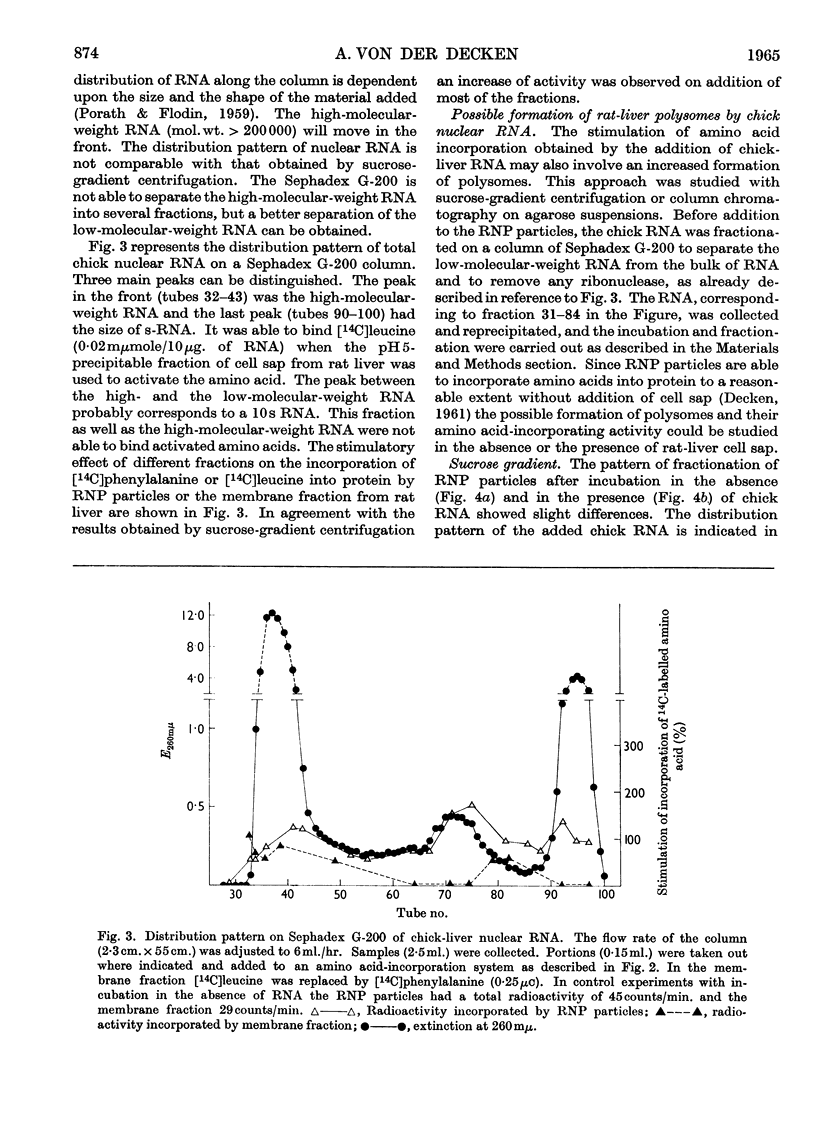
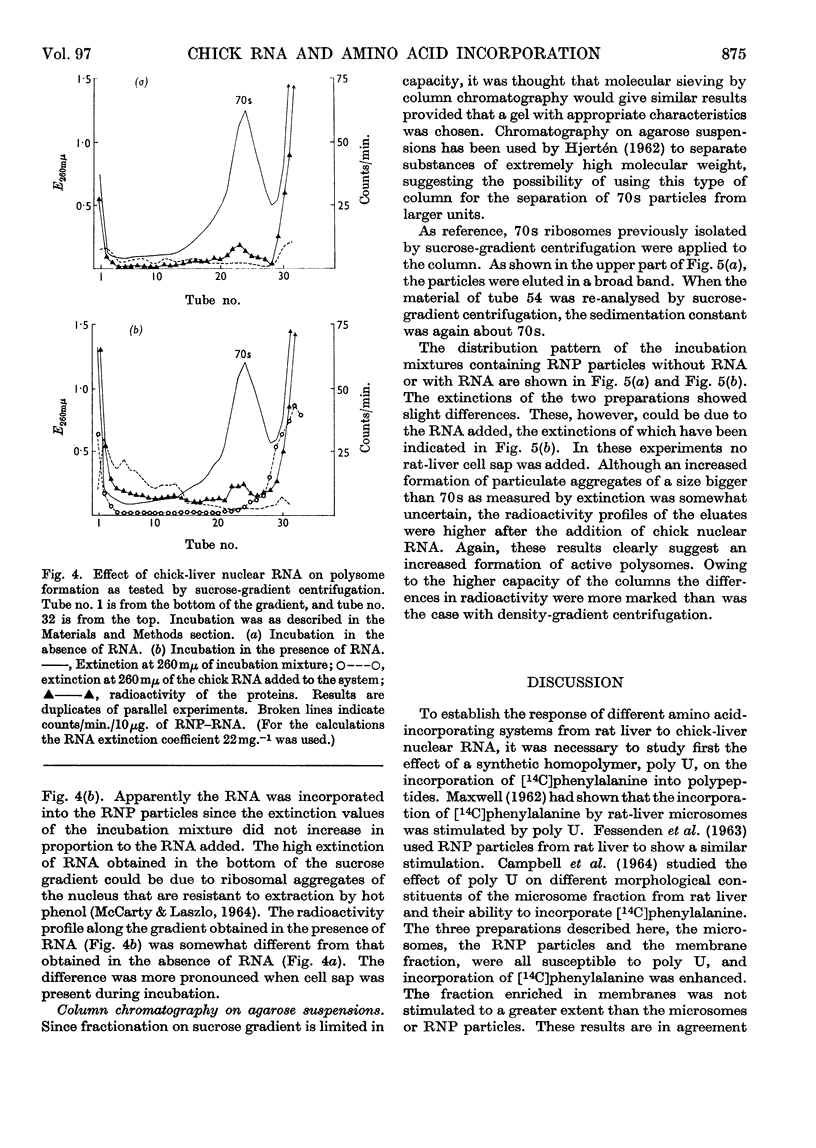
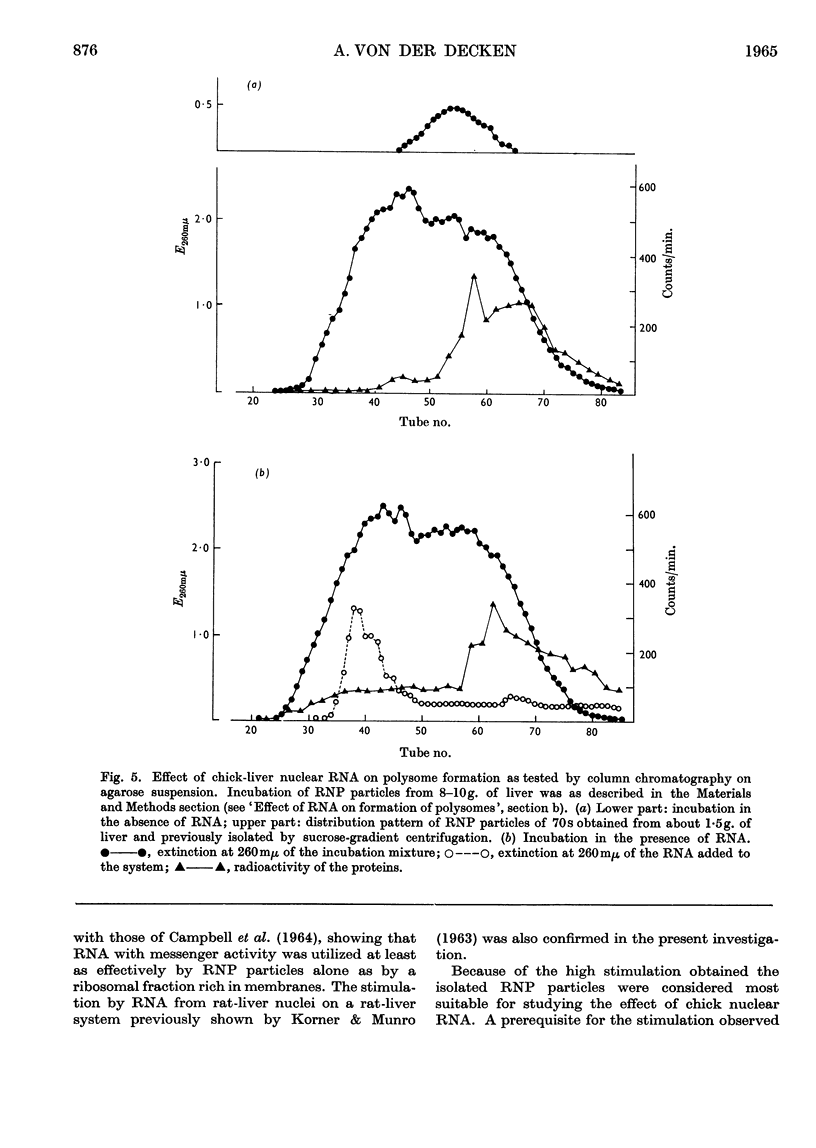
Abstract
1. Rat-liver microsomes, ribonucleoprotein particles and a fraction mainly consisting of microsomal membranes were tested for their ability to incorporate amino acids into protein in the presence of ATP, GTP, phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate kinase. Addition of polyuridylic acid or of ribonucleic acid from rat-liver nuclei stimulated the incorporating activities. 2. These protein-synthesizing systems were found to be susceptible to ribonucleic acid from chick-liver nuclei as well. The biological activity of the ribonucleic acid from chick liver was measured by its capacity to stimulate amino acid incorporation. 3. In the presence of chick-liver ribonucleic acid, the ribonucleoprotein particles from rat liver showed an increased radioactivity in ribosomal units with a sedimentation constant higher than 70s. 4. This was investigated by sucrose-gradient centrifugation or by column chromatography on agarose suspensions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARONDES S. H., DINGMAN C. W., SPORN M. B. In vitro stimulation of amino-acid incorporation into protein by liver nuclear RNA. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:145–147. doi: 10.1038/196145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWNHILL T. J., JONES A. S., STACEY M. The inactivation of ribonuclease during the isolation of ribonucleic acids and ribonucleoproteins from yeast. Biochem J. 1959 Nov;73:434–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0730434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARLWOOD P. A. Applications of radioactively labeled marker proteins in density gradient ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1963 Mar;5:226–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., SMITH K. C., ALLEN F. W. The preparation and characterization of ribonucleic acids from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N., Cooper C., Hicks M. Studies on the role of the morphological constituents of the microsome fraction from rat liver in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):225–234. doi: 10.1042/bj0920225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGMAN W., SPORN M. B. The isolation and physical characterization of nuclear and microsomal ribonucleic acid from rat brain and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:164–177. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGIEV G. P., MANTIEVA V. L. The isolation of DNA-like RNA and ribosomal RNA from the nucleolo-chromosomal apparatus of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 9;61:153–154. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S. Chromatographic separation according to size of macromolecules and cell particles on columns of agarose suspensions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Dec;99:466–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER A., MUNRO A. J. STIMULATION BY RAT LIVER RIBONUCLEIC ACID OF INCORPORATION OF AMINO-ACID INTO RAT LIVER RIBOSOMES. Nature. 1963 Aug 3;199:489–490. doi: 10.1038/199489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M. A priming reaction in protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERMANN M. L., PAVLOVEC A. Ribonucleoprotein from a rat tumor, the Jensen sarcoma. III. Ribosomes purified without deoxycholate but with bentonite as ribonuclease inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORATH J., FLODIN P. Gel filtration: a method for desalting and group separation. Nature. 1959 Jun 13;183(4676):1657–1659. doi: 10.1038/1831657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENDI R., HULTIN T. Preparation and amino acid incorporating ability of ribonucleoprotein-particles from different tissues of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Mar;19:253–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUGITA A., FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. Demonstration of the messenger role of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 May 15;48:846–853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.5.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON DER DECKENA LABELLING OF IMMUNOLOGICALLY SPECIFIC PROTEINS BY RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN PARTICLES FROM RAT-LIVER AND CHICK-LIVER CELL SAP. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:385–394. doi: 10.1042/bj0880385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Der Decken A., Campbell P. N. Studies on the synthesis of serum albumin by ribonucleoprotein particles isolated from rat liver. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84(3):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj0840449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von der Decken A., Campbell P. N. The effect of ultrasonic vibrations on the protein-synthesizing activity of microsome preparations from rat liver. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj0910195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAMECNIK P. C., KELLER E. B. Relation between phosphate energy donors and incorporation of labeled amino acids into proteins. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):337–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der DECKEN, CAMPBELL P. N. Amino acid transfer from aminoacyl-ribonucleic acid to serum albumin by the microsome fraction from rat liver. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:448–454. doi: 10.1042/bj0820448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


