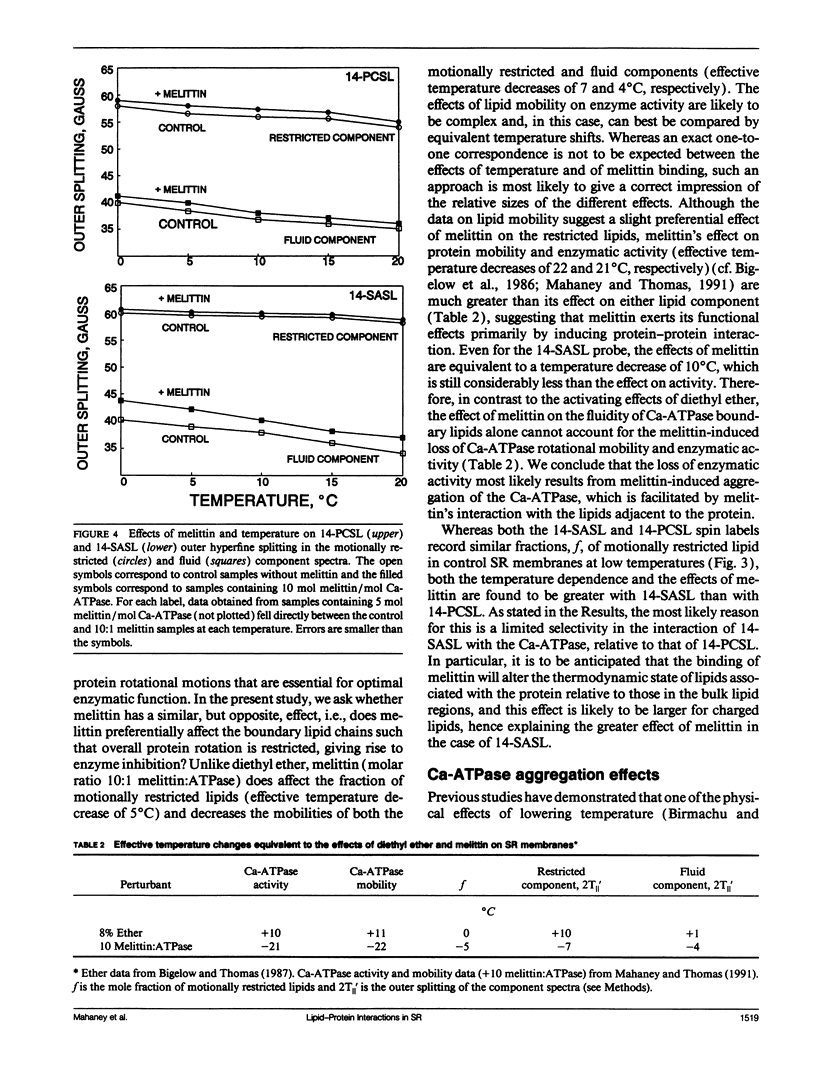
Abstract
To investigate the physical mechanism by which melittin inhibits Ca-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) membranes, we have used electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to probe the effect of melittin on lipid-protein interactions in SR. Previous studies have shown that melittin substantially restricts the rotational mobility of the Ca-ATPase but only slightly decreases the average lipid hydrocarbon chain fluidity in SR. Therefore, in the present study, we ask whether melittin has a preferential effect on Ca-ATPase boundary lipids, i.e., the annular shell of motionally restricted lipid that surrounds the protein. Paramagnetic derivatives of stearic acid and phosphatidylcholine, spin-labeled at C-14, were incorporated into SR membranes. The electronic paramagnetic resonance spectra of these probes contained two components, corresponding to motionally restricted and motionally fluid lipids, that were analyzed by spectral subtraction. The addition of increasing amounts of melittin, to the level of 10 mol melittin/mol Ca-ATPase, progressively increased the fraction of restricted lipids and increased the hyperfine splitting of both components in the composite spectra, indicating that melittin decreases the hydrocarbon chain rotational mobility for both the fluid and restricted populations of lipids. No further effects were observed above a level of 10 mol melittin/mol Ca-ATPase. In the spectra from control and melittin-containing samples, the fraction of restricted lipids decreased significantly with increasing temperature. The effect of melittin was similar to that of decreased temperature, i.e., each spectrum obtained in the presence of melittin (10:1) was nearly identical to the spectrum obtained without melittin at a temperature approximately 5 degrees C lower. The results suggest that the principal effect of melittin on SR membranes is to induce protein aggregation and this in turn, augmented by direct binding of melittin to the lipid, is responsible for the observed decreases in lipid mobility. Protein aggregation is concluded to be the main cause of inactivation of the Ca-ATPase by melittin, with possible modulation also by the decrease in mobility of the boundary layer lipids.
Full text
PDF

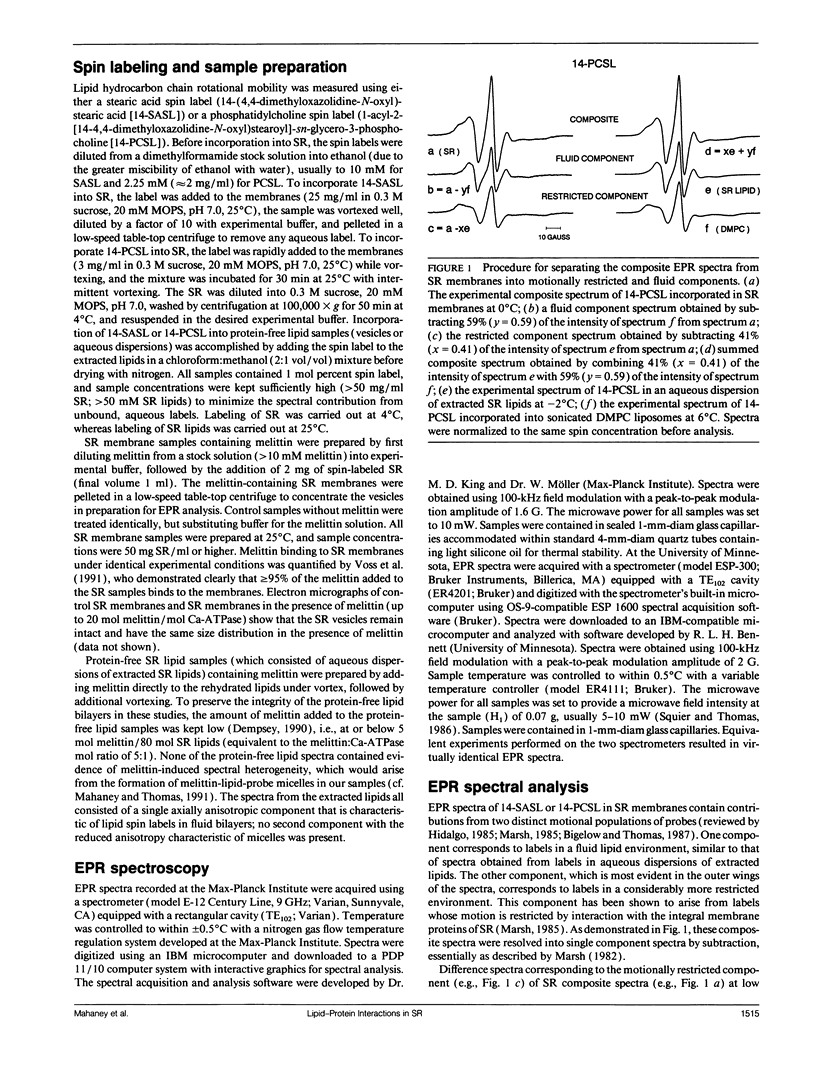
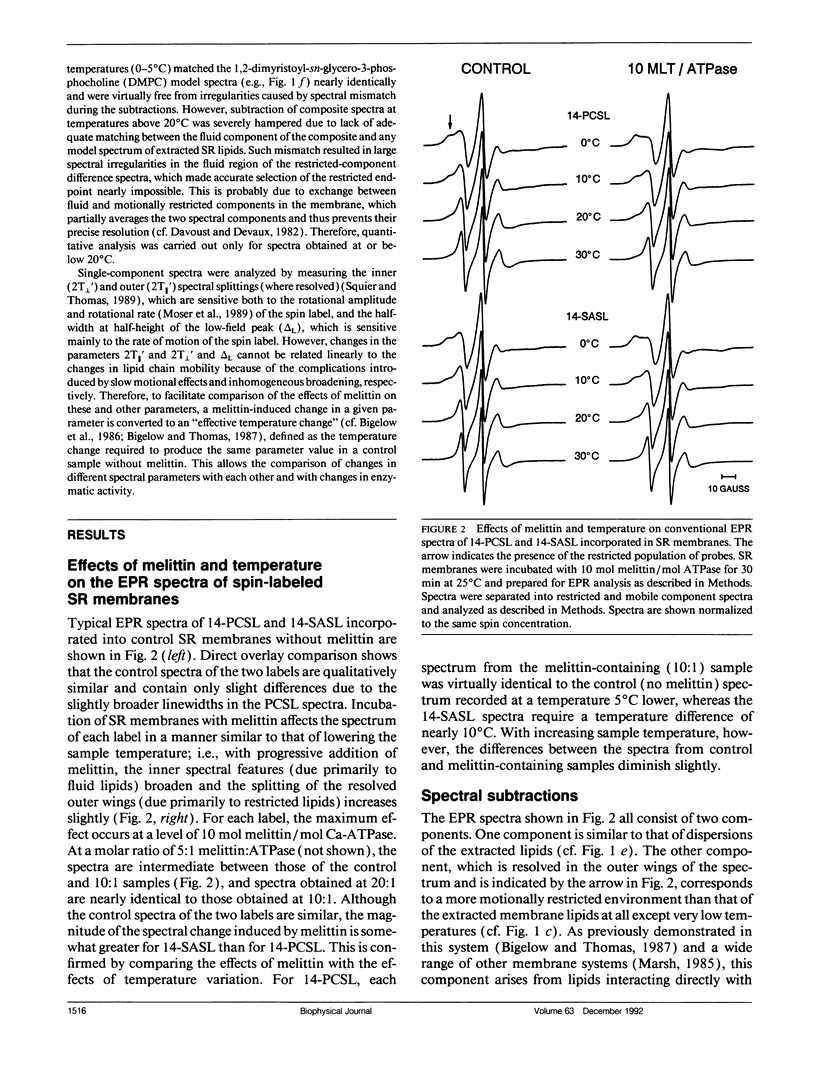
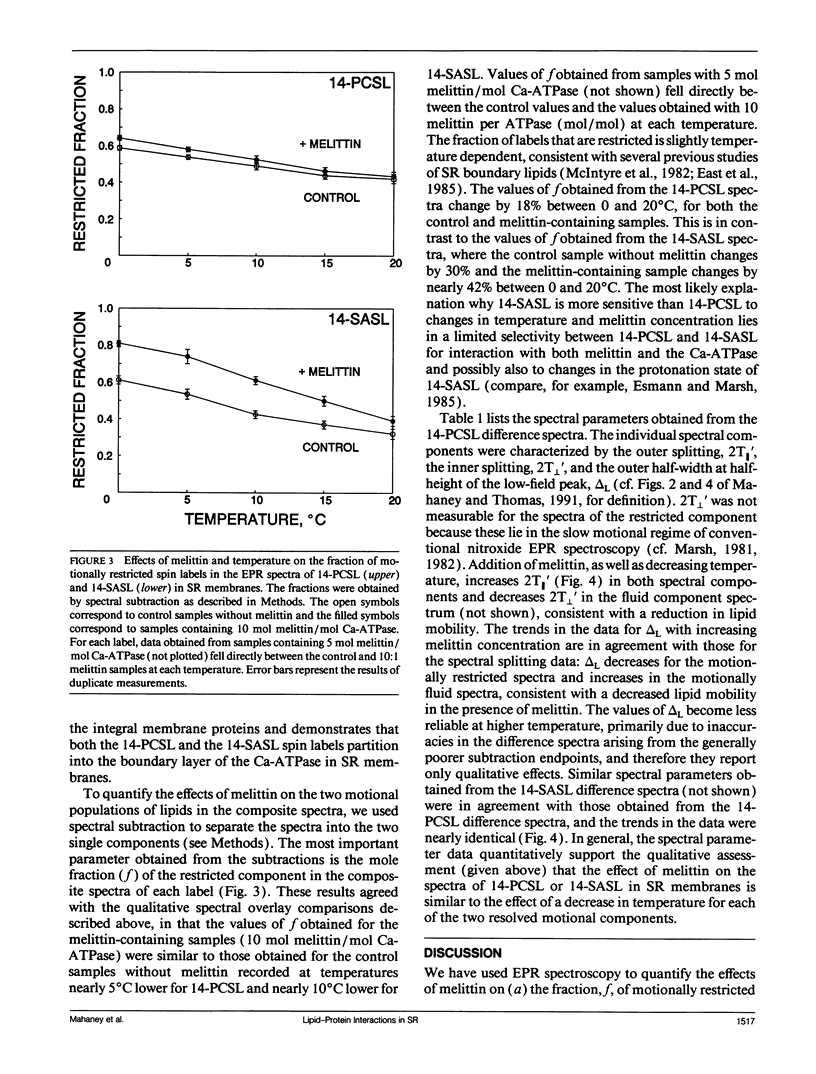
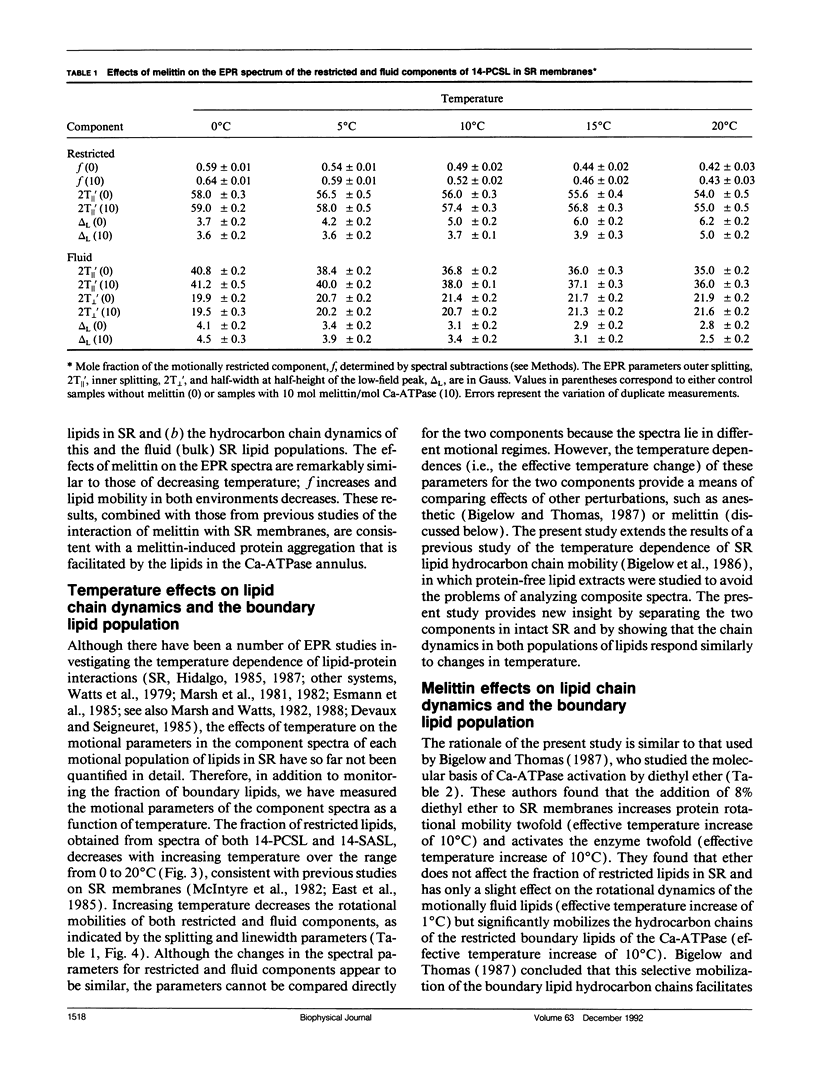



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbach C., Froncisz W., Hyde J. S., Hubbell W. L. Conformation of spin-labeled melittin at membrane surfaces investigated by pulse saturation recovery and continuous wave power saturation electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82765-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L. The aggregation state of spin-labeled melittin in solution and bound to phospholipid membranes: evidence that membrane-bound melittin is monomeric. Proteins. 1988;3(4):230–242. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., Hibbeln J. C., de Kruijff B. Lipid specific penetration of melittin into phospholipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 18;903(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Temperature dependence of rotational dynamics of protein and lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):194–202. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of lipid and the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum. The molecular basis of activation by diethyl ether. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13449–13456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmachu W., Nisswandt F. L., Thomas D. D. Conformational transitions in the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase studied by time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3940–3947. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmachu W., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum studied by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3904–3914. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Pascolini D., Asturias F., Herbette L. G., Pierce D., Scarpa A. Large-scale structural changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase appear essential for calcium transport. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):687–693. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82411-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Cherry R. J. A comparative study of band 3 aggregation in erythrocyte membranes by melittin and other cationic agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 27;980(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Cherry R. J. Comparison of p25 presequence peptide and melittin. Red blood cell haemolysis and band 3 aggregation. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):791–794. doi: 10.1042/bj2520791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppoletti J., Abbott A. J. Interaction of melittin with the (Na+ + K+)ATPase: evidence for a melittin-induced conformational change. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Dec;283(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppoletti J., Blumenthal K. M., Malinowska D. H. Melittin inhibition of the gastric (H+ + K+) ATPase and photoaffinity labeling with [125I]azidosalicylyl melittin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 15;275(1):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppoletti J. [125I]azidosalicylyl melittin binding domains: evidence for a polypeptide receptor on the gastric (H+ + K+)ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 1;278(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E. The actions of melittin on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F., Seigneuret M. Specificity of lipid-protein interactions as determined by spectroscopic techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):63–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Cherry R. J., Coleman J. W., Stanworth D. R. The capacity of basic peptides to trigger exocytosis from mast cells correlates with their capacity to immobilize band 3 proteins in erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):67–71. doi: 10.1042/bj2230067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Hider R. C., Cherry R. J. The influence of melittin on the rotation of band 3 protein in the human erythrocyte membrane. Eur Biophys J. 1984;11(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00253854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J. M., Melville D., Lee A. G. Exchange rates and numbers of annular lipids for the calcium and magnesium ion dependent adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2615–2623. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Marsh D. Spin-label studies on the origin of the specificity of lipid-protein interactions in Na+,K+-ATPase membranes from Squalus acanthias. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3572–3578. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of lipid-protein interactions in (Na+,K+)-ATPase membranes from rectal glands of Squalus acanthias. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1386–1393. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. L., Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C. Highly purified sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles are devoid of Ca2+-independent ('basal') ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):552–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N., Gergely J. Role of phospholipids in the calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Enzymatic and ESR studies with phospholipid-replaced membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4224–4232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C. Lipid-protein interactions and the function of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;21(4):319–347. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. S., Dufton M. J., Morrison I. E., Cherry R. J. Protein rotational diffusion measurements on the interaction of bee venom melittin with bacteriorhodopsin in lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 27;816(2):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90503-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart C. M., Cherry R. J. Electron microscopic observation of the aggregation of membrane proteins in human erythrocyte by melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 30;1023(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka M., Head J. F., Seaton B. A., Engelman D. M. Melittin binding causes a large calcium-dependent conformational change in calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaney J. E., Thomas D. D. Effects of melittin on molecular dynamics and Ca-ATPase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes: electron paramagnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7171–7180. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R. Association of melittin with the isolated myosin light chains. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1941–1949. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R. Effects of calmodulin and related proteins on the hemolytic activity of melittin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 16;130(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90376-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Electron spin resonance: spin labels. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1981;31:51–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81537-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Barrantes F. J. Phospholipid chain immobilization and steroid rotational immobilization in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Pates R. D., Uhl R., Knowles P. F., Esmann M. ESR spin-label studies of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84675-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer T., Lücke C., Rüterjans H. Investigation of the membrane-active peptides melittin and glucagon by photochemically induced dynamic-nuclear-polarization (photo-CIDNP) NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):135–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Samson P., Brenner S. C., Dalton L., Dalton L., Fleischer S. EPR Studies of the Motional Characteristics of the Phospholipid in Functional Reconstituted Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Vesicles. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84595-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser M., Marsh D., Meier P., Wassmer K. H., Kothe G. Chain configuration and flexibility gradient in phospholipid membranes. Comparison between spin-label electron spin resonance and deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance, and identification of new conformations. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82784-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Ward N. E. ATP-sensitive binding of melittin to the catalytic domain of protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynor R. L., Zheng B., Kuo J. F. Membrane interactions of amphiphilic polypeptides mastoparan, melittin, polymyxin B, and cardiotoxin. Differential inhibition of protein kinase C, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and synaptosomal membrane Na,K-ATPase, and Na+ pump and differentiation of HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2753–2758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Thomas D. D. Lipid fluidity directly modulates the overall protein rotational mobility of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9178–9186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Hughes S. E., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics and protein-protein interactions in the Ca-ATPase mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9162–9170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Relationship between protein rotational dynamics and phosphoenzyme decomposition in the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9171–9177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Selective detection of the rotational dynamics of the protein-associated lipid hydrocarbon chains in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):735–748. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82721-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Three-dimensional crystals of CaATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Symmetry and molecular packing. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82501-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Hidalgo C. Rotational dynamics of protein and boundary lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84671-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J., Birmachu W., Hussey D. M., Thomas D. D. Effects of melittin on molecular dynamics and Ca-ATPase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes: time-resolved optical anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7498–7506. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Volotovski I. D., Marsh D. Rhodopsin-lipid associations in bovine rod outer segment membranes. Identification of immobilized lipid by spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille B. A preparation of melittin depleted of phospholipase A2 by ion exchange chromatography in denaturing solvents. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):118–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


