Abstract
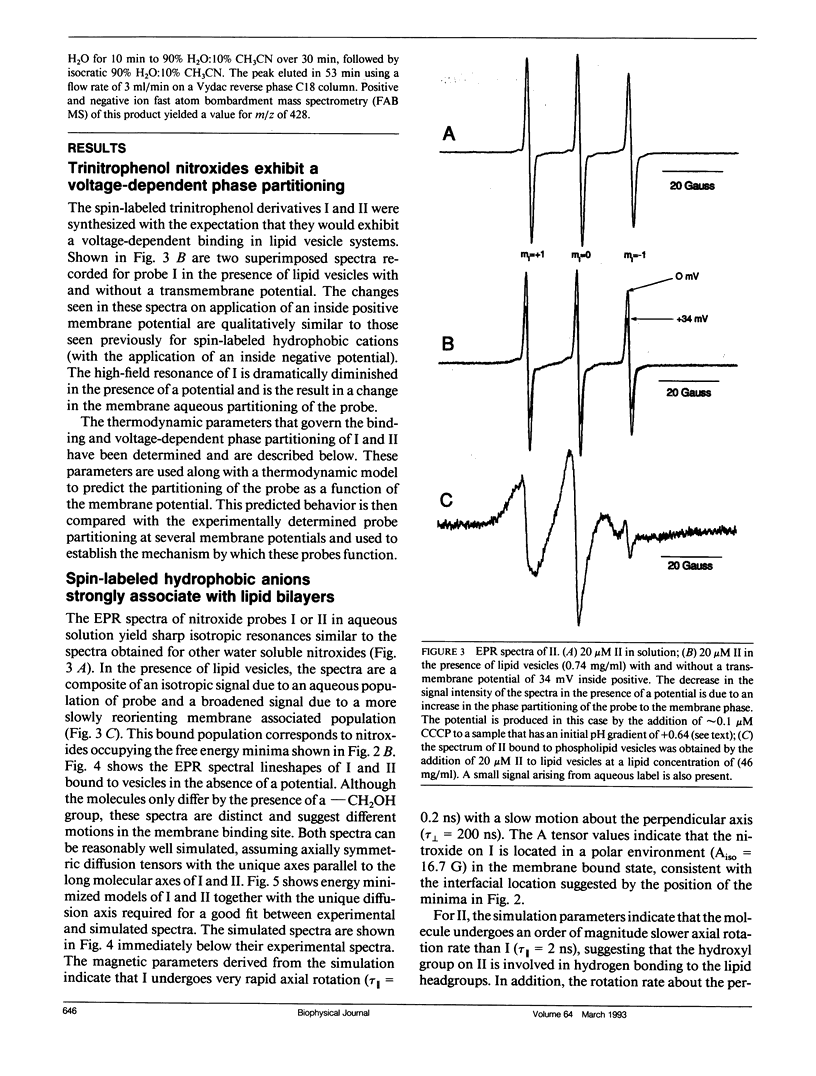
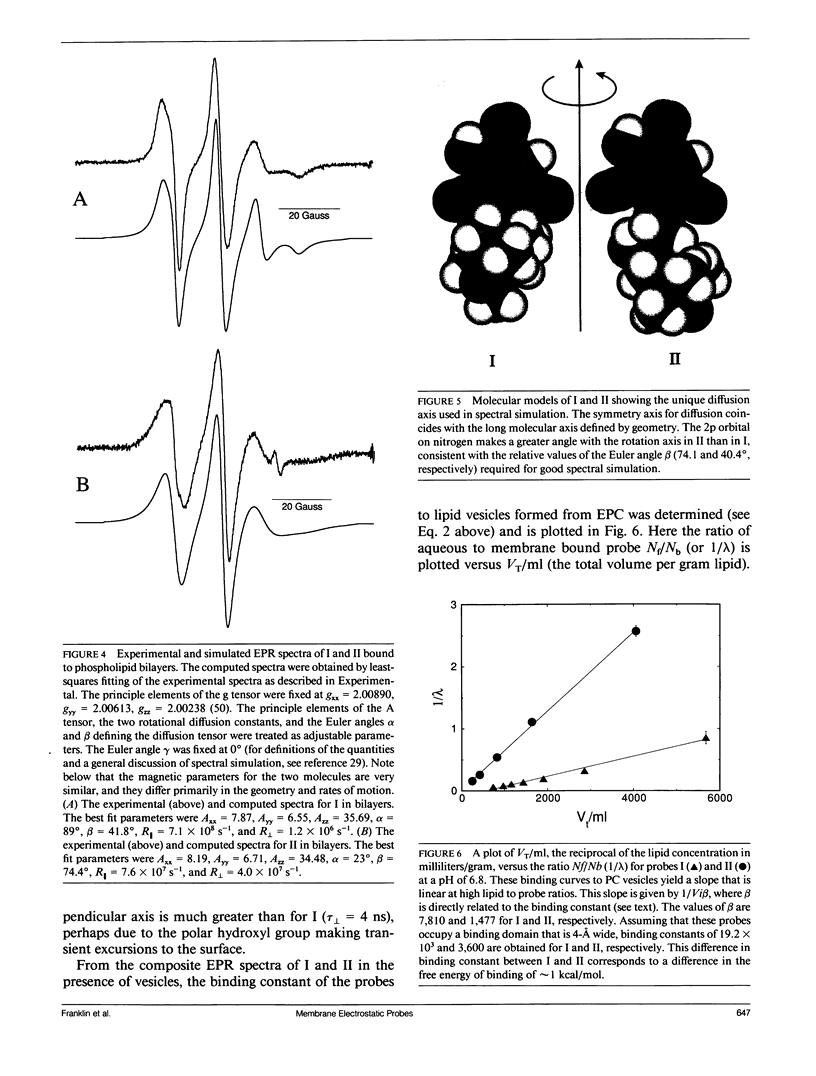
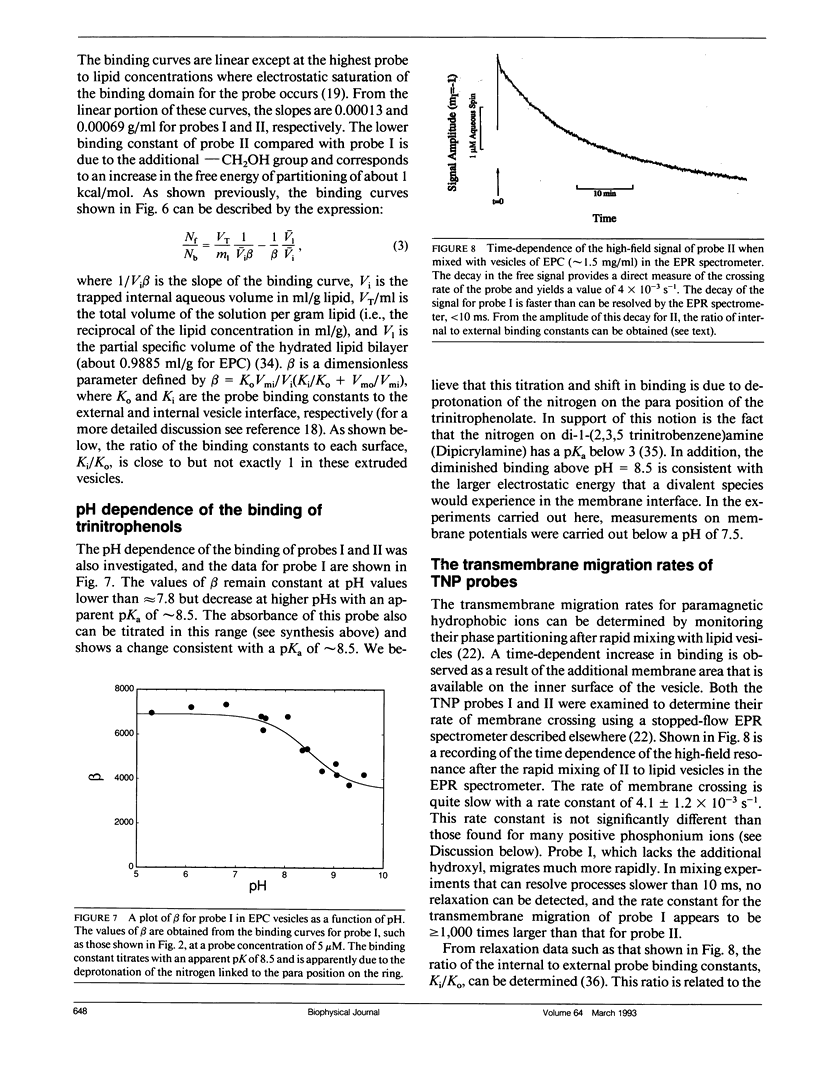
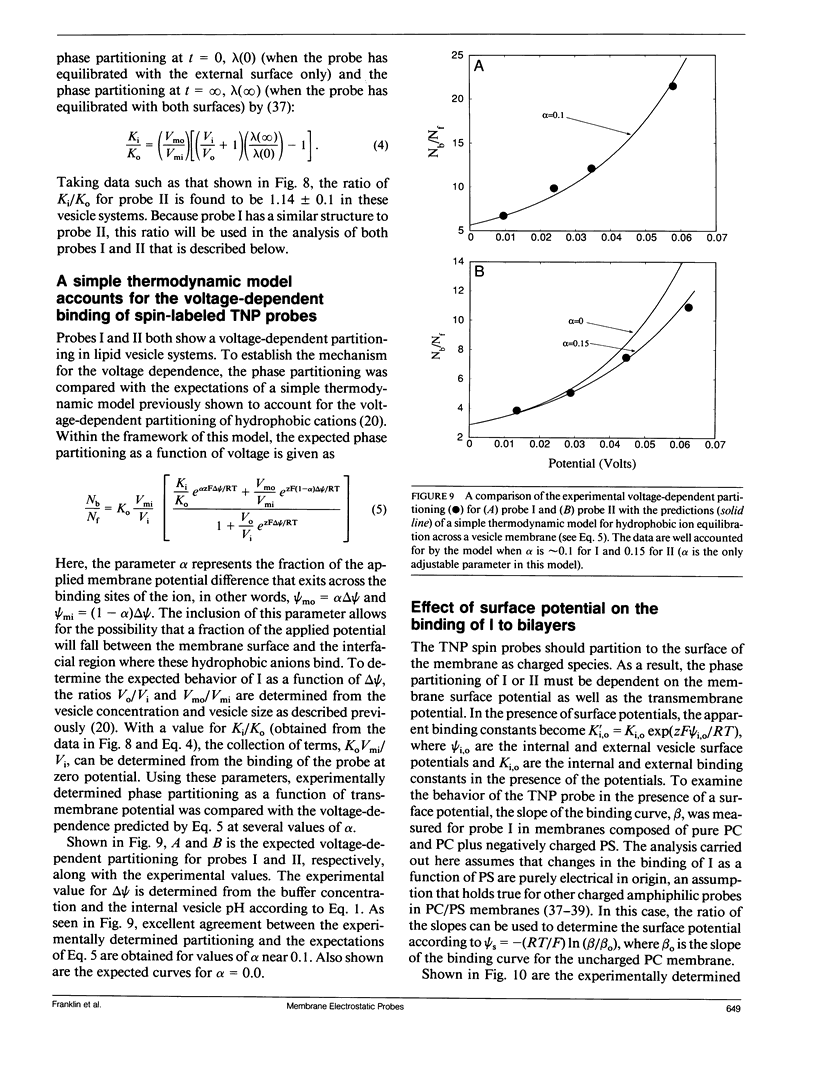
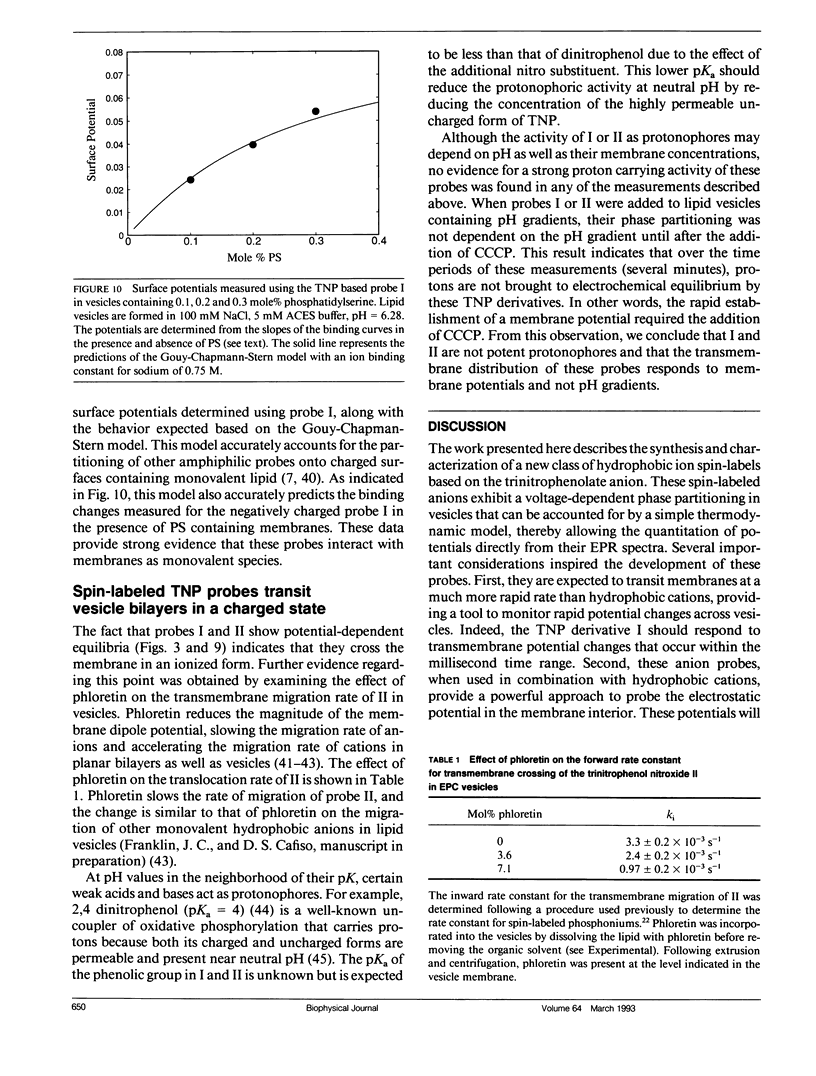
Two spin-labeled derivatives of the hydrophobic anion trinitrophenol have been synthesized and characterized in lipid vesicles. In the presence of lipid vesicles, the electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of these probes are a composite of both membrane-bound and aqueous populations; as a result, the membrane-aqueous partitioning can be determined from their electron paramagnetic resonance spectra. The effect of transmembrane potentials on the membrane-aqueous partitioning of these spin-labeled hydrophobic ions was examined in phosphatidylcholine vesicles formed by extrusion. Inside positive membrane potentials promote an increase in the binding of these probes that is quantitatively accounted for by a simple thermodynamic model used previously to describe the partitioning of paramagnetic phosphonium ions. The transmembrane migration rates of these ions are dependent on the dipole potential, indicating that these ions transit the membrane in a charged form. The partitioning of the probe is also sensitive to the membrane surface potential, and this dependence is accurately accounted for using the Gouy-Chapman Stern formalism. As a result of the membrane dipole potential, these probes exhibit a stronger binding and a more rapid transmembrane migration rate compared with positive hydrophobic ion spin labels and provide a new set of negatively charged hydrophobic ion probes to investigate membrane electrostatics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Feldberg S., Nakadomari H., Levy S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):35–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Finkelstein A., Katz I., Cass A. Effect of phloretin on the permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):749–771. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Fuchs M. Potential energy barriers to ion transport within lipid bilayers. Studies with tetraphenylborate. Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):795–830. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85856-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson H., Bakker E., von Heijne G. Different positively charged amino acids have similar effects on the topology of a polytopic transmembrane protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1491–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer S. J., Cafiso D. S. Voltage-dependent conductance for alamethicin in phospholipid vesicles. A test for the mechanism of gating. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82063-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Gisin B. F. Influence of membrane structure on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jun 9;40(4):293–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01874161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. EPR determination of membrane potentials. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:217–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Estimation of transmembrane potentials from phase equilibria of hydrophobic paramagnetic ions. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):187–195. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Light-induced interfacial potentials in photoreceptor membranes. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):243–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85092-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Transmembrane electrical currents of spin-labeled hydrophobic ions. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84516-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D., McLaughlin A., McLaughlin S., Winiski A. Measuring electrostatic potentials adjacent to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;171:342–364. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)71019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. L., Hsia J. C. Studies on motional characteristics and distribution of protonated and anionic forms of spin-labeled 2,4-dinitrophenol in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4948–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E. Positively charged residues are important determinants of membrane protein topology. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90047-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., Dominey R. N., Archer S. J., Xu Z. C., Cafiso D. S. Localization of hydrophobic ions in phospholipid bilayers using 1H nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4584–4592. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. Hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Thermodynamic analysis of tetraphenylphosphonium binding to vesicles. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83663-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. The membrane dipole potential in a total membrane potential model. Applications to hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83664-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T. The analysis of physiological activity of substituted phenols with substituent constants. J Med Chem. 1966 Nov;9(6):797–803. doi: 10.1021/jm00324a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Ruston D., Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Fuller N. Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1213–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81931-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A., Lodish H. F. Predicting the orientation of eukaryotic membrane-spanning proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartsel S. C., Cafiso D. S. A test of discreteness-of-charge effects in phospholipid vesicles: measurements using paramagnetic amphiphiles. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8214–8219. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B. H., Hubbell W. L., Flewelling R. F. Electrostatic interactions in membranes and proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:163–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Mason J. T. Geometric packing constraints in egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):308–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mosior M., Chung L. A., Wu H., McLaughlin S. Binding of peptides with basic residues to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82037-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner M., Cafiso D., Marcelja S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatics of phosphoinositide bilayer membranes. Theoretical and experimental results. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):335–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82535-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Topaly V. P. Selective transport of ions through bimolecular phospholipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P., Benz R., Stark G., Bamberg E., Jordan P. C., Fahr A., Brock W. Relaxation studies of ion transport systems in lipid bilayer membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Nov;14(4):513–598. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000247x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Dilger J. P. Transport of protons across membranes by weak acids. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):825–863. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnik E., Latorre R., Hall J. E., Tosteson D. C. Phloretin-induced changes in ion transport across lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):243–257. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines D. E., Cafiso D. S. Potential-dependent phase partitioning of fluorescent hydrophobic ions in phospholipid vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01871633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Fink C. A., Kenworthy A. K., McIntosh T. J. The hydration pressure between lipid bilayers. Comparison of measurements using x-ray diffraction and calorimetry. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):538–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82270-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Hubbell W. L. Investigation of surface potential asymmetry in phospholipid vesicles by a spin label relaxation method. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83665-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiski A. P., McLaughlin A. C., McDaniel R. V., Eisenberg M., McLaughlin S. An experimental test of the discreteness-of-charge effect in positive and negative lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8206–8214. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]