Abstract
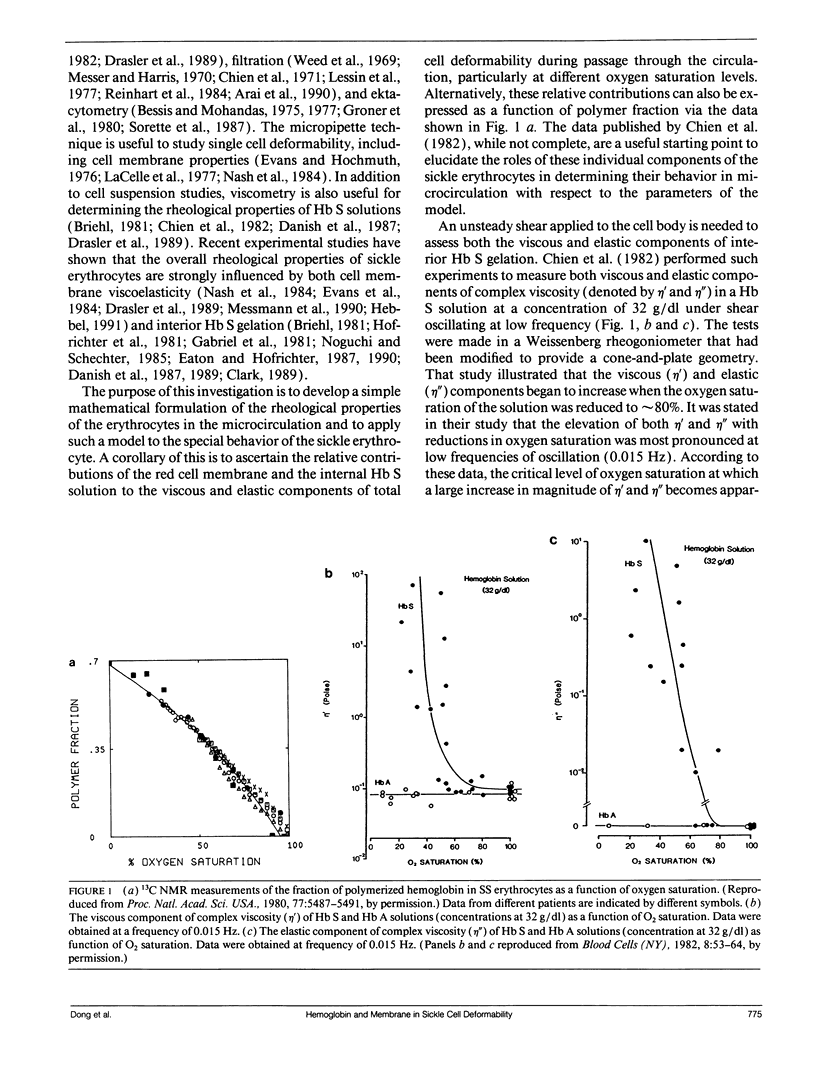
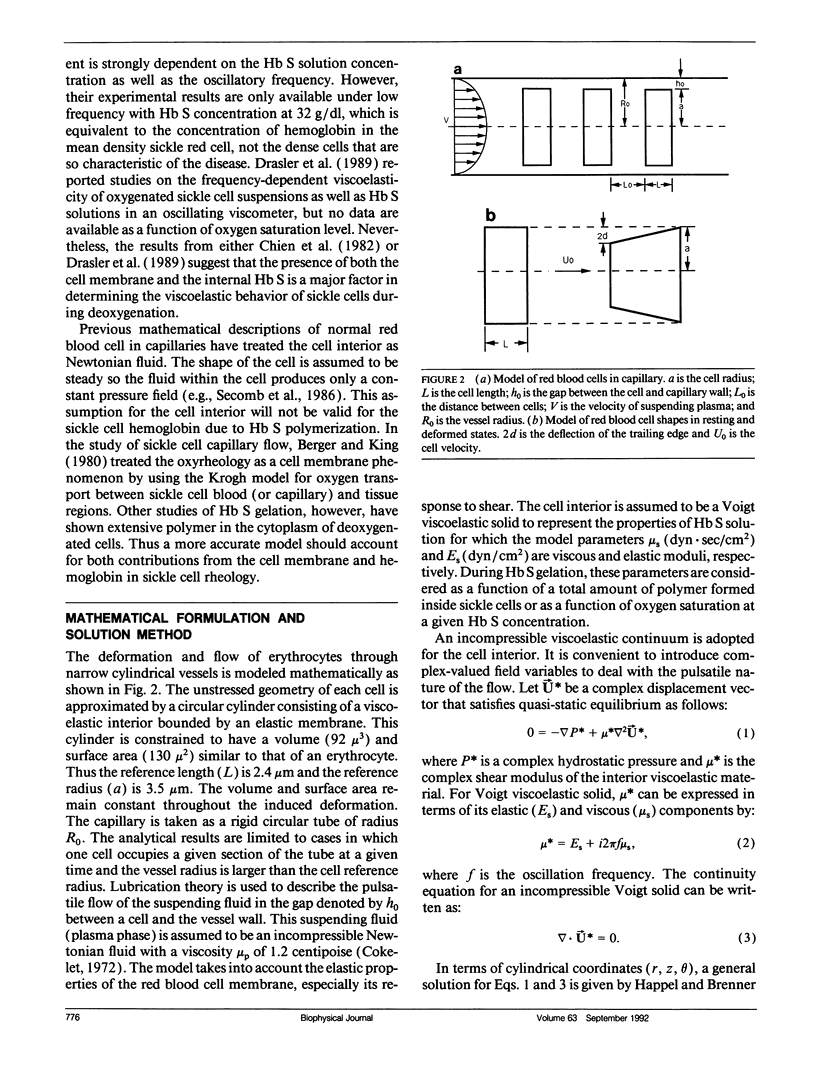
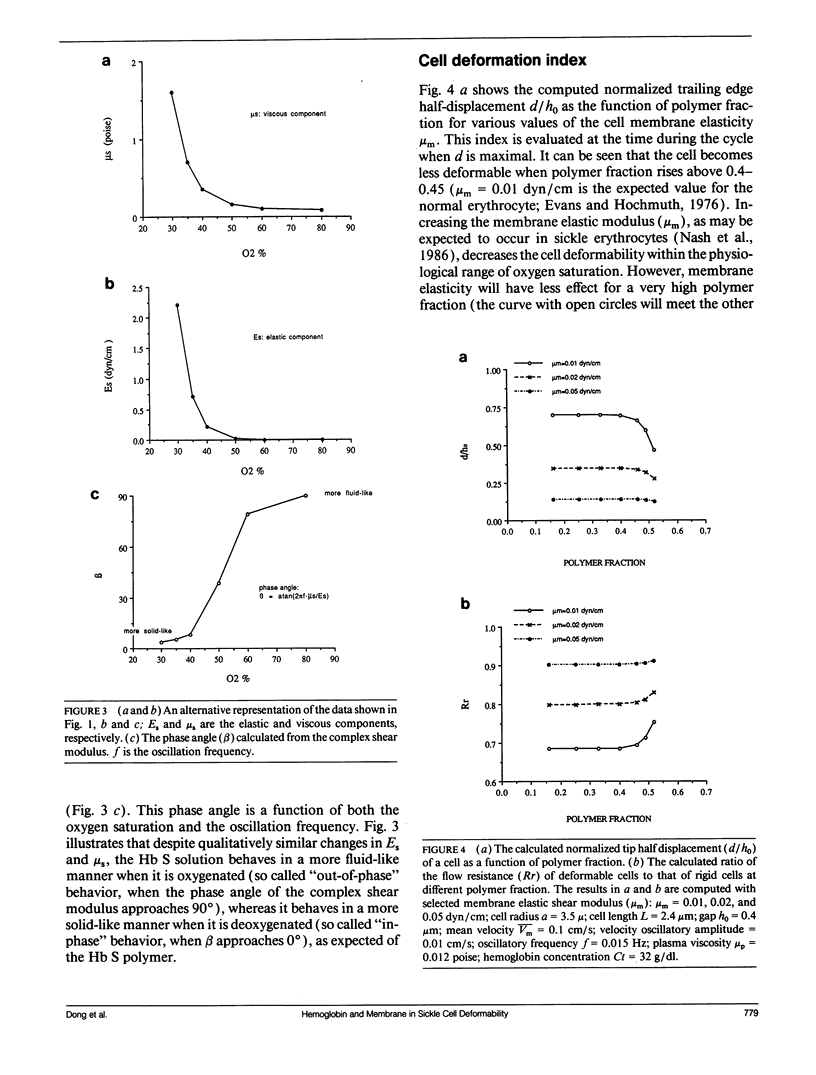
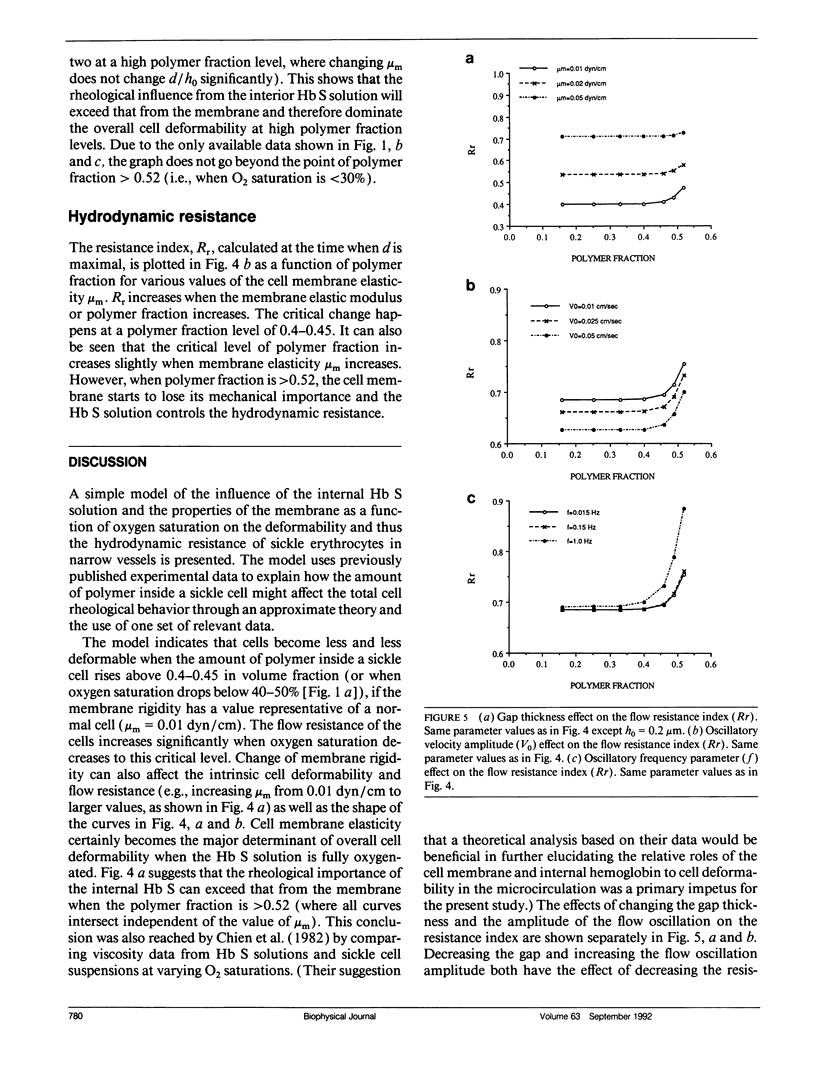
The rheological properties of normal erythrocytes appear to be largely determined by those of the red cell membrane. In sickle cell disease, the intracellular polymerization of sickle hemoglobin upon deoxygenation leads to a marked increase in intracellular viscosity and elastic stiffness as well as having indirect effects on the cell membrane. To estimate the components of abnormal cell rheology due to the polymerization process and that due to the membrane abnormalities, we have developed a simple mathematical model of whole cell deformability in narrow vessels. This model uses hydrodynamic lubrication theory to describe the pulsatile flow in the gap between a cell and the vessel wall. The interior of the cell is modeled as a Voigt viscoelastic solid with parameters for the viscous and elastic moduli, while the membrane is assigned an elastic shear modulus. In response to an oscillatory fluid shear stress, the cell--modeled as a cylinder of constant volume and surface area--undergoes a conical deformation which may be calculated. We use published values of normal and sickle cell membrane elastic modulus and of sickle hemoglobin viscous and elastic moduli as a function of oxygen saturation, to estimate normalized tip displacement, d/ho, and relative hydrodynamic resistance, Rr, as a function of polymer fraction of hemoglobin for sickle erythrocytes. These results show the transition from membrane to internal polymer dominance of deformability as oxygen saturation is lowered. More detailed experimental data, including those at other oscillatory frequencies and for cells with higher concentrations of hemoglobin S, are needed to apply fully this approach to understanding the deformability of sickle erythrocytes in the microcirculation. The model should be useful for reconciling the vast and disparate sets of data available on the abnormal properties of sickle cell hemoglobin and sickle erythrocyte membranes, the two main factors that lead to pathology in patients with this disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Iino M., Shio H., Uyesaka N. Further investigations of red cell deformability with nickel mesh. Biorheology. 1990;27(1):47–65. doi: 10.3233/bir-1990-27105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. A., King W. S. The flow of sickle-cell blood in the capillaries. Biophys J. 1980 Jan;29(1):119–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85121-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARACHE S., CONLEY C. L. RATE OF SICKLING OF RED CELLS DURING DEOXYGENATION OF BLOOD FROM PERSONS WITH VARIOUS SICKLING DISORDERS. Blood. 1964 Jul;24:25–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Kaperonis A. A., King R. G., Lipowsky H. H., Schmalzer E. A., Sung L. A., Sung K. L., Usami S. Rheology of sickle cells and its role in microcirculatory dynamics. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;240:151–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., King R. G., Kaperonis A. A., Usami S. Viscoelastic properties of sickle cells and hemoglobin. Blood Cells. 1982;8(1):53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Luse S. A., Bryant C. A. Hemolysis during filtration through micropores: a scanning electron microscopic and hemorheologic correlation. Microvasc Res. 1971 Apr;3(2):183–203. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(71)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Usami S., Bertles J. F. Abnormal rheology of oxygenated blood in sickle cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):623–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI106273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R. Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration and cell deformability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;565:284–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINTENFASS L. RHEOLOGY OF PACKED RED BLOOD CELLS CONTAINING HEMOGLOBINS A-A, S-A, AND S-S. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danish E. H., Harris J. W., Moore C. R., Krieger I. M. Rheologic behavior of deoxyhemoglobin S gels. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90702-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danish E. H., Harris J. W., Oh K. Solidity of sickle hemoglobin gels: relevance to pathophysiology of sickling disorders. Cleve Clin J Med. 1989 Nov-Dec;56(8):793–800. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.56.8.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasler W. J., Smith C. M., 2nd, Keller K. H. Viscoelastic properties of the oxygenated sickle erythrocyte membrane. Biorheology. 1989;26(5):935–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Hofrichter J. Hemoglobin S gelation and sickle cell disease. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1245–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Hofrichter J. Sickle cell hemoglobin polymerization. Adv Protein Chem. 1990;40:63–279. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Hochmuth R. M. Membrane viscoelasticity. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85658-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Mohandas N., Leung A. Static and dynamic rigidities of normal and sickle erythrocytes. Major influence of cell hemoglobin concentration. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):477–488. doi: 10.1172/JCI111234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis R. B., Jr, Johnson C. S. Vascular occlusion in sickle cell disease: current concepts and unanswered questions. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1405–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel D. A., Smith L. A., Johnson C. S., Jr Elastic properties of deoxy hemoglobin S (deoxy-HbS) gels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 15;211(2):774–776. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90514-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. A., Noguchi C. T., Keidan A. J., Marwah S. S., Stuart J. Polymerization of sickle cell hemoglobin at arterial oxygen saturation impairs erythrocyte deformability. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1669–1674. doi: 10.1172/JCI113504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner W., Mohandas N., Bessis M. New optical technique for measuring erythrocyte deformability with the ektacytometer. Clin Chem. 1980 Sep;26(10):1435–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P. Beyond hemoglobin polymerization: the red blood cell membrane and sickle disease pathophysiology. Blood. 1991 Jan 15;77(2):214–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug P. P., Lessin L. S., Radice P. Rheological aspects of sickle cell disease. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Apr;133(4):577–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaCelle P. L. Alteration of membrane deformability in hemolytic anemias. Semin Hematol. 1970 Oct;7(4):355–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linderkamp O., Meiselman H. J. Geometric, osmotic, and membrane mechanical properties of density-separated human red cells. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1121–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer M. J., Harris J. W. Filtration characteristics of sickle cells: rates of alteration of filterability after deoxygenation and reoxygenation, and correlations with sickling and unsickling. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):537–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messmann R., Gannon S., Sarnaik S., Johnson R. M. Mechanical properties of sickle cell membranes. Blood. 1990 Apr 15;75(8):1711–1717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Phillips W. M., Bessis M. Red blood cell deformability and hemolytic anemias. Semin Hematol. 1979 Apr;16(2):95–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
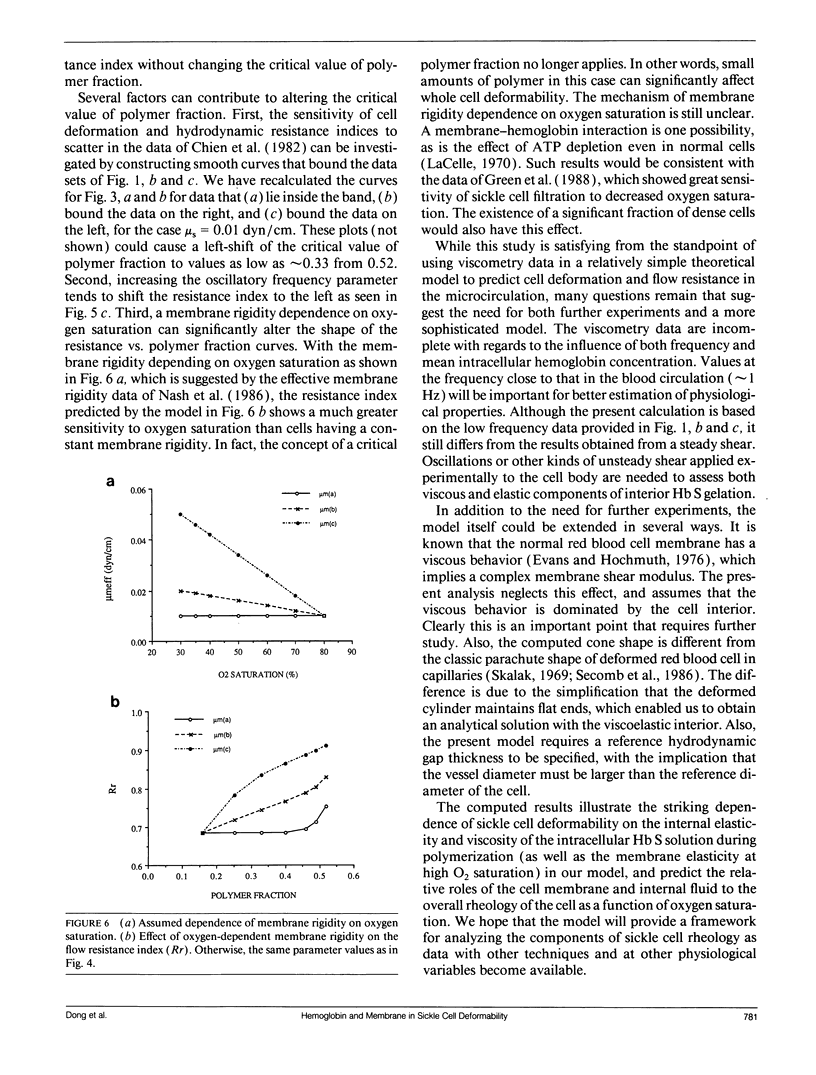
- Nash G. B., Johnson C. S., Meiselman H. J. Influence of oxygen tension on the viscoelastic behavior of red blood cells in sickle cell disease. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):110–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash G. B., Johnson C. S., Meiselman H. J. Mechanical properties of oxygenated red blood cells in sickle cell (HbSS) disease. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash G. B., Meiselman H. J. Red cell and ghost viscoelasticity. Effects of hemoglobin concentration and in vivo aging. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84324-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Schechter A. N. Sickle hemoglobin polymerization in solution and in cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:239–263. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Torchia D. A., Schechter A. N. Determination of deoxyhemoglobin S polymer in sickle erythrocytes upon deoxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfafferott C., Nash G. B., Meiselman H. J. Red blood cell deformation in shear flow. Effects of internal and external phase viscosity and of in vivo aging. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):695–704. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83966-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart W. H., Usami S., Schmalzer E. A., Lee M. M., Chien S. Evaluation of red blood cell filterability test: influences of pore size, hematocrit level, and flow rate. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Oct;104(4):501–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. P., Schechter A. N., Noguchi C. T., Klein H. G., Nienhuis A. W., Bonner R. F. Periodic microcirculatory flow in patients with sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 13;311(24):1534–1538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412133112403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalak R., Branemark P. I. Deformation of red blood cells in capillaries. Science. 1969 May 9;164(3880):717–719. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3880.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorette M. P., Lavenant M. G., Clark M. R. Ektacytometric measurement of sickle cell deformability as a continuous function of oxygen tension. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):316–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weed R. I., LaCelle P. L., Merrill E. W. Metabolic dependence of red cell deformability. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):795–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI106038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


