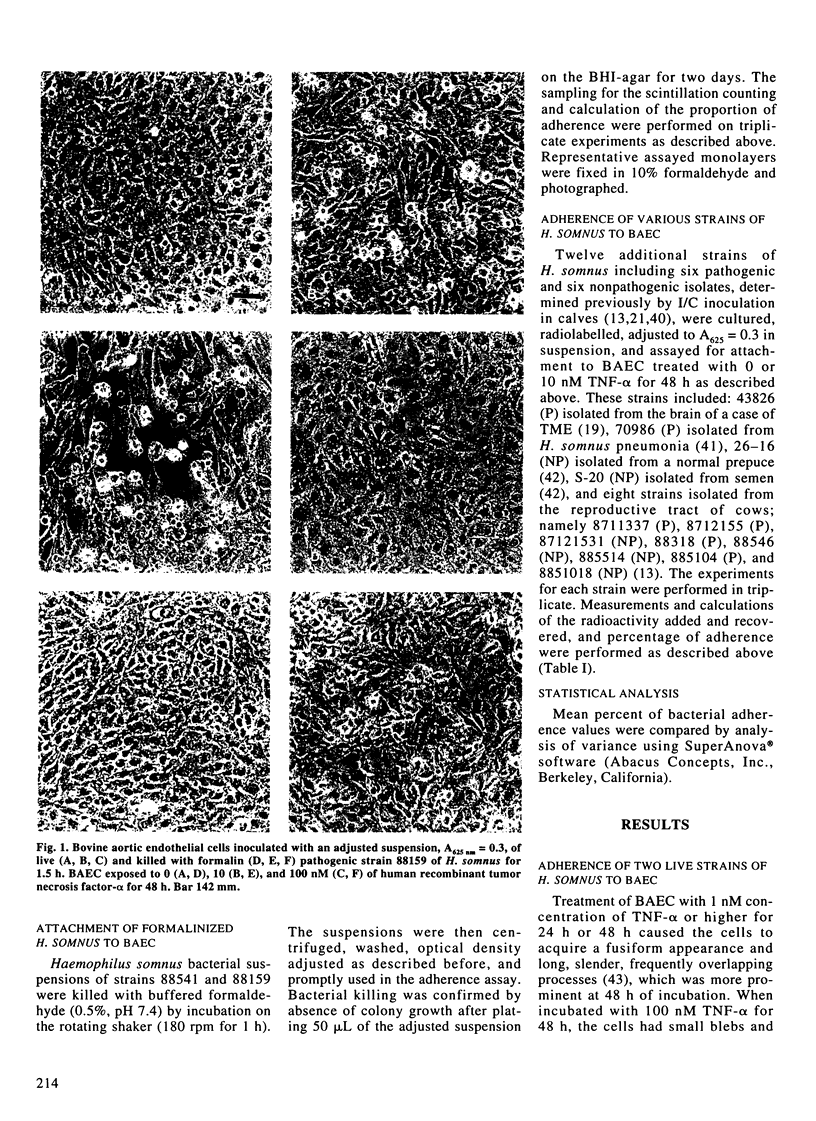
Abstract
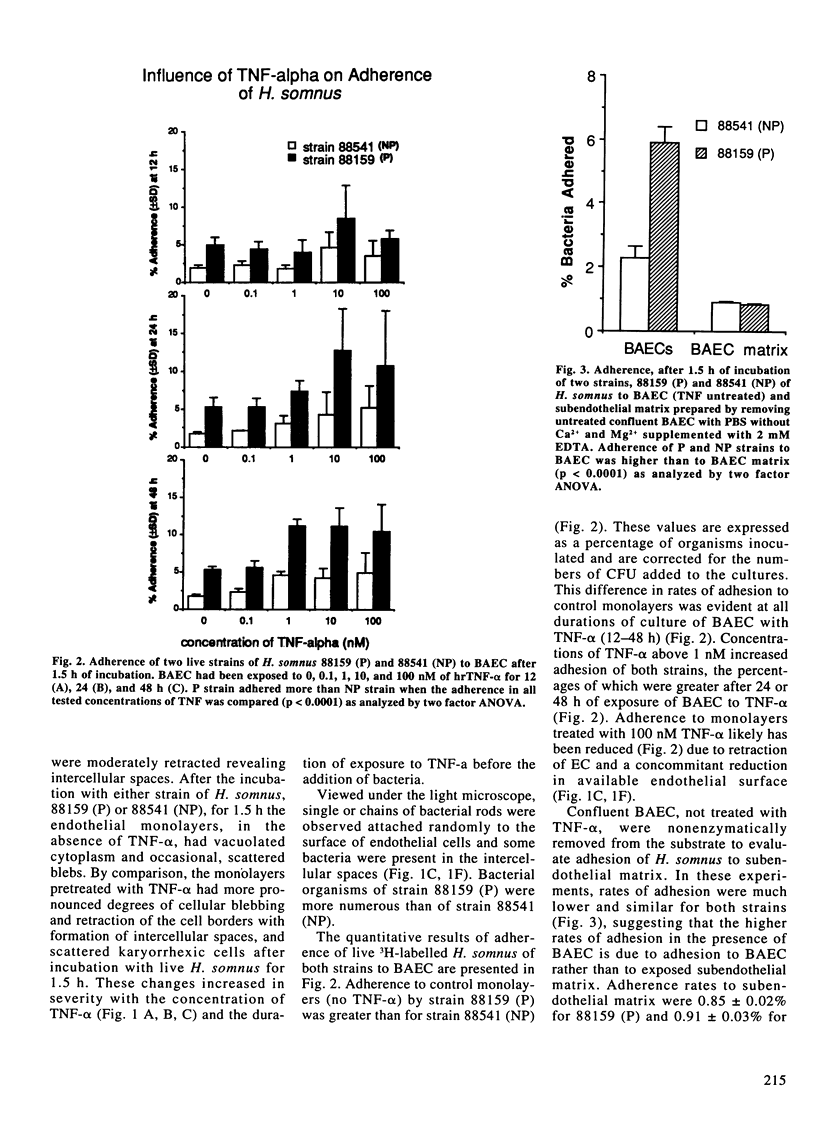
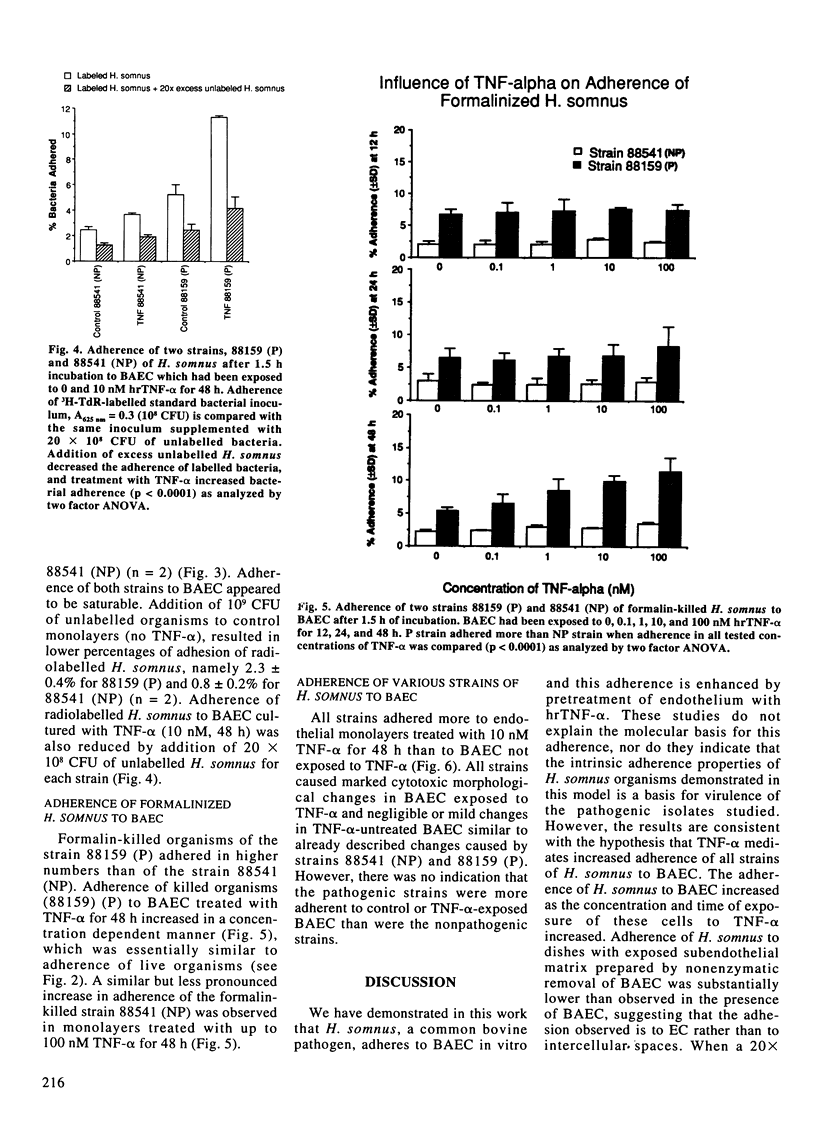
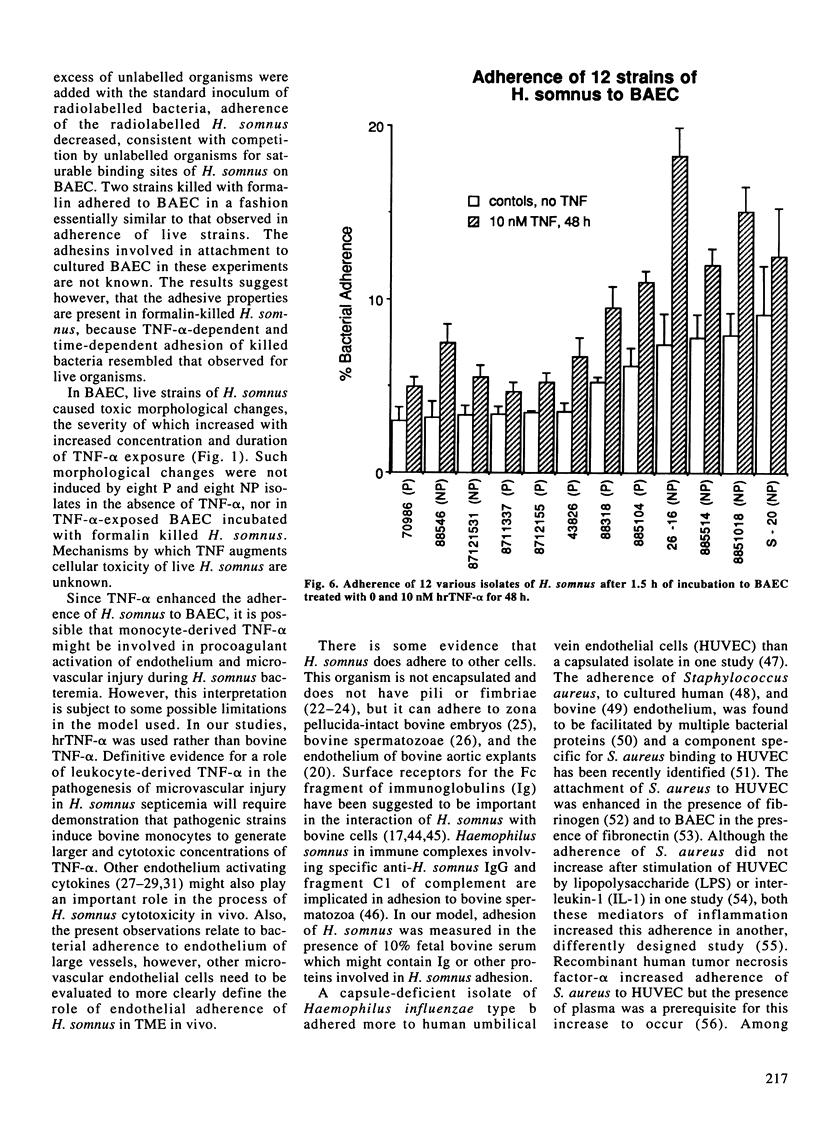
Vascular thrombosis and tissue infarction is a principal lesion in Haemophilus somnus septicemia known also as thrombotic meningoencephalitis. This study was undertaken to examine whether tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) can influence the adherence of H. somnus to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAEC). Confluent BAEC were exposed to 0-100 nM of human recombinant TNF-alpha for 12-48 h. Suspensions of different strains of H. somnus (approximately 1.5-3 x 10(8) labelled with [methyl-3H]-thymidine, were added to BAEC and incubated for 1.5 h. Initial studies with one pathogenic (P) strain and one non-pathogenic (NP) strain revealed that both strains adhered to normal endothelial cells but minimally to subendothelial matrix remaining after removal of BAEC. Adherence to BAEC was reduced by an excess of unlabelled H. somnus of the same strain. Adherence was enhanced for both strains by exposure of BAEC to TNF-alpha in a manner that increased with TNF-alpha concentration and with duration of exposure to TNF-alpha prior to addition of bacteria. A survey of adherence of six live P strains and six NP strains demonstrated considerable variation but no difference in adherence between P and NP strains to normal or to TNF-alpha-stimulated BAEC. However, TNF-alpha consistently increased adhesion of each strain to BAEC. Both P and NP strains caused more severe cytotoxic changes in TNF-alpha-treated BAEC. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha also increased adhesion of formalin-killed bacteria of P and NP strains.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. J., Anderson T. D., Slife L. N., Stevenson G. W. Microscopic lesions associated with the isolation of Haemophilus somnus from pneumonic bovine lungs. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong K. R., Osborne A. D., Janzen E. D. Haemophilus somnus Mastitis in a Dairy Cow. Can Vet J. 1986 May;27(5):211–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt A. R., Simmons D. L., Tansey J., Newbold C. I., Marsh K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):57–59. doi: 10.1038/341057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg E. A., Hatcher V. B., Lowy F. D. Acidic fibroblast growth factor modulates Staphylococcus aureus adherence to human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1470–1474. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1470-1474.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Koomey J. M., Lee S., Jaffe E. A., Fischetti V. A. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to cultured human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3827–3831. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3827-3831.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Krishnan M., Jaffe E. A., Fischetti V. A. Fibrinogen acts as a bridging molecule in the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2236–2245. doi: 10.1172/JCI115259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chełmońska A. The influence of Haemophilus somnus on bull sperms examined in vitro. Pol Arch Weter. 1990;30(3-4):141–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B. Molecular aspects of some virulence factors of Haemophilus somnus. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Apr;54 (Suppl):S57–S62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Widders P. R., Gogolewski R., Arthur J., Inzana T. J., Ward A. C. Haemophilus somnus: Bovine Reproductive and Respiratory Disease. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Chan M. K., Movat H. Z. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Hamilton H. L. Bovine neutrophils ingest but do not kill Haemophilus somnus in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):431–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.431-436.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Schaefer D. C., Wasson S. K., Corbeil R. R., Corbeil L. B. Pulmonary persistence of Haemophilus somnus in the presence of specific antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1767-1774.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groom S. C., Little P. B., Rosendal S. Virulence differences among three strains of Haemophilus somnus following intratracheal inoculation of calves. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):349–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guichon P. T., Pritchard J., Jim G. K. Haemophilus somnus myocarditis in a feedlot steer. Can Vet J. 1988 Dec;29(12):1012–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson K. S., Vercellotti G. M., Bendel C. M., Hostetter M. K. Molecular mimicry in Candida albicans. Role of an integrin analogue in adhesion of the yeast to human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1896–1902. doi: 10.1172/JCI115214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill R. J., Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells: model for postadherence events in endovascular infections. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.833-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Martin J. R., Larouche Y., Goyette G. Mastitis Caused by Haemophilus somnus in a Dairy Cow. Can Vet J. 1987 Mar;28(3):117–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. D., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A., Chiang Y. W. Haemophilus somnus-induced interference with bovine neutrophil functions. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jun;12(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Stephens L. R., Thorsen J. Occurrence of "Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):215–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Corbeil L. B. Development of a defined medium for Haemophilus somnus isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):366–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., BIBERSTEIN E. L., HOWARTH J. A., FRAZIER L. M., DUNGWORTH D. L. Infectious meningo-encephalitis in cattle, caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecien J. M., Little P. B. Haemophilus somnus and reproductive disease in the cow: A review. Can Vet J. 1991 Oct;32(10):595–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecien J. M., Little P. B. Isolation of pathogenic strains of Haemophilus somnus from the female bovine reproductive tract. Can J Vet Res. 1992 Apr;56(2):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer J. A., Brown J. F., Czuprynski C. J. "Haemophilus somnus," a facultative intracellular pathogen of bovine mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.381-387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarak E. J., Howard B. V., Kefalides N. A. Properties of calf endothelial cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Bussolino F., Dejana E. Cytokine regulation of endothelial cell function. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2591–2599. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Dejana E. Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):370–375. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S. K., Yurberg E. R., Hatcher V. B., Levitt M. A., Lowy F. D. Bacterial adherence to human endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.218-224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Dahlgren R. R., Rinker H. B. Observations on septicemia of cattle caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Pathol Vet. 1968;5(3):212–216. doi: 10.1177/030098586800500303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Goodwin J. D., Vann J. M., Selvaraj M. P., Hart M. A. Role of C1q in phagocytosis of Salmonella minnesota by pulmonary endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1356-1362.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva S. V., Mok T., Little P. B. The development of protein A-gold electron microscopy for immunological studies of Haemophilus somnus. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Mar;27(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90060-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Humphrey J. D., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Vaccination of cattle against experimentally induced thromboembolic meningoencephalitis with a Haemophilus somnus bacterin. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Aug;43(8):1339–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B. Ultrastructure of Haemophilus somnus, causative agent of bovine infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Sep;42(9):1638–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Humoral immunity in experimental thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle caused by Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):468–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Feb 15;178(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. D., Hampson F. W., Hunninghake G. W. Bacterial adherence to human endothelial cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Sep;65(3):1372–1376. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.3.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. G., Little P. B. Effect of Haemophilus somnus on bovine endothelial cell in organ culture. Am J Vet Res. 1981 May;42(5):748–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson M. S., Stringfellow D. A., Lauerman L. H. Adherence of Haemophilus somnus to bovine embryos after in vitro exposure. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jan;49(1):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. C., Blackwell L. J., Hatcher V. B., Elliott D. A., O'Hagan-Sotsky C., Lowy F. D. Staphylococcus aureus proteins that bind to human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):965–969. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.965-969.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. C., Hatcher V. B., Patel D., Orr G. A., Higgins L. L., Lowy F. D. A human endothelial cell membrane protein that binds Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI114560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Hamill R. J., Albrecht R. M., Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of fibronectin in adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):538–542. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Kayhty H., Ferguson D. J., Alexandrescu C., Moxon E. R. Interactions of Haemophilus influenzae with cultured human endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1991 Mar;10(3):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90057-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Nivard J. R., Maheswaran S. K. Morphologic features, structure, and adherence to bovine turbinate cells of three haemophilus somnus variants. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Feb;45(2):336–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Dorrance L. A., Yarnall M., Corbeil L. B. Immunoglobulin-binding activity among pathogenic and carrier isolates of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):639–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.639-642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Gogolewski R. P., Corbeil L. B. Characterization of two Haemophilus somnus Fc receptors. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1993–1999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]