Abstract
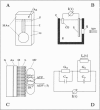
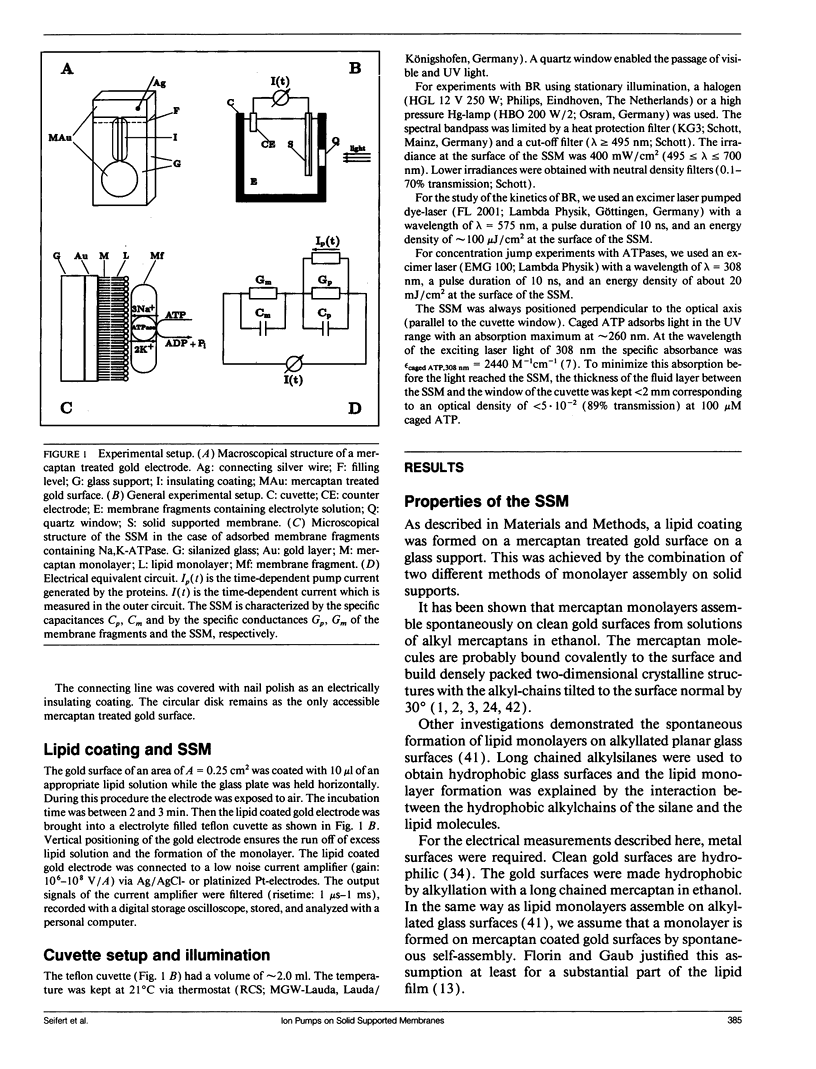
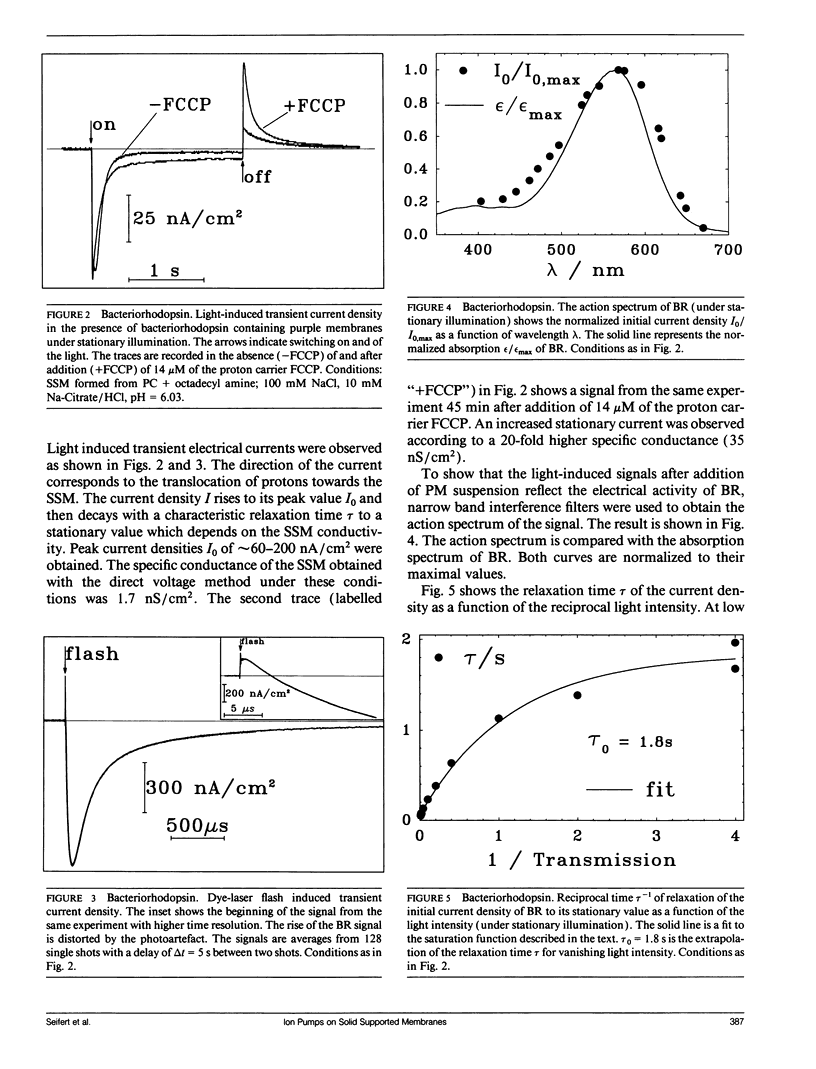
A new method for the investigation of ion translocating membrane proteins is presented. Protein containing membrane fragments or vesicles are adsorbed to a solid supported membrane. The solid supported membrane consists of a lipid monolayer on a gold evaporated or gold sputtered glass substrate which is coated with a long chained mercaptan (CH3(CH2)mSH, m = 15, 17). Specific conductance and specific capacitance of the solid supported membrane are comparable to those of a black lipid membrane. However, the solid supported membrane has the advantage of a much higher mechanical stability. The electrical activity of bacteriorhodopsin, Na,K-ATPase, H,K-ATPase, and Ca-ATPase on the solid supported membrane is measured and compared to signals obtained on a conventionally prepared black lipid membrane. It is shown that both methods yield similar results. The solid supported membrane therefore represents an alternative method for the investigation of electrical properties of ion translocating transmembrane proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain C. D., Whitesides G. M. Molecular-Level Control over Surface Order in Self-Assembled Monolayer Films of Thiols on Gold. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):62–63. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4848.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borlinghaus R., Apell H. J., Läuger P. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: I. Current and voltage transients after photochemical release of ATP. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):161–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01869220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Bamberg E., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D. Aspartic acids 96 and 85 play a central role in the function of bacteriorhodopsin as a proton pump. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1657–1663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancsházy Z., Karvaly B. Incorporation of bacteriorhodopsin into a bilayer lipid membrane; a photoelectric-spectroscopic study. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):136–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80829-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Bamberg E. Kinetics of pump currents generated by the Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80427-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Haubs M., Bamberg E. Pump currents generated by the purified Na+K+-ATPase from kidney on black lipid membranes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin E. L., Gaub H. E. Painted supported lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):375–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81378-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W., MAKINOSE M. UBER DEN MECHANISMUS DES CALCIUMTRANSPORTES DURCH DIE MEMBRANEN DES SARKOPLASMATISCHEN RETICULUMS. Biochem Z. 1963 Oct 14;339:94–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung K., Grell E., Hasselbach W., Bamberg E. Electrical pump currents generated by the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles adsorbed on black lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 30;900(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W. The reversibility of the sarcoplasmic calcium pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 10;515(1):23–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. The purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:87–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T. R., Rayfield G. W. The electrical response to light of bacteriorhodopsin in planar membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):111–125. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85512-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. IV. Estimation of the purity and of the molecular weight and polypeptide content per enzyme unit in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laibinis P. E., Hickman J. J., Wrighton M. S., Whitesides G. M. Orthogonal self-assembled monolayers: alkanethiols on gold and alkane carboxylic acids on alumina. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):845–847. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4920.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungström M., Norberg L., Olaisson H., Wernstedt C., Vega F. V., Arvidson G., Mårdh S. Characterization of proton-transporting membranes from resting pig gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 11;769(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P., Benz R., Stark G., Bamberg E., Jordan P. C., Fahr A., Brock W. Relaxation studies of ion transport systems in lipid bilayer membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Nov;14(4):513–598. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000247x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray J. A., Herbette L., Kihara T., Trentham D. R. A new approach to time-resolved studies of ATP-requiring biological systems; laser flash photolysis of caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel G., Fendler K., Grell E., Bamberg E. Na+ currents generated by the purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase on planar lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 23;901(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe U., Aurich H. Lipid-coated particles--a new approach to fix membrane-bound enzymes onto carrier surfaces. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1989 Feb;11(1):18–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-8744.1989.tb00048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccomani G., Stewart H. B., Shaw D., Lewin M., Sachs G. Characterization of gastric mucosal membranes. IX. Fractionation and purification of K+-ATPase-containing vesicles by zonal centrifugation and free-flow electrophoresis technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):311–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales D., Giuseppeinesi Assembly of ATPase protein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):735–751. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85725-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm L. K. Lateral diffusion and fluorescence microscope studies on a monoclonal antibody specifically bound to supported phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1450–1457. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Brian A. A., McConnell H. M. Covalent linkage of a synthetic peptide to a fluorescent phospholipid and its incorporation into supported phospholipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 25;772(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90512-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toeckenius W., Kunau W. H. Further characterization of particulate fractions from lysed cell envelopes of Halobacterium halobium and isolation of gas vacuole membranes. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):337–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W. Photoelectric measurements of purple membranes. Photochem Photobiol. 1990 Jun;51(6):793–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hijden H. T., Grell E., de Pont J. J., Bamberg E. Demonstration of the electrogenicity of proton translocation during the phosphorylation step in gastric H+K(+)-ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1990 Apr;114(3):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01869218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., McConnell H. M. Physical properties of lipid monolayers on alkylated planar glass surfaces. Biophys J. 1981 Nov;36(2):421–427. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84741-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]