Abstract
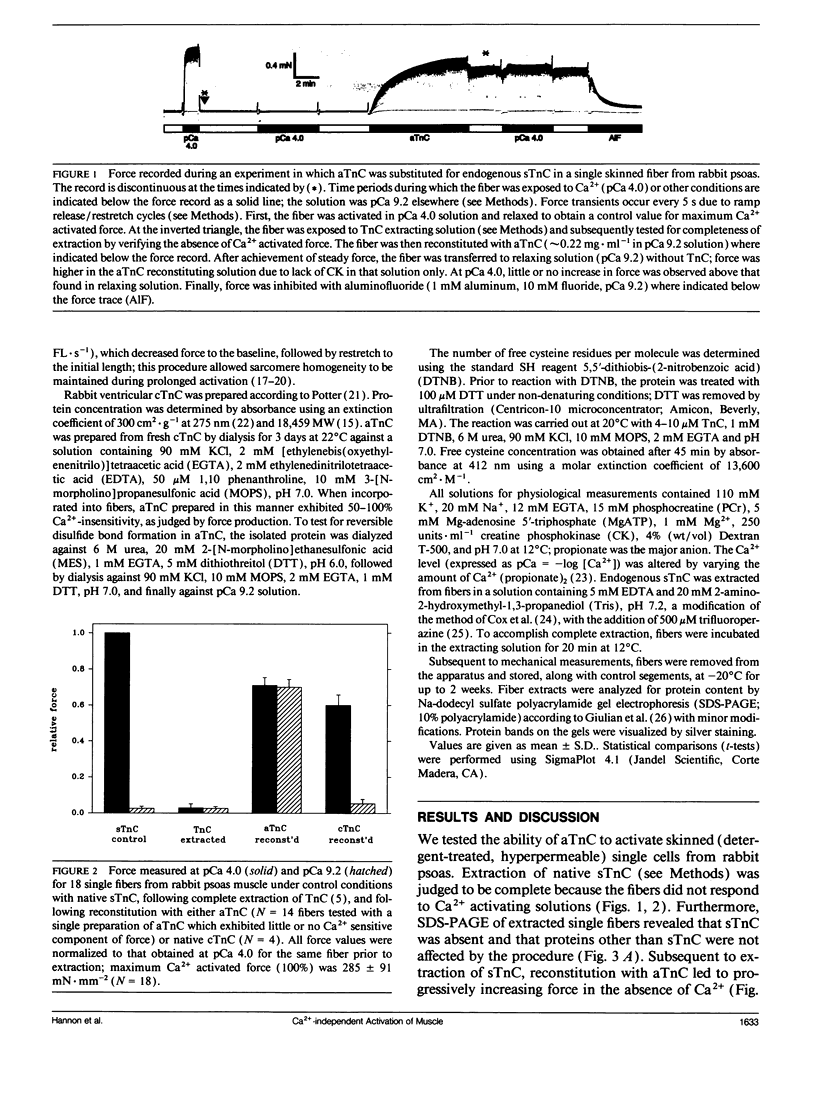
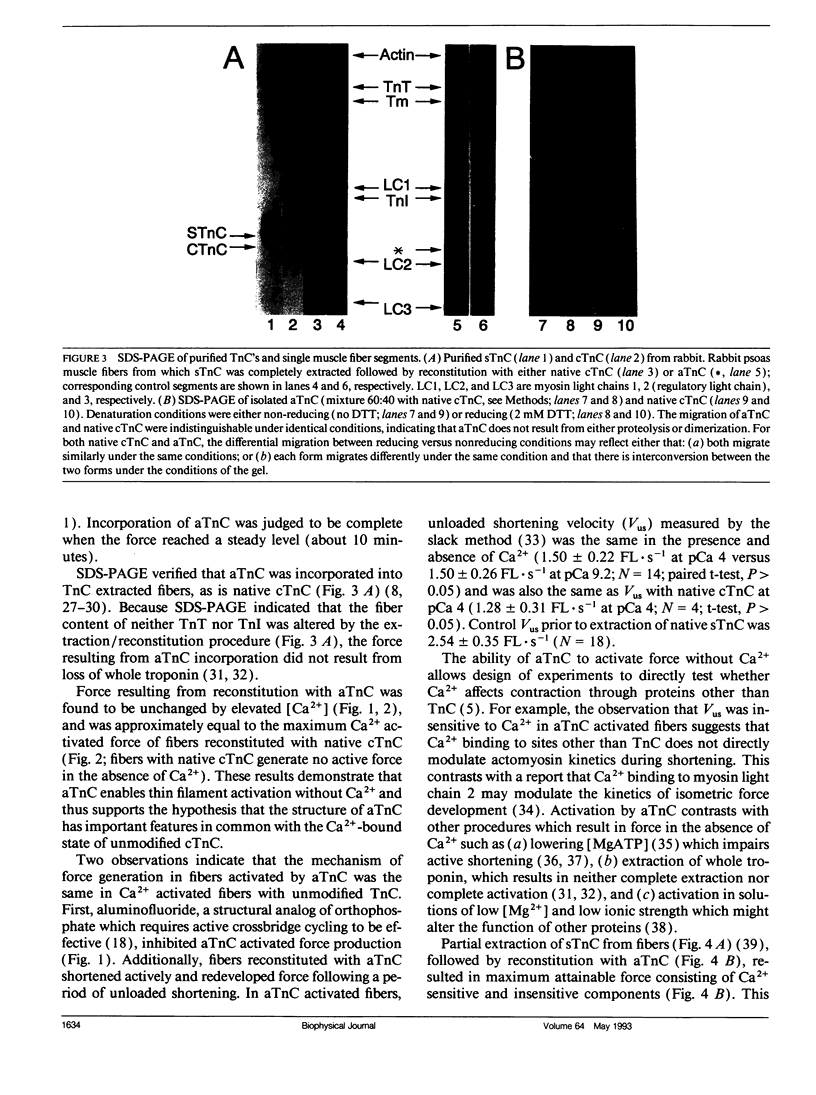
A conformational change accompanying Ca2+ binding to troponin C (TnC) constitutes the initial event in contractile regulation of vertebrate striated muscle. We replaced endogenous TnC in single skinned fibers from rabbit psoas muscle with a modified form of cardiac TnC (cTnC) which, unlike native cTnC, probably contains an intramolecular disulfide bond. We found that such activating TnC (aTnC) enables force generation and shortening in the absence of calcium. With aTnC, both force and shortening velocity were the same at pCa 9.2 and pCa 4.0. aTnc could not be extracted under conditions which resulted in extraction of endogenous TnC. Thus, aTnC provides a stable model for structural studies of a calcium binding protein in the active conformation as well as a useful tool for physiological studies on the primary and secondary effects of Ca2+ on the molecular kinetics of muscle contraction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. D., Moss R. L. Factors influencing the ascending limb of the sarcomere length-tension relationship in rabbit skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:119–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jan;41(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of action of troponin . tropomyosin. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity without inhibition of myosin binding to actin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):575–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Kushmerick M. J. Effects of pH on contraction of rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83174-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Effects of inorganic phosphate analogues on stiffness and unloaded shortening of skinned muscle fibres from rabbit. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:231–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Bialek W. Contraction of glycerinated muscle fibers as a function of the ATP concentration. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85174-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Comte M., Stein E. A. Calmodulin-free skeletal-muscle troponin C prepared in the absence of urea. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):205–211. doi: 10.1042/bj1950205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A. The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:143–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F., Liou Y. M., Grabarek Z. The reactivity of sulfhydryl groups of bovine cardiac troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20344–20349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori K., Sorenson M., Herzberg O., Moult J., Reinach F. C. Probing the calcium-induced conformational transition of troponin C with site-directed mutants. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):182–184. doi: 10.1038/345182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian G. G., Moss R. L., Greaser M. Improved methodology for analysis and quantitation of proteins on one-dimensional silver-stained slab gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Godt R. E., Donaldson S. K., Harris C. E. Tension in skinned frog muscle fibers in solutions of varying ionic strength and neutral salt composition. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Nov;62(5):550–574. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.5.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Tan R. Y., Wang J., Tao T., Gergely J. Inhibition of mutant troponin C activity by an intra-domain disulphide bond. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):132–135. doi: 10.1038/345132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Tao T., Gergely J. Molecular mechanism of troponin-C function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Aug;13(4):383–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01738034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati J., Sonnenblick E., Babu A. The role of troponin C in the length dependence of Ca(2+)-sensitive force of mammalian skeletal and cardiac muscles. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:305–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Refined crystal structure of troponin C from turkey skeletal muscle at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):761–779. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavis P. C., Gergely J. Thin filament proteins and thin filament-linked regulation of vertebrate muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(3):235–305. doi: 10.3109/10409238409108717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M. Length and myofilament spacing-dependent changes in calcium sensitivity of skeletal fibres: effects of pH and ionic strength. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Oct;9(5):428–445. doi: 10.1007/BF01774069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Variations in cross-bridge attachment rate and tension with phosphorylation of myosin in mammalian skinned skeletal muscle fibers. Implications for twitch potentiation in intact muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):855–883. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Myosin light chain 2 modulates calcium-sensitive cross-bridge transitions in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):460–468. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81614-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Allen J. D., Greaser M. L. Effects of partial extraction of troponin complex upon the tension-pCa relation in rabbit skeletal muscle. Further evidence that tension development involves cooperative effects within the thin filament. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):761–774. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L. Ca2+ regulation of mechanical properties of striated muscle. Mechanistic studies using extraction and replacement of regulatory proteins. Circ Res. 1992 May;70(5):865–884. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.5.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. The effects of partial extraction of TnC upon the tension-pCa relationship in rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Oct;86(4):585–600. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Haworth R. A. Contraction of rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibers at low levels of magnesium adenosine triphosphate. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84216-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Nwoye L. O., Greaser M. L. Substitution of cardiac troponin C into rabbit muscle does not alter the length dependence of Ca2+ sensitivity of tension. J Physiol. 1991;440:273–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negele J. C., Dotson D. G., Liu W., Sweeney H. L., Putkey J. A. Mutation of the high affinity calcium binding sites in cardiac troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):825–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4628–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D. Preparation of troponin and its subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):241–263. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Sweeney H. L., Campbell S. T. Site-directed mutation of the trigger calcium-binding sites in cardiac troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12370–12378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyshur K. A., Rao S. T., Pyzalska D., Drendel W., Greaser M., Sundaralingam M. Refined structure of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C in the two-calcium state at 2-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1628–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Brito R. M., Rosevear P. R., Putkey J. A. The low-affinity Ca2(+)-binding sites in cardiac/slow skeletal muscle troponin C perform distinct functions: site I alone cannot trigger contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9538–9542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Corteselli S. A., Kushmerick M. J. Measurements on permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers during continuous activation. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C575–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva A. C., Reinach F. C. Calcium binding induces conformational changes in muscle regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90024-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Saleh S. C., Warber K. D., Potter J. D. The role of tropomyosin-troponin in the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Oct;7(5):387–404. doi: 10.1007/BF01753582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eerd J. P., Takahshi K. Determination of the complete amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin C. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1171–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]