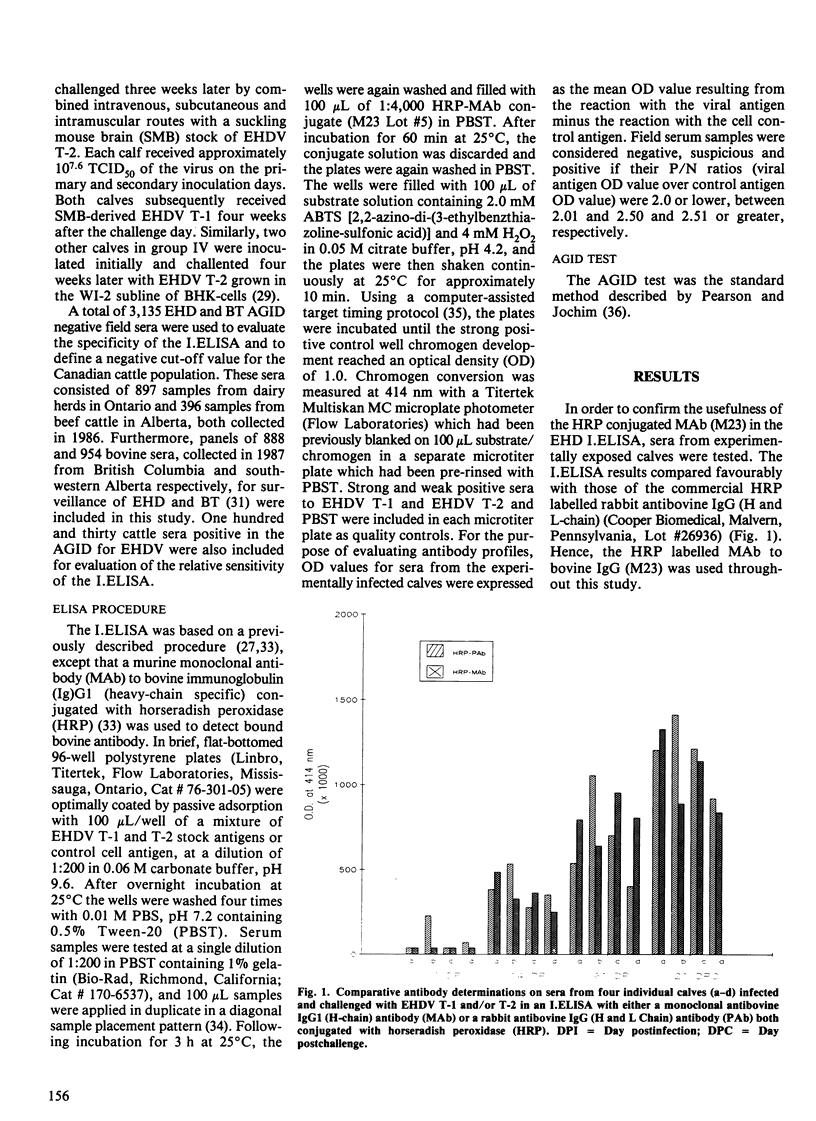
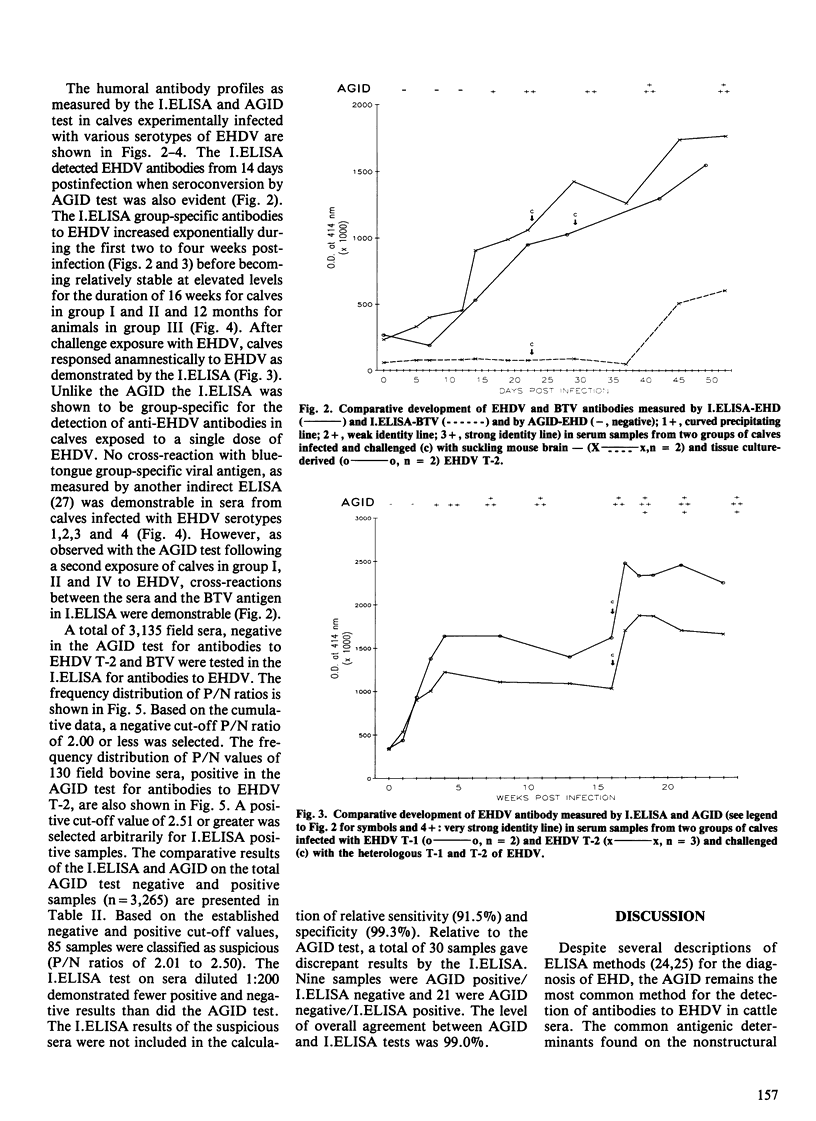
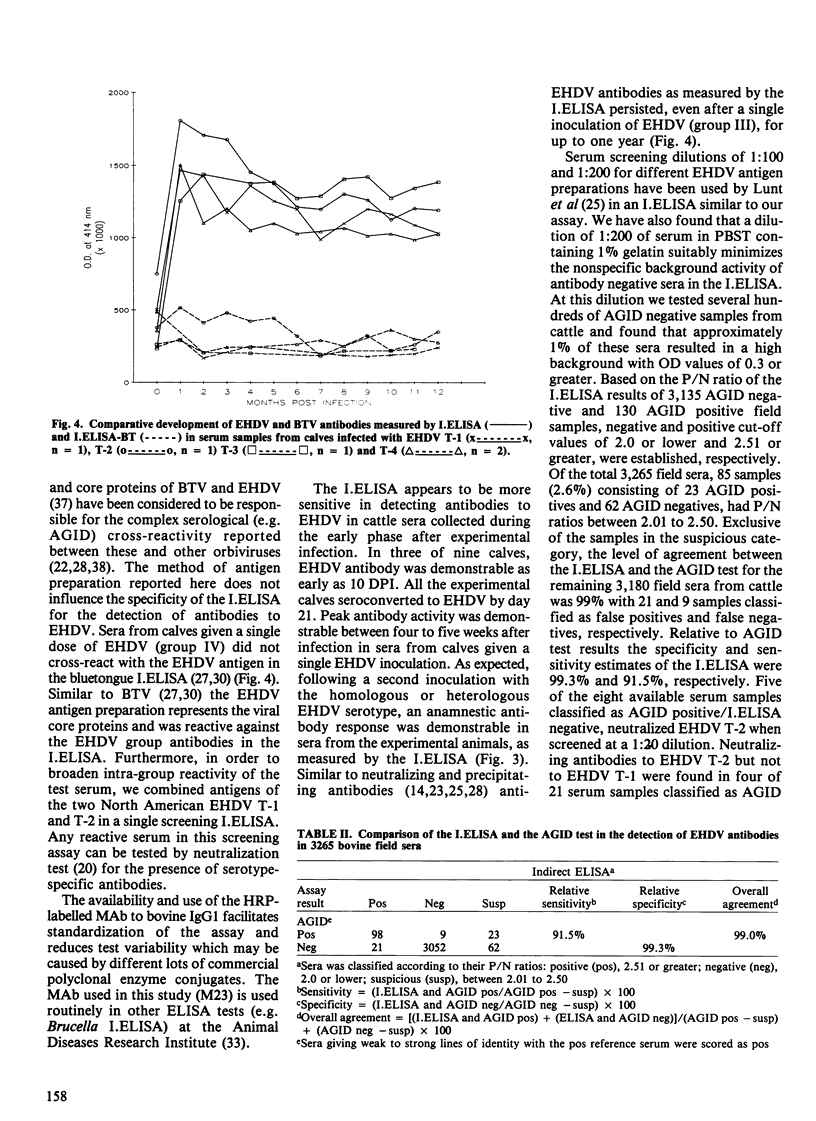
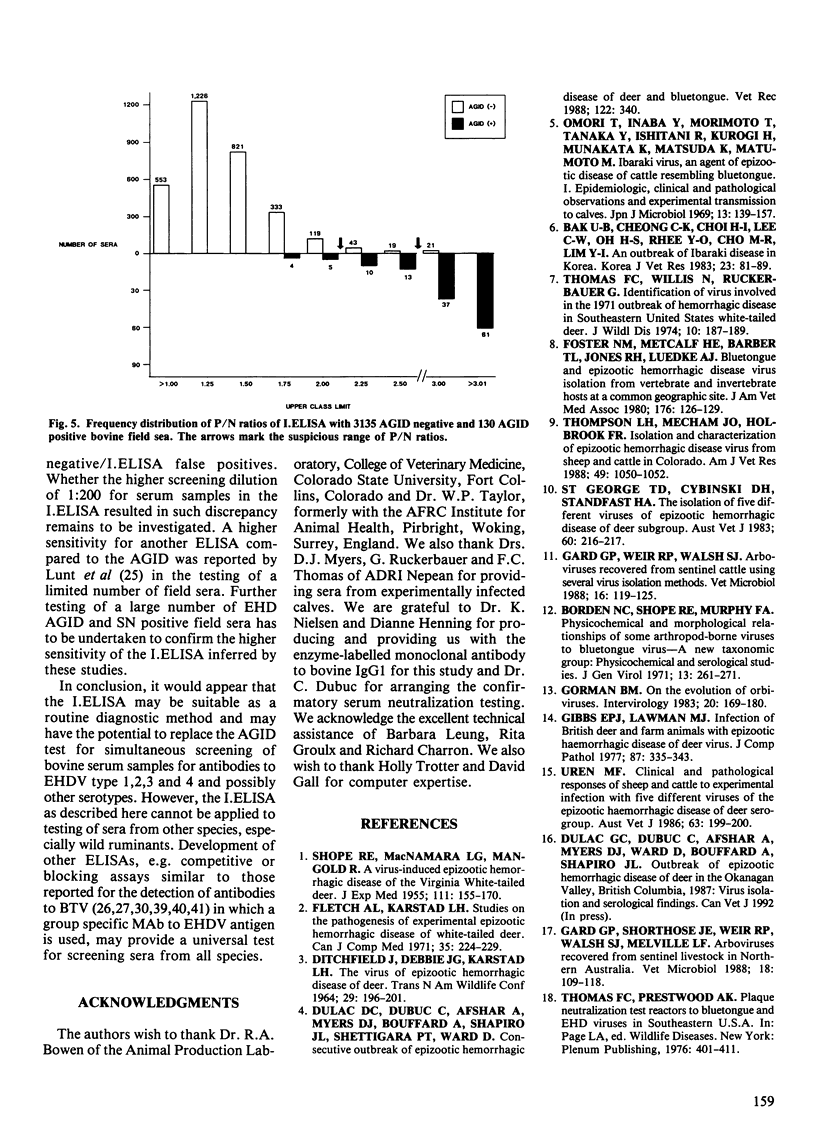
Abstract
An indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (I.ELISA) is described for detection of bovine serum antibody to epizootic hemorrhagic diseases of deer virus (EHDV). Serum samples, at a dilution of 1:200, were incubated with group-specific EHDV antigens, pre-adsorbed to microtiter plates. Bound antibodies were detected by a murine monoclonal antibody to bovine immunoglobulin (Ig)G1 (heavy-chain specific) conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. The performance of the I.ELISA in detecting antibodies to EHDV in sequential serum samples from calves experimentally infected with serotypes 1,2,3 and 4 was evaluated. The I.ELISA detected EHDV antibodies from 14 days postinfection when seroconversion by the standard agar gel immunodiffusion (AGID) test was also evident. The group-specific antibodies to EHDV increased exponentially during the first two to four weeks postinfection and remained relatively stable for about 12 months in some calves. Unlike observations with the AGID test, no reaction was seen in the I.ELISA between blue-tongue virus (BTV) antigen and sera from calves given a single dose of EHDV. The performance of the I.ELISA and AGID were compared using 3,135 AGID negative bovine field sera from herds in Ontario, Alberta and British Columbia and 130 AGID positive samples collected from cattle in 1987 and 1988 during and after outbreaks of EHD in the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia. The specificity and sensitivity of the assay relative to the AGID test were 99.3% and 91.5% respectively, with an overall agreement of 99.0% between the tests.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afshar A., Thomas F. C., Wright P. F., Shapiro J. L., Anderson J. Comparison of competitive ELISA, indirect ELISA and standard AGID tests for detecting blue-tongue virus antibodies in cattle and sheep. Vet Rec. 1989 Feb 11;124(6):136–141. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.6.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afshar A., Thomas F. C., Wright P. F., Shapiro J. L., Shettigara P. T., Anderson J. Comparison of competitive and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of bluetongue virus antibodies in serum and whole blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1705–1710. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1705-1710.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. Use of monoclonal antibody in a blocking ELISA to detect group specific antibodies to bluetongue virus. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 16;74(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C., Shope R. E., Murphy F. A. Physicochemical and morphological relationships of some arthropod-borne viruses to bluetongue virus--a new taxonomic group. Physiocochemical and serological studies. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):261–271. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen R. A. Serologic responses of calves to sequential infections with epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotypes. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Oct;48(10):1449–1452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulac G. C., Dubuc C., Afshar A., Myers D. J., Bouffard A., Shapiro J., Shettigara P. T., Ward D., Bouttard A. Consecutive outbreaks of epizootic haemorrhagic disease of deer and bluetongue. Vet Rec. 1988 Apr 2;122(14):340–340. doi: 10.1136/vr.122.14.340-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletch A. L., Karstad L. H. Studies on the pathogenesis of experimental epizootic hemorrhagic disease of white-tailed deer. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jul;35(3):224–229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. M., Metcalf H. E., Barber T. L., Jones R. H., Luedke A. J. Bluetongue and epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus isolation from vertebrate and invertebrate hosts at a common geographic site. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1980 Jan 15;176(2):126–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard G. P., Shorthose J. E., Weir R. P., Walsh S. J., Melville L. F. Arboviruses recovered from sentinel livestock in northern Australia. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Oct;18(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard G. P., Weir R. P., Walsh S. J. Arboviruses recovered from sentinel cattle using several virus isolation methods. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Oct;18(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. P., Lawman M. J. Infection of British deer and farm animals with epizootic haemorrhagic disease of deer virus. J Comp Pathol. 1977 Jul;87(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman B. M. On the evolution of orbiviruses. Intervirology. 1983;20(2-3):169–180. doi: 10.1159/000149388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., House J. A., Berninger M. L. Detection of bluetongue group-specific antibody by competitive ELISA. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Apr;2(2):137–139. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Bremer C. W., Barber T. L. The nucleic acid and proteins of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1979 Jun;46(2):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt R. A., White J. R., Blacksell S. D. Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody blocking ELISA for the detection of group-specific antibodies to bluetongue virus in experimental and field sera. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2729–2740. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt R. A., White J. R., Della-Porta A. J. Studies with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the serodiagnosis of bluetongue and epizootic haemorrhagic disease of deer. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Apr;16(4):323–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. L. Bluetongue and related viruses in Ibadan, Nigeria: serologic comparison of bluetongue, epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer, and Abadina (Palyam) viral isolates. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Aug;35(8):1109–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. H., Henning M. D., Duncan J. R. Monoclonal antibodies in veterinary medicine. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1986;4:311–353. doi: 10.1080/02648725.1986.10647831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori T., Inaba Y., Morimoto T., Tanaka Y., Ishitani R. Ibaraki virus, an agent of epizootic disease of cattle resembling bluetongue. I. Epidemiologic, clinical and pathologic observations and experimental transmission to calves. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Jun;13(2):139–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. L., Wiegers A., Dulac G. C., Bouffard A., Afshar A., Myers D. J., Dubuc C., Martin M. W., Koller M. A survey of cattle for antibodies against bluetongue and epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer viruses in British Columbia and southwestern Alberta in 1987. Can J Vet Res. 1991 Apr;55(2):203–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George T. D., Cybinski D. H., Standfast H. A., Gard G. P., Della-Porta A. J. The isolation of five different viruses of the epizootic haemorrhagic disease of deer serogroup. Aust Vet J. 1983 Jul;60(7):216–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb09587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemshorn B. W., Buckley D. J., St Amour G., Lin C. S., Duncan J. R. A computer-interfaced photometer and systematic spacing of duplicates to control within-plate enzyme-immunoassay variation. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Girard A., Boulanger P., Ruckerbauer G. A comparison of some serological tests for bluetongue virus infection. Can J Comp Med. 1976 Jul;40(3):291–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Willis N., Ruckerbauer G. Identification of viruses involved in the 1971 outbreak of hemorrhagic disease in southeastern United States white-tailed deer. J Wildl Dis. 1974 Jul;10(3):187–189. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-10.3.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mecham J. O., Holbrook F. R. Isolation and characterization of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus from sheep and cattle in Colorado. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1050–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhisa S., Inaba Y., Miura Y., Sato K., Akashi H., Tsuda T., Shibata I. Hemagglutination of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus. Arch Virol. 1981;69(3-4):291–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01317344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uren M. F. Clinical and pathological responses of sheep and cattle to experimental infection with five different viruses of the epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer serogroup. Aust Vet J. 1986 Jun;63(6):199–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb02980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis N. G., Corey P. N., Campbell J. B., Macpherson L. W. Development and statistic evaluation of a plaque assay for the virus of epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Dec;16(12):1293–1301. doi: 10.1139/m70-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. F., Kelly W. A., Gall D. E. Application of a timing protocol to the reduction of inter-plate variability in the indirect enzyme immunoassay for detection of anti-Brucella antibody. J Immunoassay. 1985;6(3):189–205. doi: 10.1080/01971528508063029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


