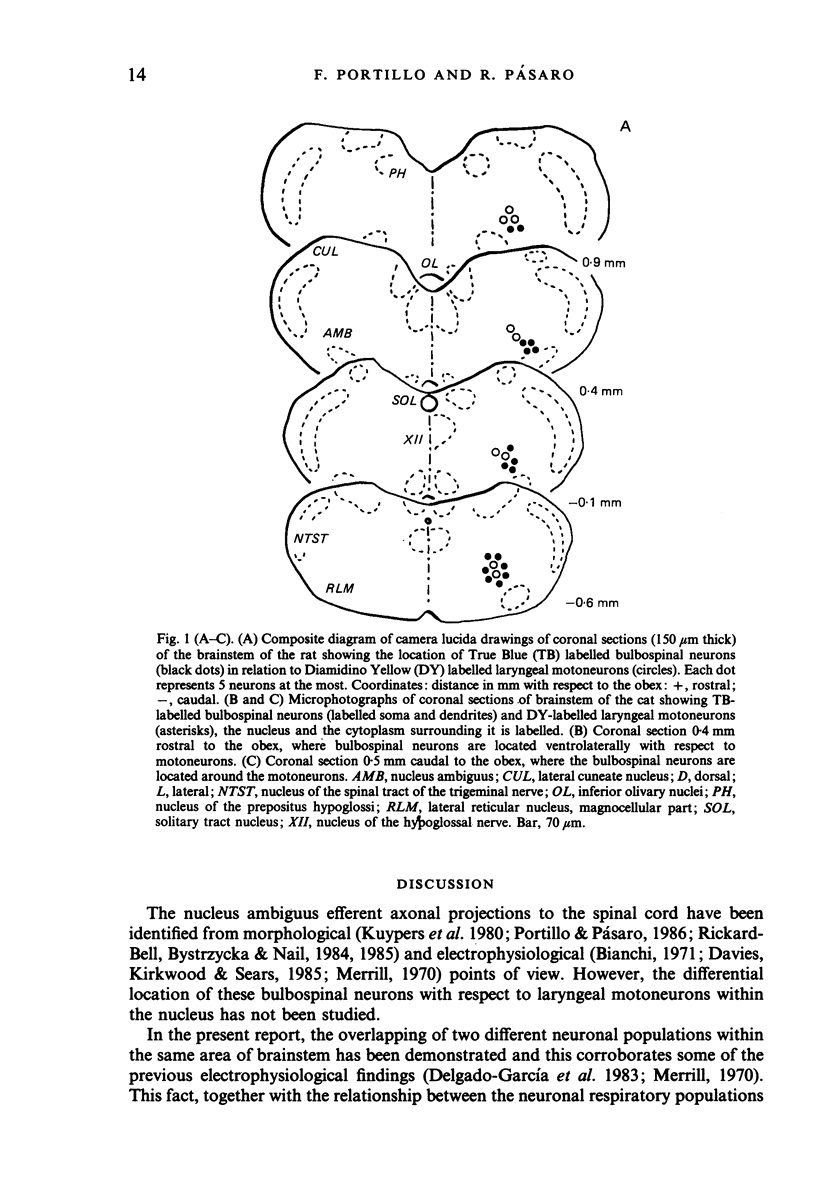
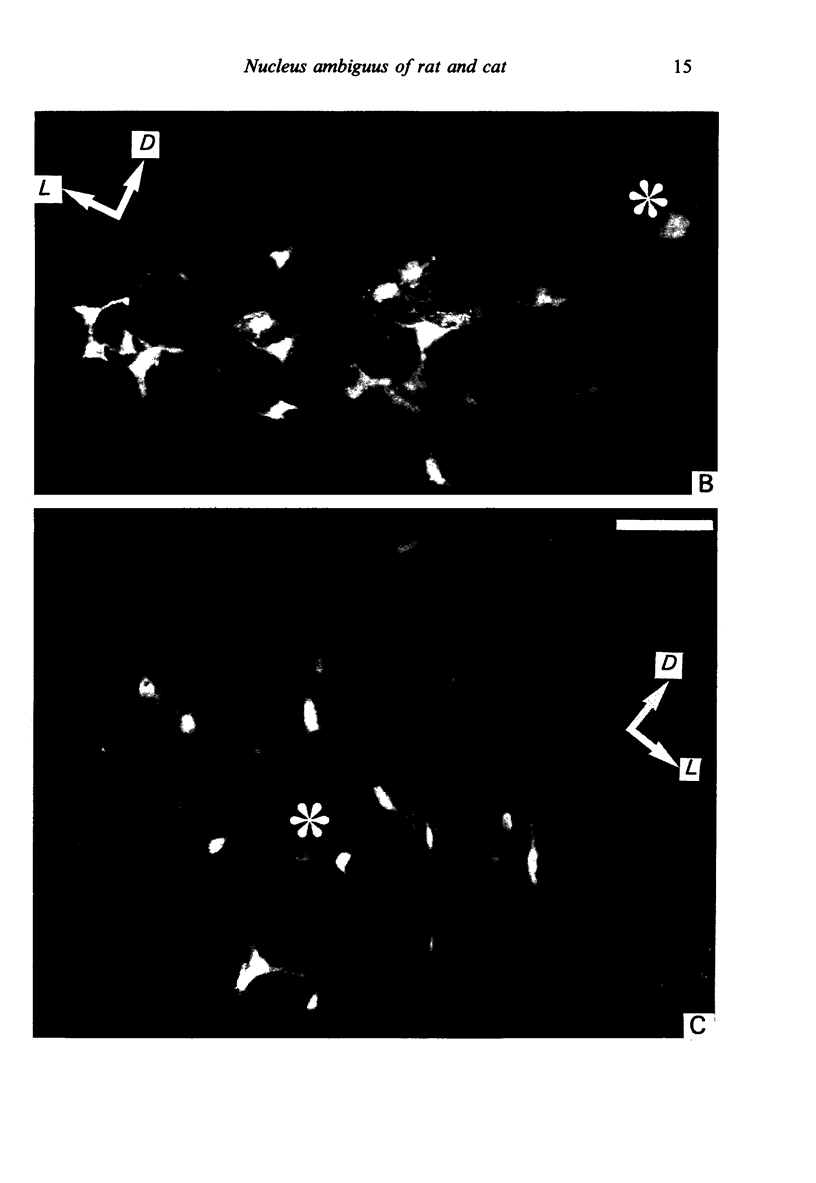
The location of bulbospinal neurons within the nucleus ambiguus with respect to laryngeal motoneurons has been studied by means of retrograde fluorescent neuronal markers (True Blue and Diamidino Yellow in rats, and Fast Blue and Diamidino Yellow in cats). One marker was injected into the cervical spinal cord, and the other into the intrinsic laryngeal muscles. Afterwards, the precise location of each neuronal pool was observed with the fluorescent microscope. The bulbospinal neurons in the rostral part of the nucleus were located ventrolaterally with respect to motoneurons, both in cats and rats; at more caudal levels of the nucleus the bulbospinal neurons were arranged ventromedially and ventrolaterally with respect to motoneurons in cats, and around the motoneurons in rats.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentivoglio M., Kuypers H. G., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Loewe H., Dann O. Two new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers which are transported over long distances. Neurosci Lett. 1980 May 15;18(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. L. Localisation et étude des neurones respiratoires bulbaires. Mise en jeu antidromique par stimulation spinale ou vagale. J Physiol (Paris) 1971 Jan-Feb;63(1):5–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The distribution of monosynaptic connexions from inspiratory bulbospinal neurones to inspiratory motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:63–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-García J. M., López-Barneo J., Serra R., González-Barón S. Electrophysiological and functional identification of different neuronal types within the nucleus ambiguus in the cat. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 31;277(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90930-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstege G., Kuypers H. G. The anatomy of brain stem pathways to the spinal cord in cat. A labeled amino acid tracing study. Prog Brain Res. 1982;57:145–175. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64128-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer K., Kuypers H. G., Huisman A. M., Dann O. Diamidino yellow dihydrochloride (DY . 2HCl); a new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracer, which migrates only very slowly out of the cell. Exp Brain Res. 1983;51(2):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00237193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. G., Bentivoglio M., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Bharos A. T. Double retrograde neuronal labeling through divergent axon collaterals, using two fluorescent tracers with the same excitation wavelength which label different features of the cell. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40(4):383–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00236147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. The localization, in the nucleus ambiguus of the rabbit, of the cells of origin of motor nerve fibers in the glossopharyngeal nerve and various branches of the vagus nerve by means of retrograde degeneration. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jun;127(2):293–306. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. The nucleus ambiguus of the rabbit. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jun;127(2):307–320. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobera B., Pásaro R., González-Barón S., Delgado-García J. M. A morphological study of ambiguus nucleus motoneurons innervating the laryngeal muscles in the rat and cat. Neurosci Lett. 1981 May 6;23(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. E., Duffin J. The medullary respiratory neurons: a review. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;62(2):161–182. doi: 10.1139/y84-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G. The lateral respiratory neurones of the medulla: their associations with nucleus ambiguus, nucleus retroambigualis, the spinal accessory nucleus and the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1970 Nov 11;24(1):11–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Pásaro R., Delgado-García J. M. Spinal projections of brainstem respiratory related neurons in the cat as revealed by retrograde fluorescent markers. Rev Esp Fisiol. 1986 Dec;42(4):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pásaro R., Lobera B., González-Barón S., Delgado-García J. M. Cytoarchitectonic organization of laryngeal motoneurons within the nucleus ambiguus of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1983 Dec;82(3):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(83)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pásaro R., Lobera B., González-Barón S., Delgado-García J. M. Localización de las motoneuronas de los músculos intrínsecos de la laringe en la rata. Rev Esp Fisiol. 1981 Sep;37(3):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikard-Bell G. C., Bystrzycka E. K., Nail B. S. The identification of brainstem neurones projecting to thoracic respiratory motoneurones in the cat as demonstrated by retrograde transport of HRP. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Jan;14(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Hayashi Y. Identification of motoneurons in the nucleus ambiguus by antidromic stimulation of the superior and the recurrent laryngeal nerves in rats. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 12;288(1-2):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]