Abstract
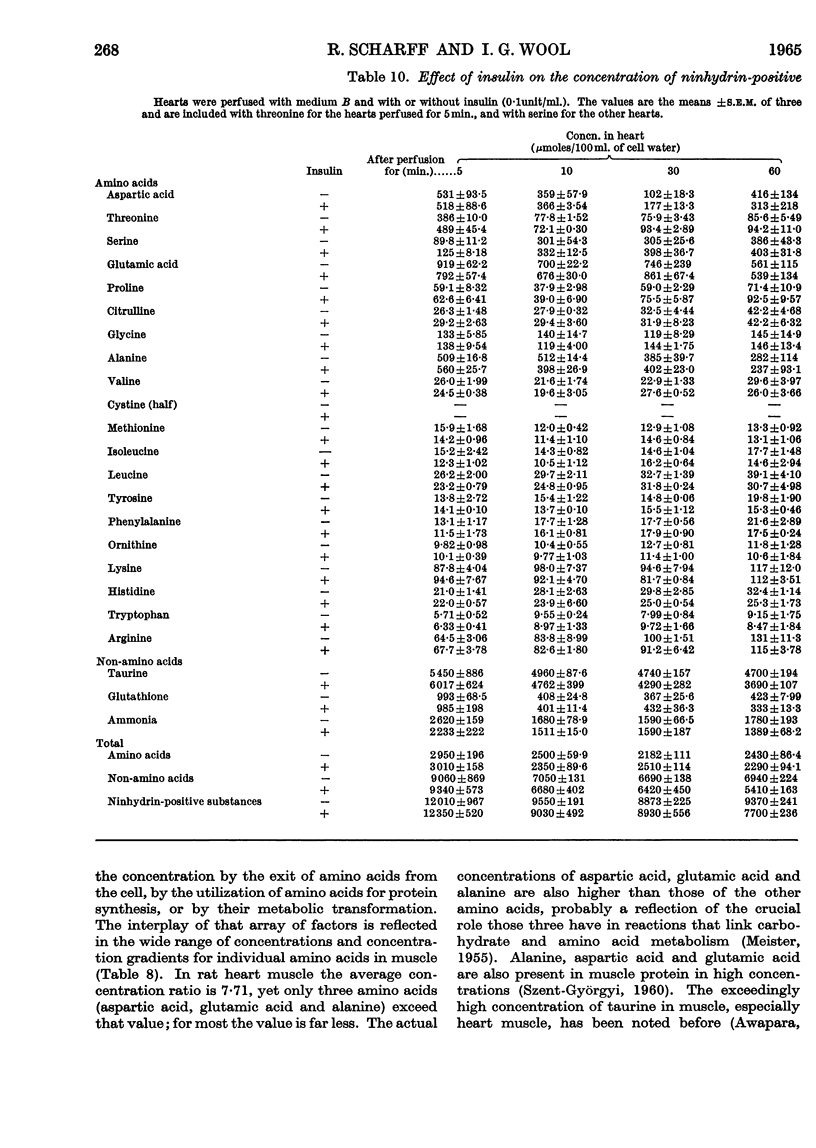
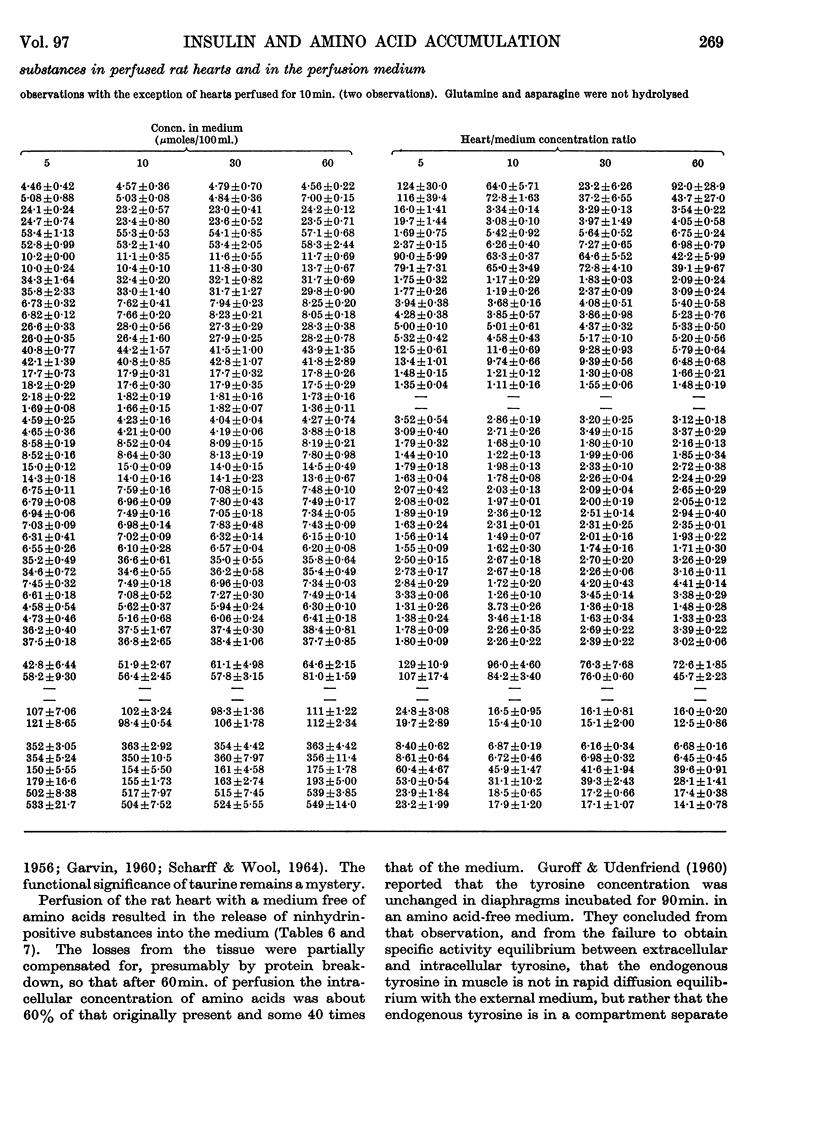
1. Rat heart perfused with Krebs–Henseleit bicarbonate buffer released material containing ninhydrin-positive nitrogen, but the amount was less than that reported to be released by diaphragm; glucose, but not insulin, decreased the release of ninhydrin-positive nitrogen and increased the concentration of the same material in the intracellular water of heart. 2. When heart was perfused with a mixture of amino acids and glucose, there was actually a net uptake, and an increase in intracellular concentration, of ninhydrin-positive nitrogen. Changes in the concentration of ninhydrin-positive nitrogen did not accurately reflect changes in concentration of amino acids. 3. The effect of insulin on the actual concentration of individual amino acids in heart muscle was examined by perfusing the heart with a mixture of amino acids and other ninhydrin-positive substances in the same concentration as they are found in plasma. 4. The effect of insulin on the concentrations of amino acids in the medium and in the intracellular water of the heart was determined after perfusion for different periods of time. No clear or meaningful effect of insulin was observed, despite the fact that insulin significantly increased the accumulation, in each of the same hearts, of radioactivity from amino[14C]isobutyric acid.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKEDO H., CHRISTENSEN H. N. Nature of insulin action on amino acid uptake by the isolated diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:118–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AWAPARA J. The taurine concentration of organs from fed and fasted rats. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEEHEN N. M., FISHER R. B. The action of insulin in the isolated rat heart. J Physiol. 1954 Feb 26;123(2):260–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E. Mechanism and extent of distribution of inulin and sucrose in chloride space of tissues. Am J Physiol. 1954 Mar;176(3):396–410. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., YOUNG D. A. Direct determination of extracellular fluid in the rat heart. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:50–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND P. B., NEWSHOLME E. A., RANDLE P. J. Effect of fatty acids, ketone bodies, diabetes and starvation on pyruvate metabolism in rat heart and diaphragm muscle. Nature. 1962 Jul 28;195:381–383. doi: 10.1038/195381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARVIN J. E. A new method for the determination of taurine in tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Dec;91:219–225. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUROFF G., UDENFRIEND S. The failure of insulin to effect the transport of tyrosine in the isolated rat diaphragm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 15;46:386–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90764-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUROFF G., UNDENFRIEND S. The uptake of tyrosine by isolated rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3518–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON P. B. Ion exchange chromatography of amino acids--microdetermination of free amino acids in serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 31;102:55–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb13625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., NOALL M. W. Stimulation of amino acid transport by insulin in the isolated rat diaphragm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Apr;28(1):226–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90466-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINE D. L. A procedure for the study of factors which effect the nitrogen metabolism of isolated tissues; hormonal influences. Endocrinology. 1949 Dec;45(6):596–604. doi: 10.1210/endo-45-6-596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L. Insulin and incorporation of amino acids into protein of muscle. Cellular amino acid levels and aminoisobutyric acid uptake. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:135–147. doi: 10.1042/bj0810135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., WOOL I. G. INSULIN AND INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACIDS INTO PROTEIN OF MUSCLE. 1. ACCUMULATION AND INCORPORATION STUDIES WITH THE PERFUSED RAT HEART. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:202–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0890202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., YOUNG F. G. The effect of insulin in vitro on the accumulation of amino acids by isolated rat diaphragm. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:487–495. doi: 10.1042/bj0750487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., HENDERSON M. J., REGEN D. M., PARK C. R. Regulation of glucose uptake in muscle. I. The effects of insulin and anoxia on glucose transport and phosphorylation in the isolated, perfused heart of normal rats. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWEY H., SMYTH D. H. EFFECTS OF SUGARS ON INTESTINAL TRANSFER OF AMINO-ACIDS. Nature. 1964 Apr 25;202:400–401. doi: 10.1038/202400b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEZ K. A., MORRIS L. A modified procedure for the automatic analysis of amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Nov;1:187–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN W. L., CARVER M. J. IMMEDIATED AND PROLONGED EFFECTS OF HYDROCORTISONE ON THE FREE AMINO ACIDS OF RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Dec;114:816–819. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHARFF R., WOOL I. G. CONCENTRATION OF AMINO ACIDS IN RAT MUSCLE AND PLASMA. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:603–604. doi: 10.1038/202603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff R., Wool I. G. Accumulation of amino acids in muscle of perfused rat heart. Effect of insulin in the presence of puromycin. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):272–276. doi: 10.1042/bj0970272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON A. R., MILES B. J. ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF AMINO-ACIDS: IMPROVEMENTS IN THE SINGLE COLUMN SYSTEM. Nature. 1964 Aug 1;203:483–484. doi: 10.1038/203483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEE C. A., WHITE V. K., HASTINGS A. B. Metabolism of C14 labeled glucose and pyruvate by rat diaphragm muscle in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):287–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSH K. A., BROWN J. R. Internal standards for amino acid analyses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:596–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE H. L., ROLF D. Insulin space as a function of equilibration time. Am J Physiol. 1956 Apr;185(1):152–158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBRANDT W., ROSENBERG T. The concept of carrier transport and its corollaries in pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Jun;13:109–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G. EFFECT OF INSULIN ON ACCUMULATION OF RADIOACTIVITY FROM AMINO-ACIDS BY ISOLATED INTACT RAT DIAPHRAGM. Nature. 1964 Apr 11;202:196–197. doi: 10.1038/202196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G., KRAHL M. E. Incorporation of C14-amino acids into protein of isolated diaphragms: an effect of insulin independent of glucose entry. Am J Physiol. 1959 May;196(5):961–964. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.5.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G., MANCHESTER K. L. Insulin and incorporation of amino-acids into protein of rat tissues. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:345–346. doi: 10.1038/193345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACHARIAH P. Contractility and sugar permeability in the perfused rat heart. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:59–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


