Abstract
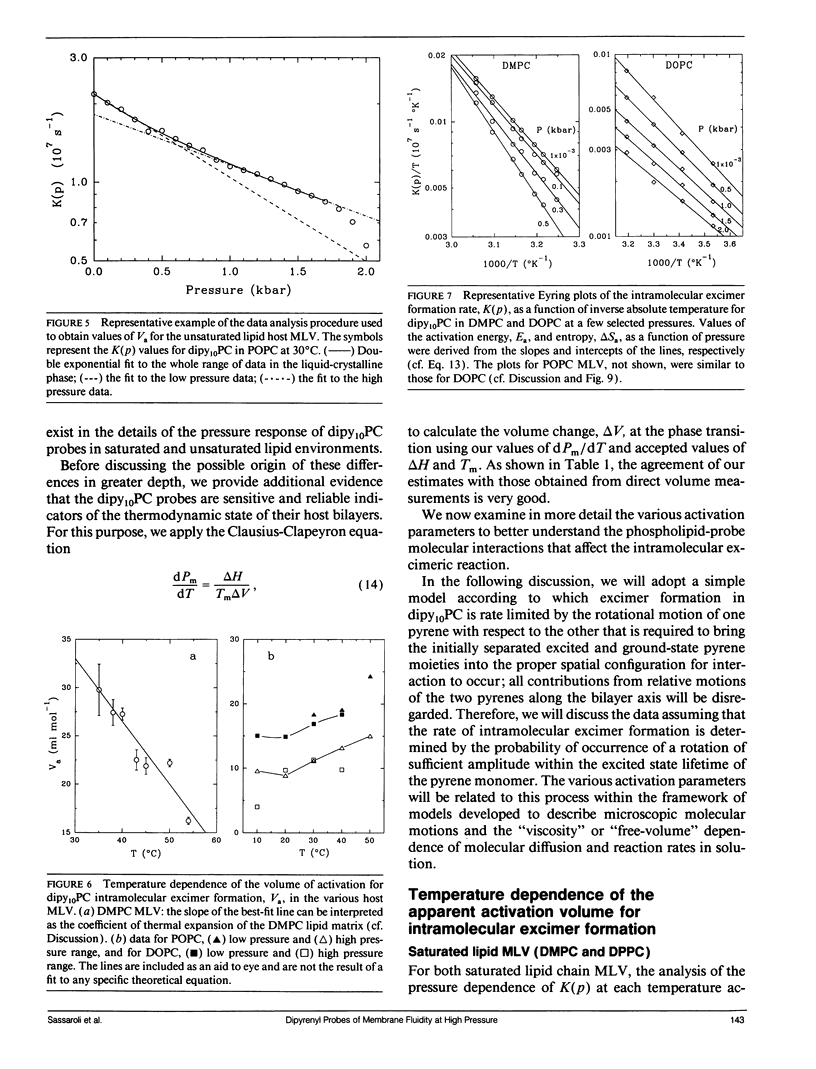
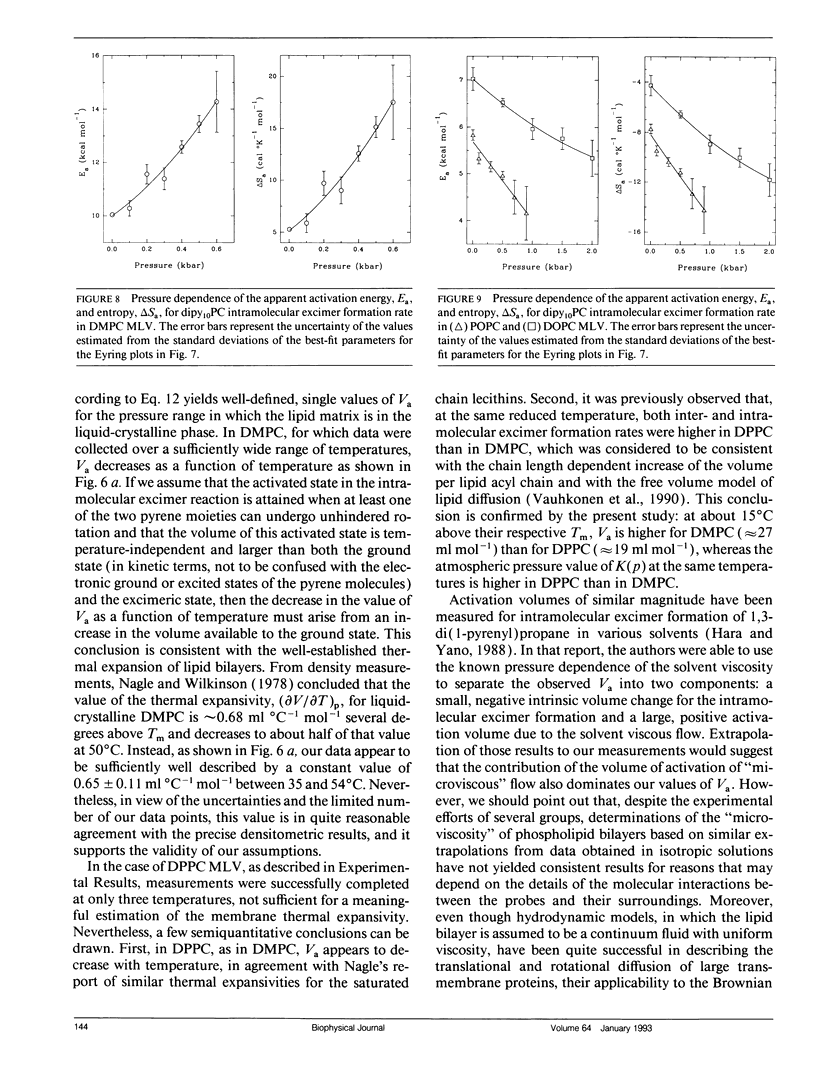
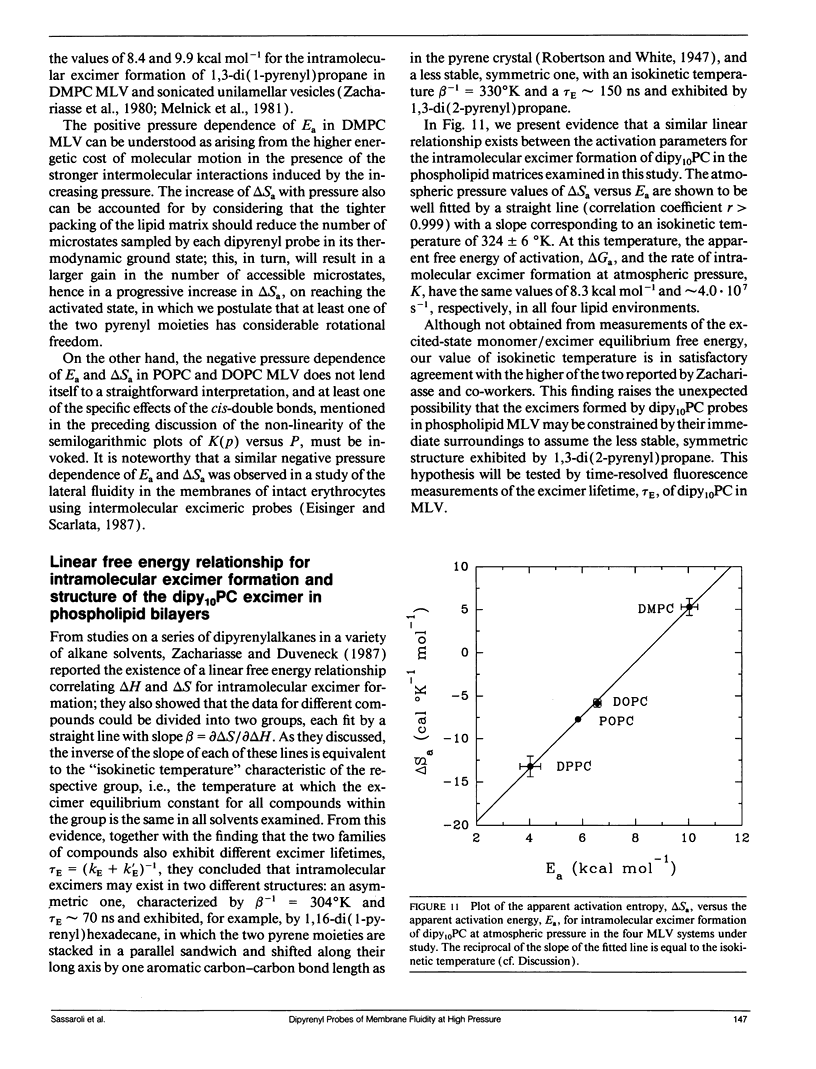
We have measured the pressure dependence of the intramolecular excimer formation rate, K(p), for di-(1'-pyrenedecanoyl)-phosphatidylcholine (dipy10PC) probes in single-component lipid multilamellar vesicles (MLV) as a function of temperature. Apparent volumes of activation (V(a)) for intramolecular excimer formation are obtained from the slopes of plots of log K(p) versus P. For liquid-crystalline saturated lipid MLV (DMPC and DPPC), these plots are linear and yield a unique V(a) at each temperature, whereas for unsaturated lipids (POPC and DOPC) they are curvilinear and V(a) appears to decrease with pressure. The isothermal pressure induced phase transition is marked by an abrupt drop in the values of K(p). The pressure to temperature equivalence values, dPm/dT, estimated from the midpoint of the transitions, are 47.0, 43.5, and 52.5 bar degree C-1 for DMPC, DPPC, and POPC, respectively. In liquid-crystalline DMPC, V(a) decreases linearly as a function of temperature, with a coefficient -dVa/dT = 0.65 +/- 0.11 ml degree C-1 mol-1. Using a modified free volume model of diffusion, we show that this value corresponds to the thermal expansivity of DMPC. Both the apparent energy and entropy of activation, Ea and delta Sa, increase with pressure in DMPC, whereas both decrease in POPC and DOPC. This difference is attributed to the sensitivity of the dynamics and/or packing of the dipy10PC probes to the location of the cis-double bonds in the chains of the unsaturated host phospholipids. Finally, the atmospheric pressure values of Ea and delta Sa for the four host MLV examined are shown to be linearly related. The relevance of this finding with respect to the structure of the excimers formed by the dipy10PC probes is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrich M. P., Vanderkooi J. M. Temperature dependence of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene fluorescence in phophoslipid artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. E., Chen L. A., Brand L. Rotational relaxation of the "microviscosity" probe diphenylhexatriene in paraffin oil and egg lecithin vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7500–7510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport L., Knutson J. R., Brand L. Fluorescence studies of membrane dynamics and heterogeneity. Subcell Biochem. 1989;14:145–188. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9362-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Flores J., Petersen W. P. A milling crowd model for local and long-range obstructed lateral diffusion. Mobility of excimeric probes in the membrane of intact erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):987–1001. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83727-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Scarlata S. F. The lateral fluidity of erythrocyte membranes. Temperature and pressure dependence. Biophys Chem. 1987 Dec;28(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischkoff S., Vanderkooi J. M. Oxygen diffusion in biological and artificial membranes determined by the fluorochrome pyrene. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):663–676. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Hartmann W., Theilen U., Sackmann E. On two-dimensional passive random walk in lipid bilayers and fluid pathways in biomembranes. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jul 31;48(3):215–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01872892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes: use of pyrene excimers as optical probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hresko R. C., Sugár I. P., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Lateral distribution of a pyrene-labeled phosphatidylcholine in phosphatidylcholine bilayers: fluorescence phase and modulation study. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3813–3823. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. D., Marsh D. Free volume model for lipid lateral diffusion coefficients. Assessment of the temperature dependence in phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 6;862(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N. I., Kay R. L. Redetermination of the pressure dependence of the lipid bilayer phase transition. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3484–3486. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick R. L., Haspel H. C., Goldenberg M., Greenbaum L. M., Weinstein S. Use of fluorescent probes that form intramolecular excimers to monitor structural changes in model and biological membranes. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):499–515. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84864-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. J., Galla H. J. Pressure variation of the lateral diffusion in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. M., Morrisett J. D., Sparrow J. T. A convenient synthesis of phosphatidylcholines: acylation of sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine with fatty acid anhydride and 4-pyrrolidinopyridine. J Lipid Res. 1979 Jul;20(5):674–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Cherry R. J. Lateral and rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid bilayers: experimental test of the Saffman-Delbrück equations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassaroli M., Vauhkonen M., Perry D., Eisinger J. Lateral diffusivity of lipid analogue excimeric probes in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82530-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlata S. F. Compression of lipid membranes as observed at varying membrane positions. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):334–340. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82058-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauhkonen M., Sassaroli M., Somerharju P., Eisinger J. Dipyrenylphosphatidylcholines as membrane fluidity probes. Relationship between intramolecular and intermolecular excimer formation rates. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82531-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Clegg R. M., Hallmann D. Translational diffusion of lipids in liquid crystalline phase phosphatidylcholine multibilayers. A comparison of experiment with theory. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):781–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruyff B., Demel R. A., Slotboom A. J., van Deenen L. L., Rosenthal A. F. The effect of the polar headgroup on the lipid-cholesterol interaction: a monolayer and differential scanning calorimetry study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 25;307(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


