Abstract
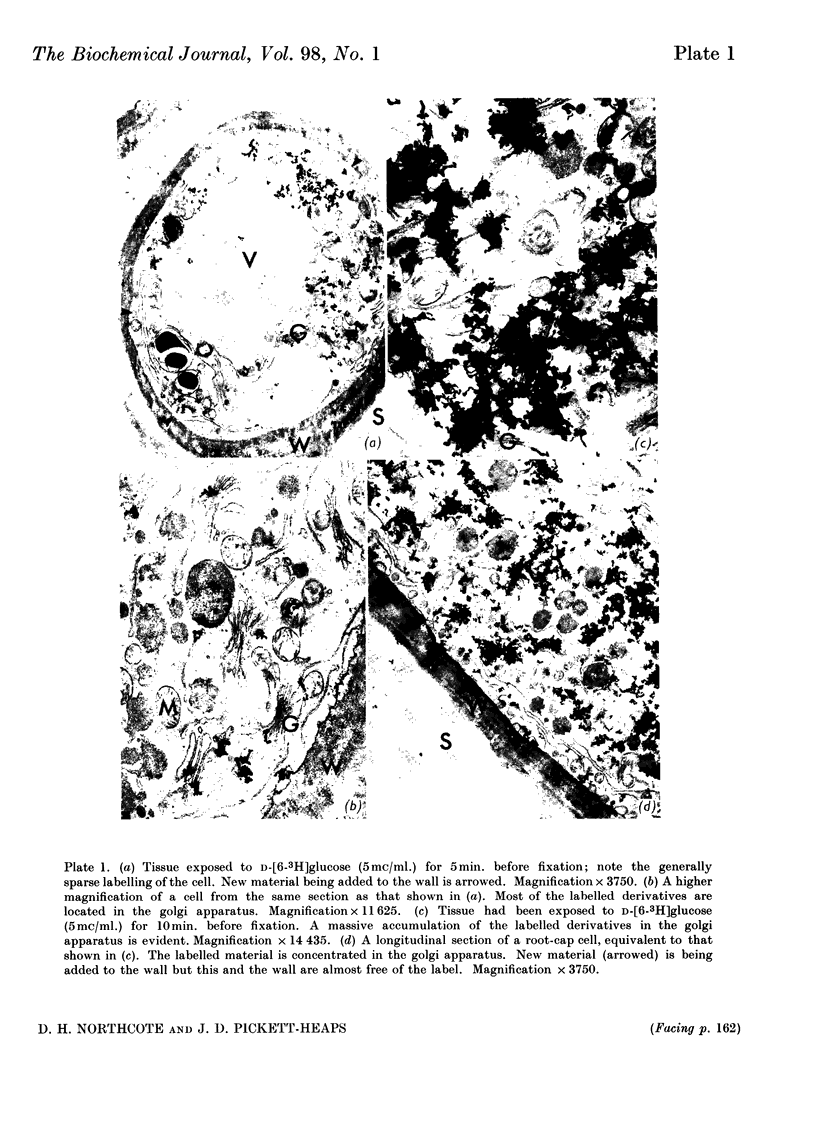
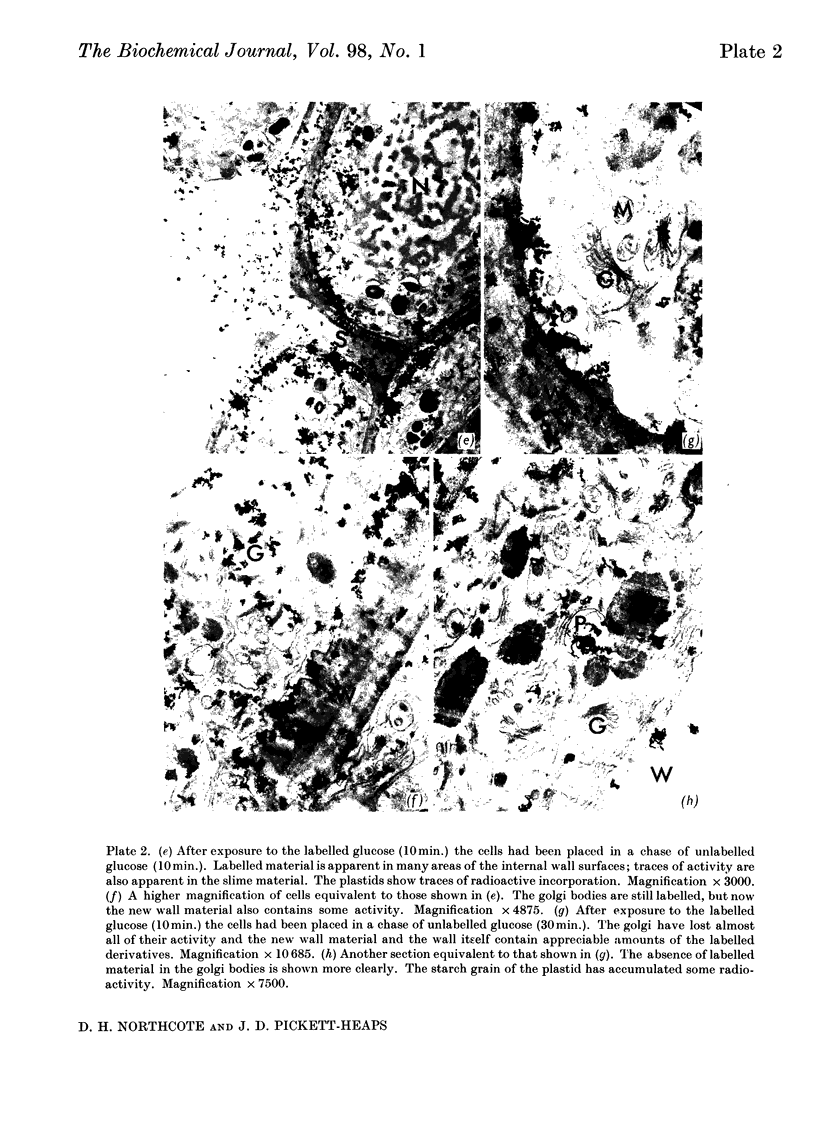
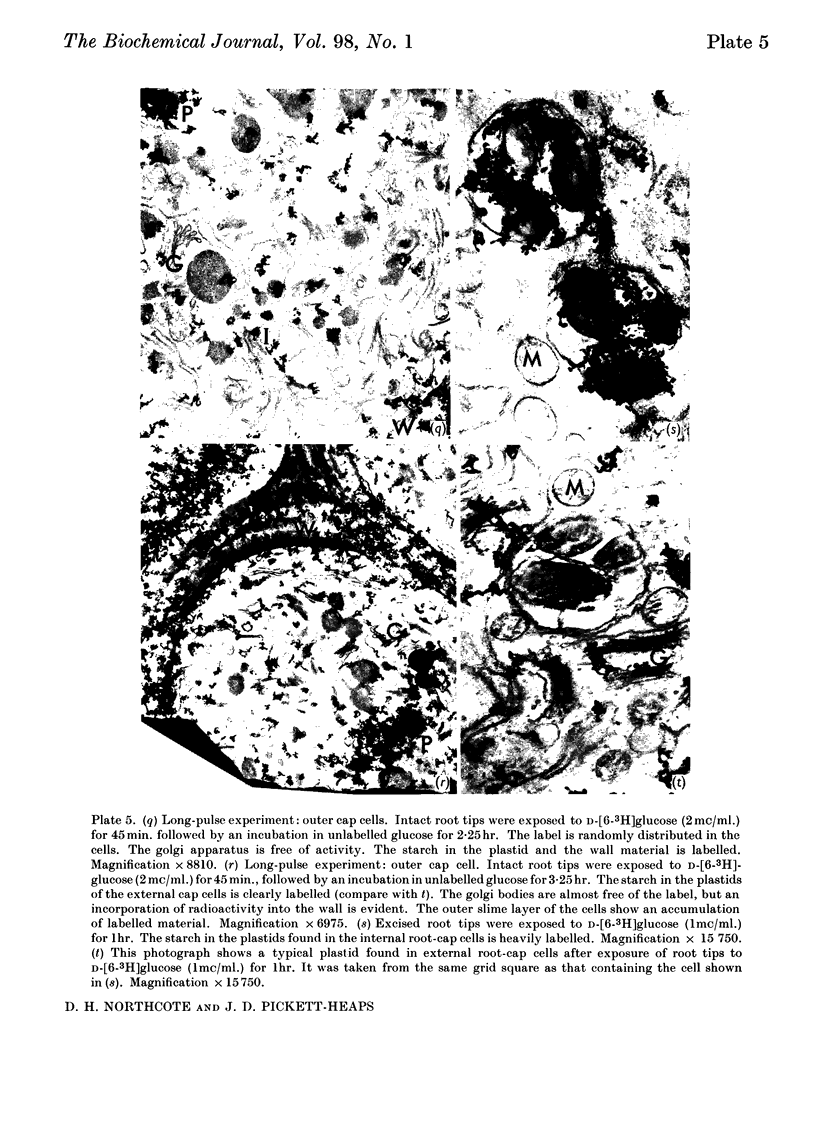
1. A radioautographic study of the cells of the root tips of wheat incubated with d-[1- or 6-3H]glucose has shown that labelled material is formed in the golgi apparatus of the root-cap cells. This material passed to the vesicles associated with the golgi bodies and then moved through the cytoplasm across the plasmalemma and was incorporated into the cell wall and slime layer of the tissue. 2. Analysis of the labelled material extracted from the root tips showed that the bulk of the radioactive material was polysaccharide; there were relatively small amounts of labelled lipids and protein in the tissue. 3. Starch was formed from the exogenous labelled glucose and it was located in the plastids of the cell. The synthesis of starch depended on the metabolic activity of the cells, which varied with the position of the cell in the various tissues of the root tip and with the amount of the exogenous glucose. 4. Isolation of the radioactive polysaccharides from the root tip incubated in the radioactive glucose has shown that the glucose was very rapidly incorporated into the galactosyl residues of the polymers. 5. Analysis of the radioactive polysaccharides has indicated that the material transported in the golgi vesicles is probably pectic substance. 6. A scheme for the synthesis of the storage and wall polysaccharides by separate routes and their location within the cell has been put forward.
Full text
PDF






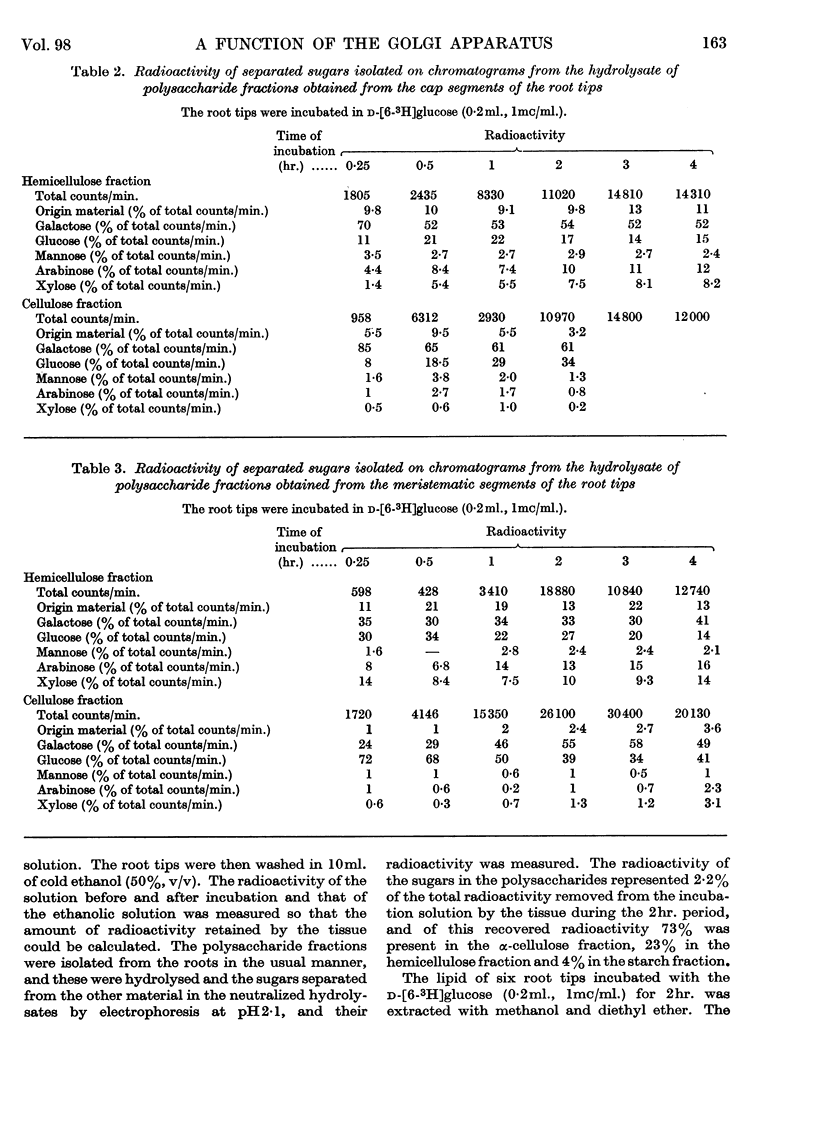


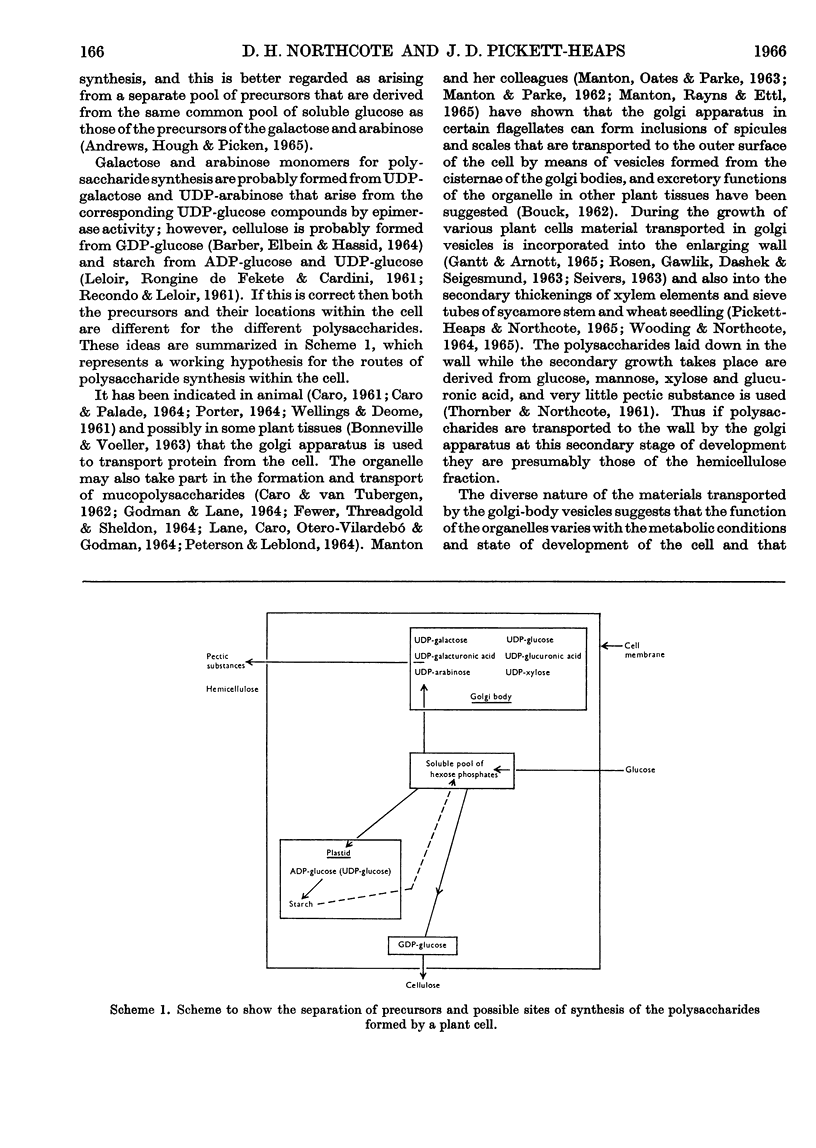

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS P., HOUGH L., PICKEN J. M. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF POLYSACCHARIDES. INCORPORATION OF D-(1-14C)GLUCOSE AND D-(6-14C)GLUCOSE INTO PLUM-LEAF POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:75–80. doi: 10.1042/bj0940075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER H. A., ELBEIN A. D., HASSID W. Z. THE SYNTHESIS OF CELLULOSE BY ENZYME SYSTEMS FROM HIGHER PLANTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4056–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT A. J., NORTHCOTE D. H. APPLE FRUIT PECTIC SUBSTANCES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:617–627. doi: 10.1042/bj0940617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONNEVILLE M. A., VOELLER B. R. A NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENT OF PLANT CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1963 Sep;18:703–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., PALADE G. E. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, STORAGE, AND DISCHARGE IN THE PANCREATIC EXOCRINE CELL. AN AUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Mar;20:473–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEWER D., THREADGOLD J., ANDSHELDON H. STUDIES ON CARTILAGE. V. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE AUTORADIOGRAPHIC LOCALIZATION OF S35 IN CELLS AND MATRIX. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Aug;11:166–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODMAN G. C., LANE N. ON THE SITE OF SULFATION IN THE CHONDROCYTE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:353–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid W. Z., Neufeld E. F., Feingold D. S. SUGAR NUCLEOTIDES IN THE INTERCONVERSION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN HIGHER PLANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jul;45(7):905–915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.7.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE N., CARO L., OTERO VILARDEBO L. R., GODMAN G. C. ON THE SITE OF SULFATION IN COLONIC GOBLET CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:339–351. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F., DE FEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. Starch and oligosaccharide synthesis from uridine diphosphate glucose. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H., WHALEY W. G. An observation on the functioning of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:222–225. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H., WHALEY W. G., LEECH J. H. A function of the Golgi apparatus in outer rootcap cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Apr;5:193–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTHCOTE D. H. The nature of plant cell surfaces. Biochem Soc Symp. 1963;22:105–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLAITAN S. A., NORTHCOTE D. H. Polysaccharides of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:509–519. doi: 10.1042/bj0820509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON M. R., LEBLOND C. P. UPTAKE BY THE GOLGI REGION OF GLUCOSE LABELED WITH TRITIUM IN THE 1 OR 6 POSITION, AS AN INDICATOR OF SYNTHESIS OF COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Apr;34:420–423. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNBER J. P., NORTHCOTE D. H. Changes in the chemical composition of a cambial cell during its differentiation into xylem and phloem tissue in trees. II. Carbohydrate constituents of each main component. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj0810455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLINGS S. R., DEOME K. B. Milk protein droplet formation in the Golgi apparatus of the C3H/Crgl mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:479–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODING F. B., NORTHCOTE D. H. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE SECONDARY WALL OF THE XYLEM IN ACER PSEUDOPLATANUS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:327–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]