Abstract
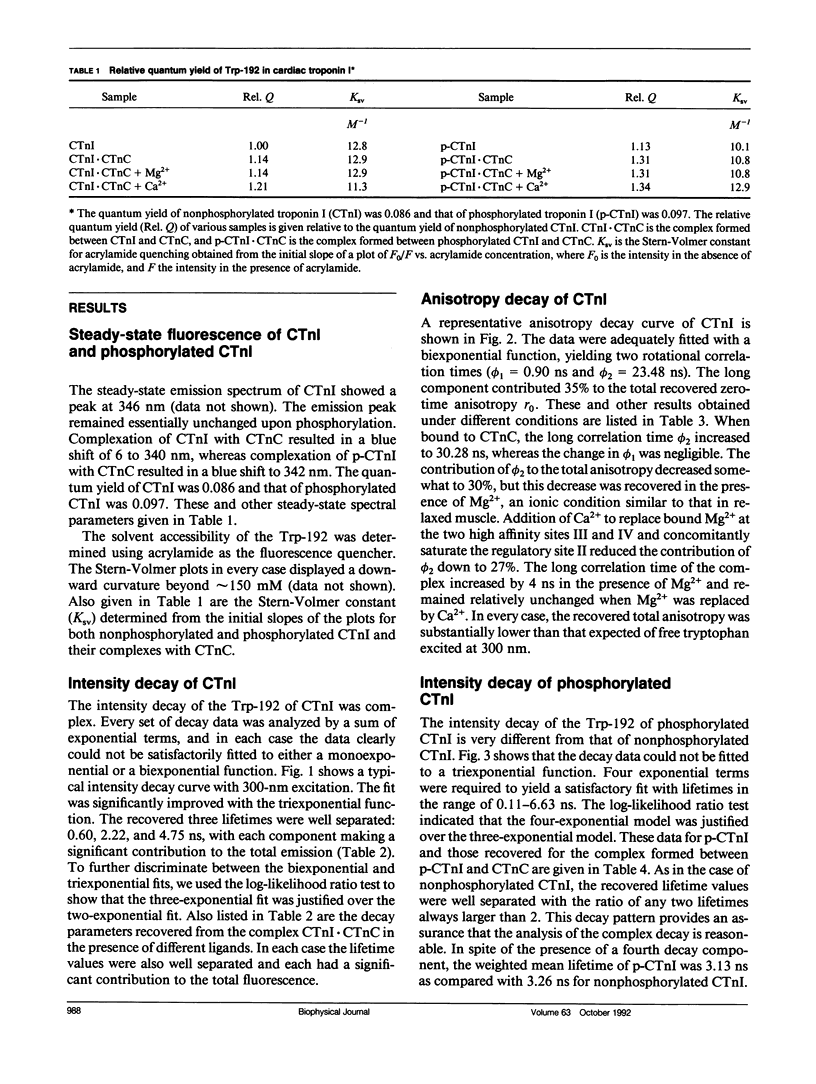
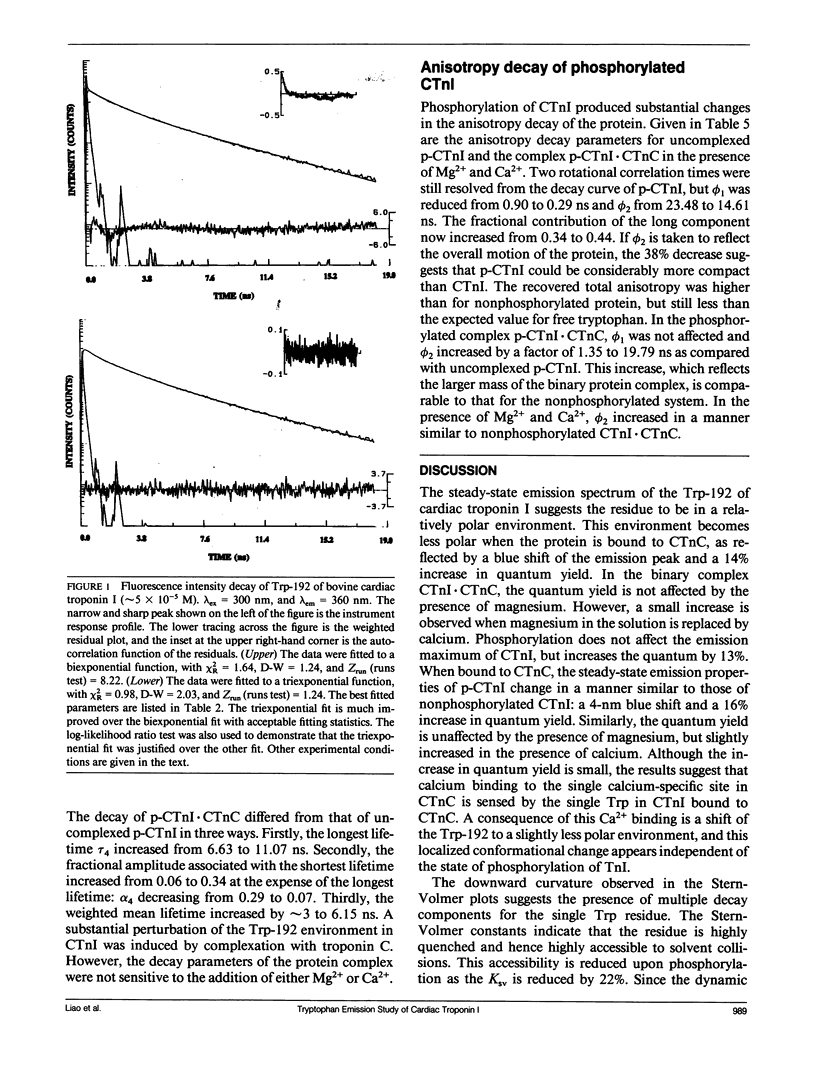
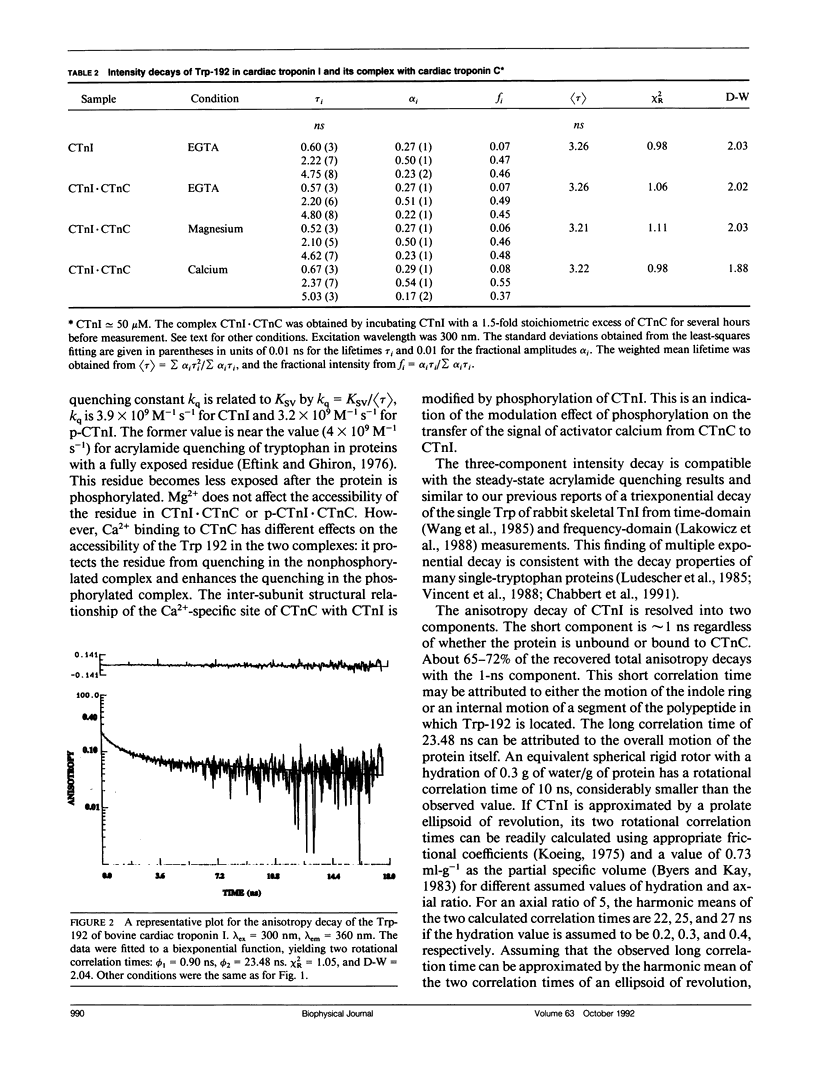
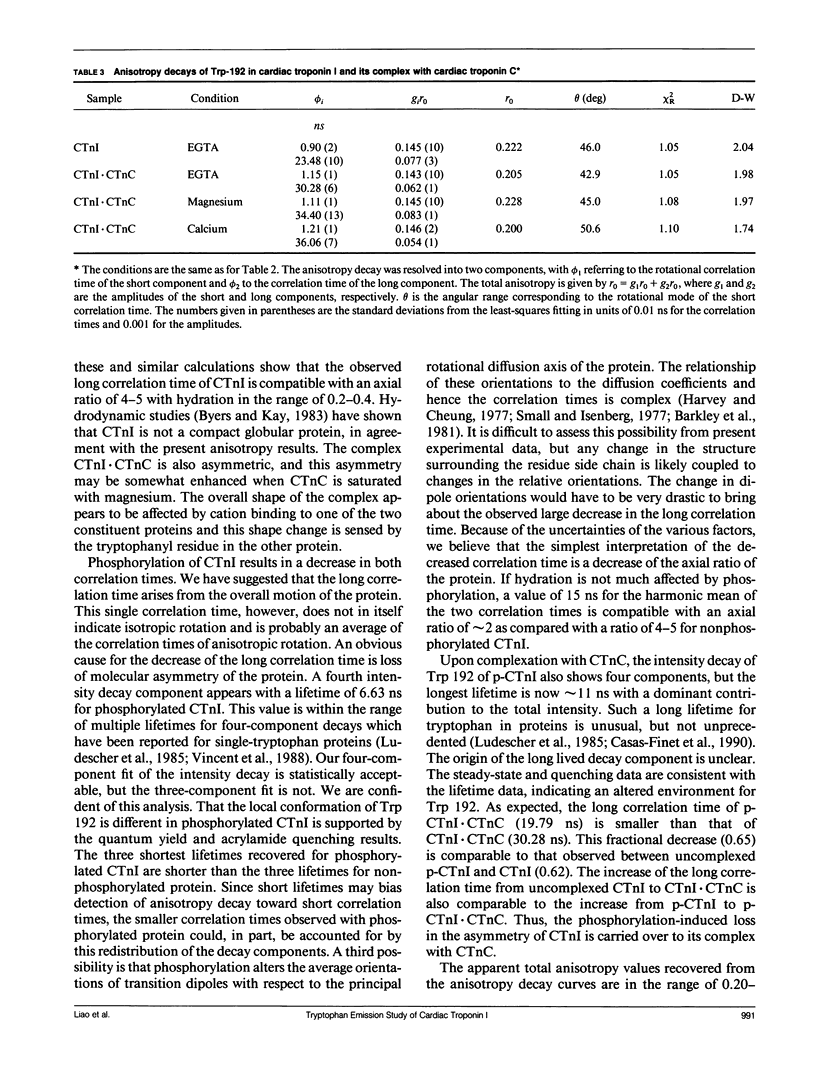
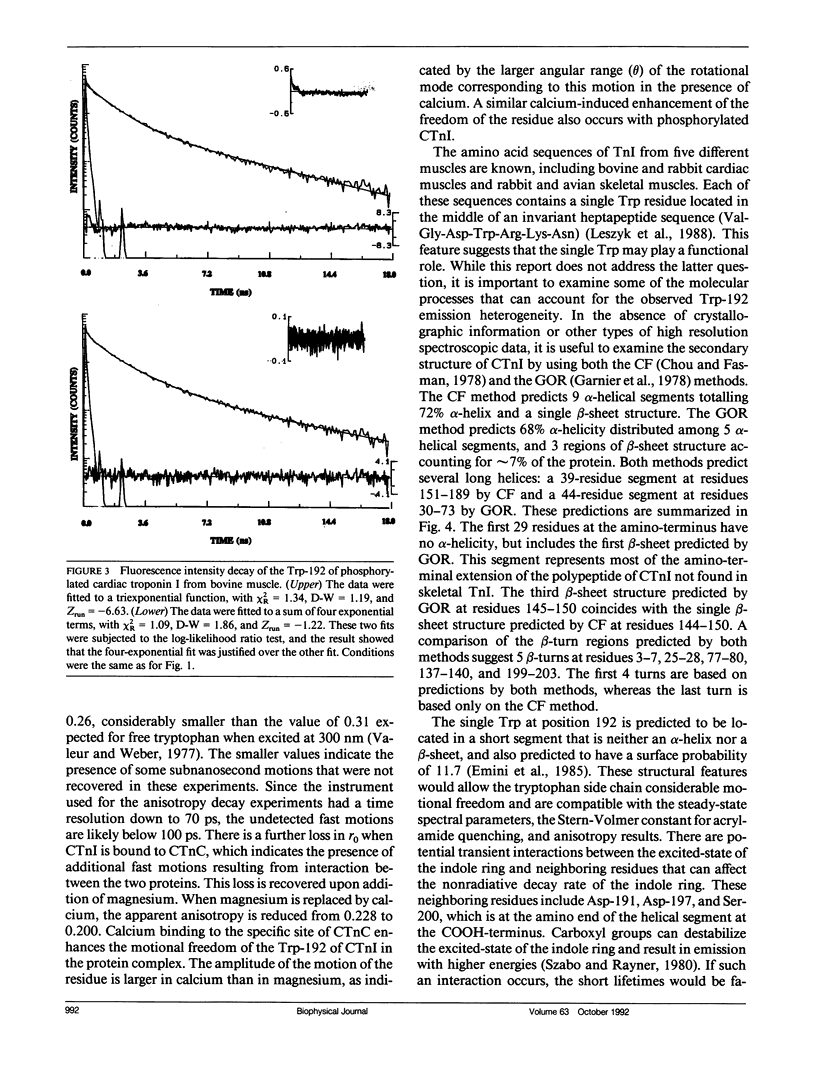
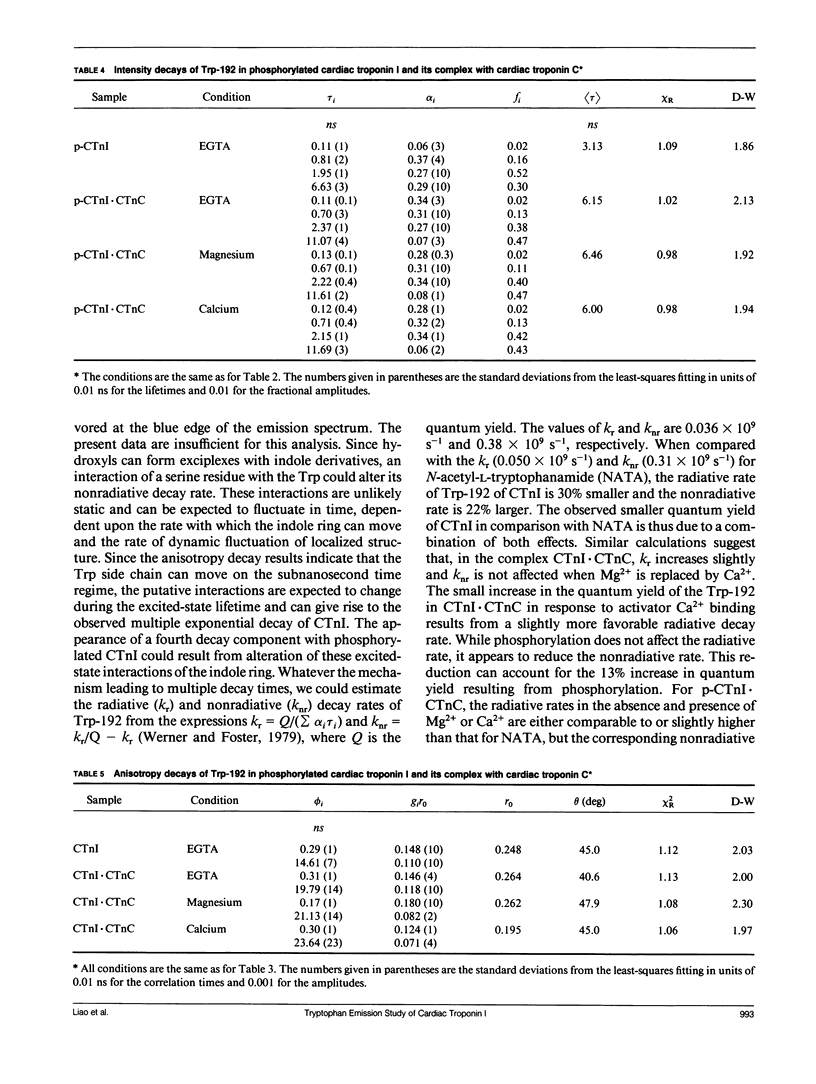
We have carried out a time-resolved fluorescence study of the single tryptophanyl residue (Trp-192) of bovine cardiac Tnl (CTnl). With excitation at 300 nm, the intensity decay was resolved into three components by a nonlinear least-squares analysis with lifetimes of 0.60, 2.22, and 4.75 ns. The corresponding fractional amplitudes were 0.27, 0.50, and 0.23, respectively. These decay parameters were not sensitive to complexation of CTnl with cardiac troponin C (CTnC), and magnesium and calcium had no significant effect on the decay parameters. After incubation with 3':5'-cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, the intensity decay of CTnl required a fourth exponential term for satisfactory fitting with lifetimes of 0.11, 0.81, 1.95, and 6.63 ns and fractional amplitudes of 0.06, 0.37, 0.27, and 0.29, respectively. When bound to CTnC, the intensity decay of phosphorylated CTnl (p-CTnl) also required four exponential terms for satisfactory fitting, but the longest lifetime increased by a factor of 1.7. The decay parameters obtained from the complex formed between p-CTnl and CTnC were not sensitive to either magnesium or calcium. The anisotropy decay was resolved into two components with rotational correlation times of 0.90 and 23.48 ns. Phosphorylation resulted in a decrease of the long correlation time to 14.61 ns. The anisotropy values recovered at zero time suggest that the side chain of the Trp-192 had considerable subnanosecond motional freedom not resolved in these experiments. Within the CTnl.CTnC complex, the unresolved fast motions appeared sensitive to calcium binding to the calcium-specific site of CTnC. The observed emission heterogeneity is discussed in terms of possible excited-state interactions in conjunction with the predicted secondary structure of CTnl. The loss of molecular asymmetry of cardiac troponin I induced by phosphorylation as demonstrated in this work may be related to the known physiological effect of beta-agonists on cardiac contractility.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers D. M., Kay C. M. Hydrodynamic properties of bovine cardiac troponin-I and troponin-T. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2951–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert M., Lukas T. J., Watterson D. M., Axelsen P. H., Prendergast F. G. Fluorescence analysis of calmodulin mutants containing tryptophan: conformational changes induced by calmodulin-binding peptides from myosin light chain kinase and protein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7615–7630. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. C., Wang C. K., Gryczynski I., Wiczk W., Laczko G., Johnson M. L., Lakowicz J. R. Distance distributions and anisotropy decays of troponin C and its complex with troponin I. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5238–5247. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. C., Wang C. K., Malik N. A. Interactions of troponin subunits: free energy of binary and ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5904–5907. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Fleming G. R. Analysis of time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy decays. Biophys J. 1984 Jul;46(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)83997-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A. Exposure of tryptophanyl residues in proteins. Quantitative determination by fluorescence quenching studies. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):672–680. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Steinberg I. Z. On the analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics by the method of least-squares. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C., Cheung H. C. Fluorescence depolarization studies on the flexibility of myosin rod. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5181–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock S. E., Huxley H. E., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Calcium sensitive binding of troponin to actin-tropomyosin: a two-site model for troponin action. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):825–836. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Collins J. H., Robertson S. P., Potter J. D. A fluorescent probe study of Ca2+ binding to the Ca2+-specific sites of cardiac troponin and troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9635–9640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Gryczynski I., Cheung H. C., Wang C. K., Johnson M. L., Joshi N. Distance distributions in proteins recovered by using frequency-domain fluorometry. Applications to troponin I and its complex with troponin C. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9149–9160. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszyk J., Dumaswala R., Potter J. D., Collins J. H. Amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin I. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2821–2827. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludescher R. D., Volwerk J. J., de Haas G. H., Hudson B. S. Complex photophysics of the single tryptophan of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2, its zymogen, and an enzyme/micelle complex. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7240–7249. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Cohen C. Letter: Troponin subunit interactions. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Perry S. V. The sites of phosphorylation of rabbit cardiac troponin I by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Effect of interaction with troponin C. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):333–343. doi: 10.1042/bj1670333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. Troponin, tropomyosin, and actin interactions in the Ca2+ regulation of muscle contraction. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2697–2703. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D. Preparation of troponin and its subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):241–263. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Holroyde M. J., Kranias E. G., Potter J. D., Solaro R. J. The effect of troponin I phosphorylation on the Ca2+-binding properties of the Ca2+-regulatory site of bovine cardiac troponin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero A., Hudson B. Critical density fluctuations in lipid bilayers detected by fluorescence lifetime heterogeneity. Biophys J. 1989 Jun;55(6):1111–1124. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82908-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small E. W., Isenberg I. Hydrodynamic properties of a rigid molecule: rotational and linear diffusion and fluorescence anisotropy. Biopolymers. 1977 Sep;16(9):1907–1928. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Moir A. J., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of troponin I and the inotropic effect of adrenaline in the perfused rabbit heart. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):615–617. doi: 10.1038/262615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Buss J. E. Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiderek K., Jaquet K., Meyer H. E., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Cardiac troponin I, isolated from bovine heart, contains two adjacent phosphoserines. A first example of phosphoserine determination by derivatization to S-ethylcysteine. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gong B. J., Leavis P. C. Calcium-induced movement of troponin-I relative to actin in skeletal muscle thin filaments. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2138356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gowell E., Strasburg G. M., Gergely J., Leavis P. C. Ca2+ dependence of the distance between Cys-98 of troponin C and Cys-133 of troponin I in the ternary troponin complex. Resonance energy transfer measurements. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5902–5908. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeur B., Weber G. Resolution of the fluorescence excitation spectrum of indole into the 1La and 1Lb excitation bands. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 May;25(5):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb09168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Brochon J. C., Merola F., Jordi W., Gallay J. Nanosecond dynamics of horse heart apocytochrome c in aqueous solution as studied by time-resolved fluorescence of the single tryptophan residue (Trp-59). Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8752–8761. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. K., Cheung H. C. Proximity relationship in the binary complex formed between troponin I and troponin C. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eerd J. P., Takahshi K. Determination of the complete amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin C. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1171–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


