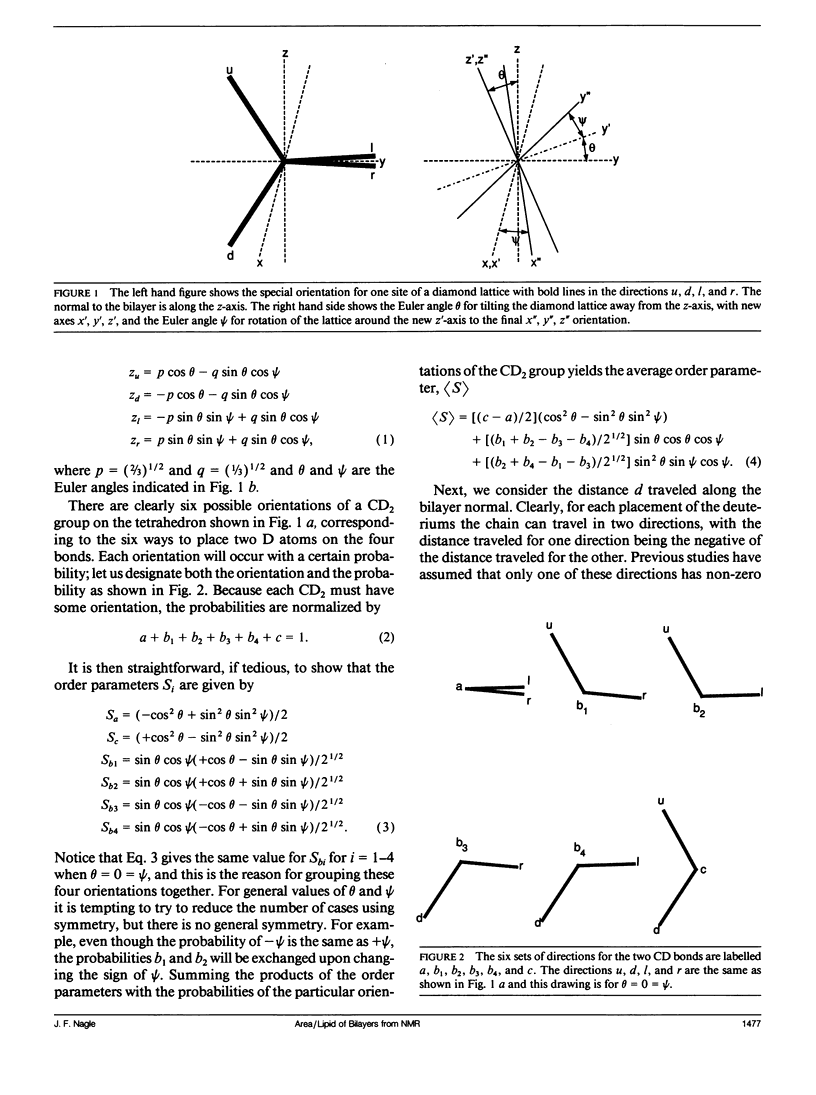
Abstract
Values of area per lipid A ranging from 56 to 72 A 2 have been reported from essentially the same SCD data from DPPC in the L alpha phase. The differences are due primarily to three separate binary choices in interpretation. It is argued that one particular combination is best; this yields A = 62 +/- 2 A 2 for DPPC at 50 degrees C. Each preceding interpretation agrees with at least one of the three present choices and disagrees with at least one.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boden N., Jones S. A., Sixl F. On the use of deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance as a probe of chain packing in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2146–2155. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young L. R., Dill K. A. Solute partitioning into lipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5281–5289. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M. R., Whitehead J. P., Lu D. Chain-length dependence of lipid bilayer properties near the liquid crystal to gel phase transition. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Structure of fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Seelig J. Deuterium order parameters in relation to thermodynamic properties of a phospholiped bilayer. A statistical mechanical interpretation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2283–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L. Monte Carlo calculations of order parameter profiles in models of lipid-protein interactions in bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6122–6126. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond R. L., Dodd S. W., Brown M. F. Molecular areas of phospholipids as determined by 2H NMR spectroscopy. Comparison of phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82203-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristram-Nagle S., Zhang R., Suter R. M., Worthington C. R., Sun W. J., Nagle J. F. Measurement of chain tilt angle in fully hydrated bilayers of gel phase lecithins. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1097–1109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81475-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Suter R. M., Nagle J. F. Structure of the fully hydrated gel phase of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82807-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Tristram-Nagle S., Wilkinson D. A., Campbell L. E., Nagle J. F. Specific volumes of lipids in fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 18;938(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. C., Cafiso D. S. Phospholipid packing and conformation in small vesicles revealed by two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance cross-relaxation spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):779–783. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83705-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


