Abstract
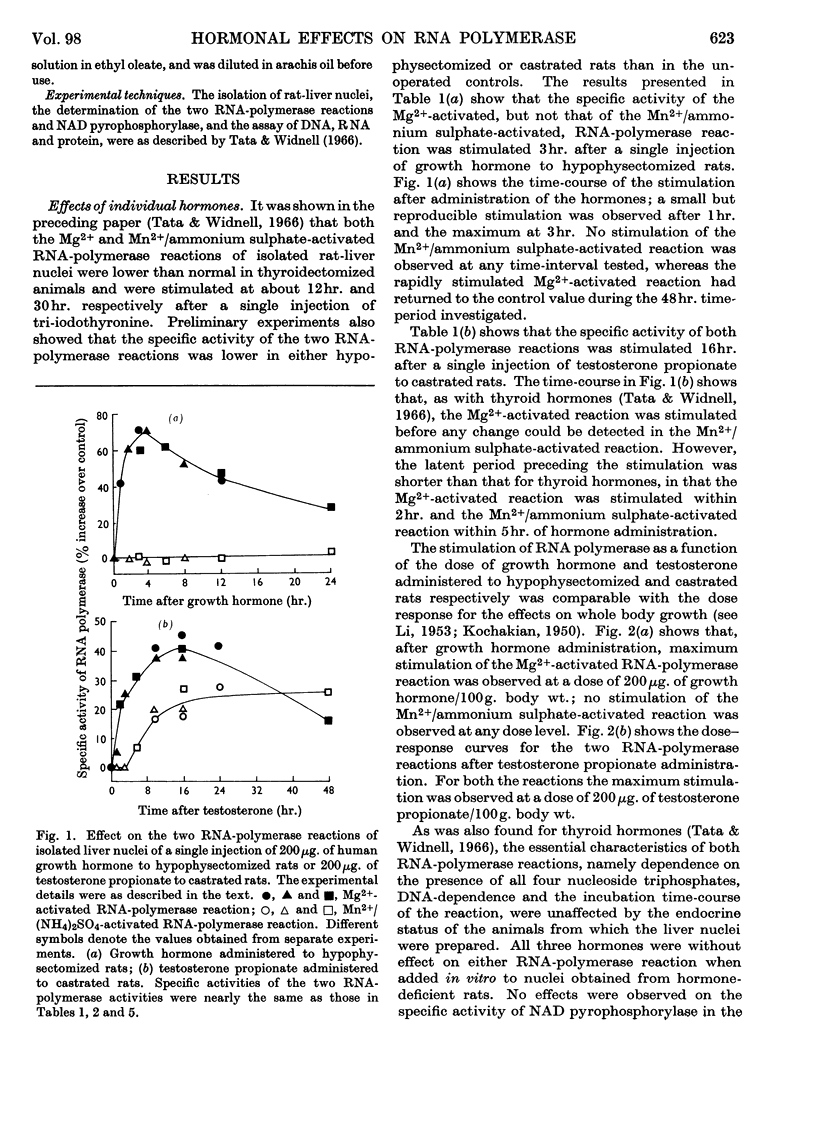
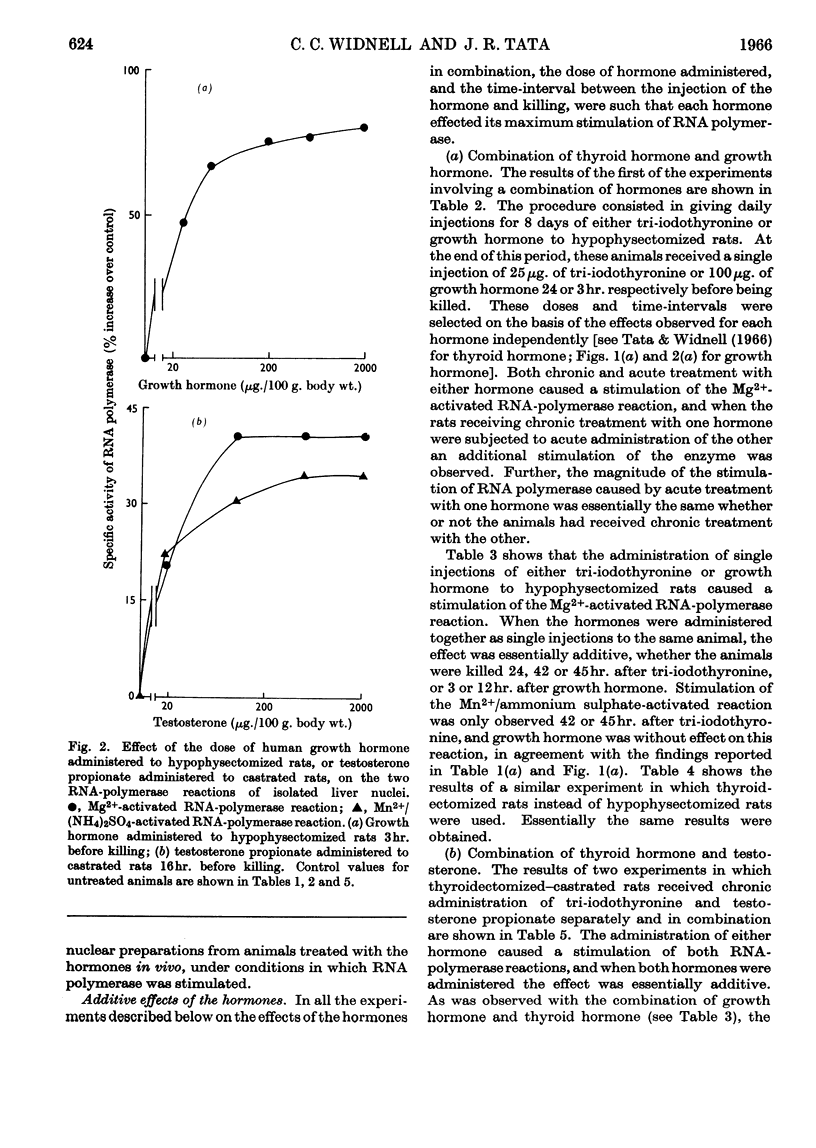
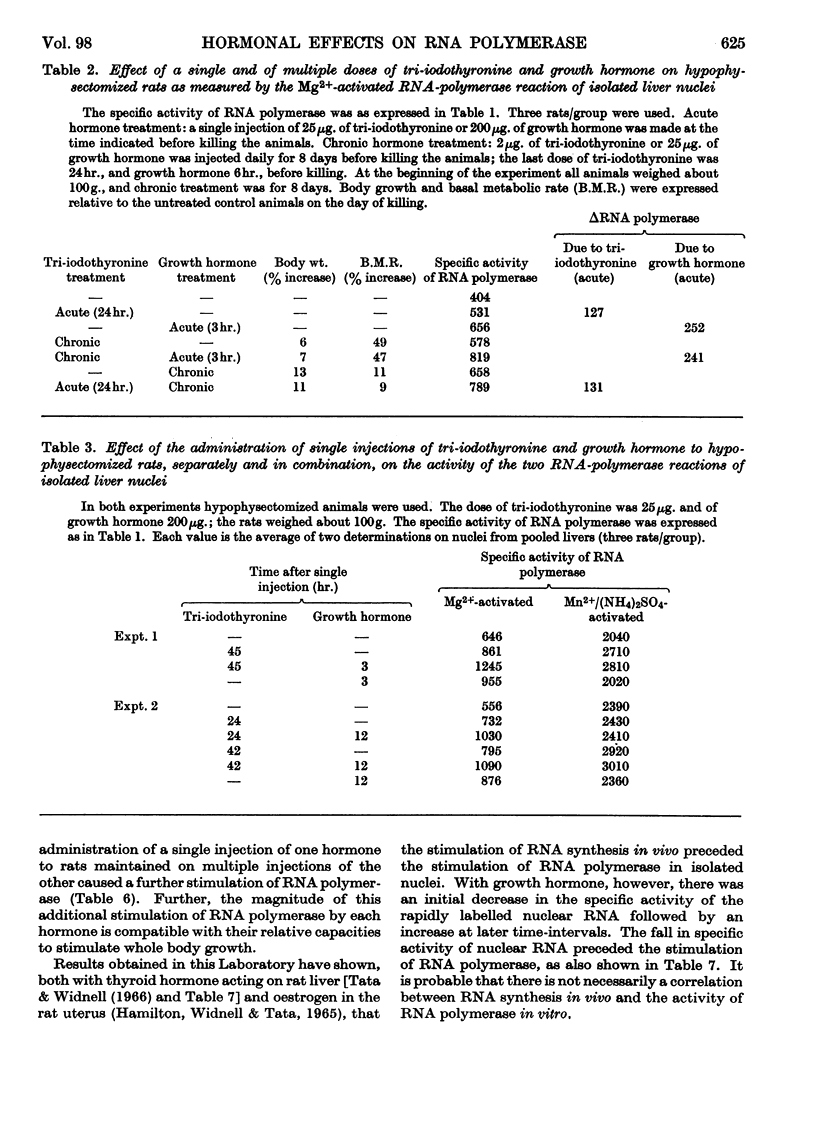
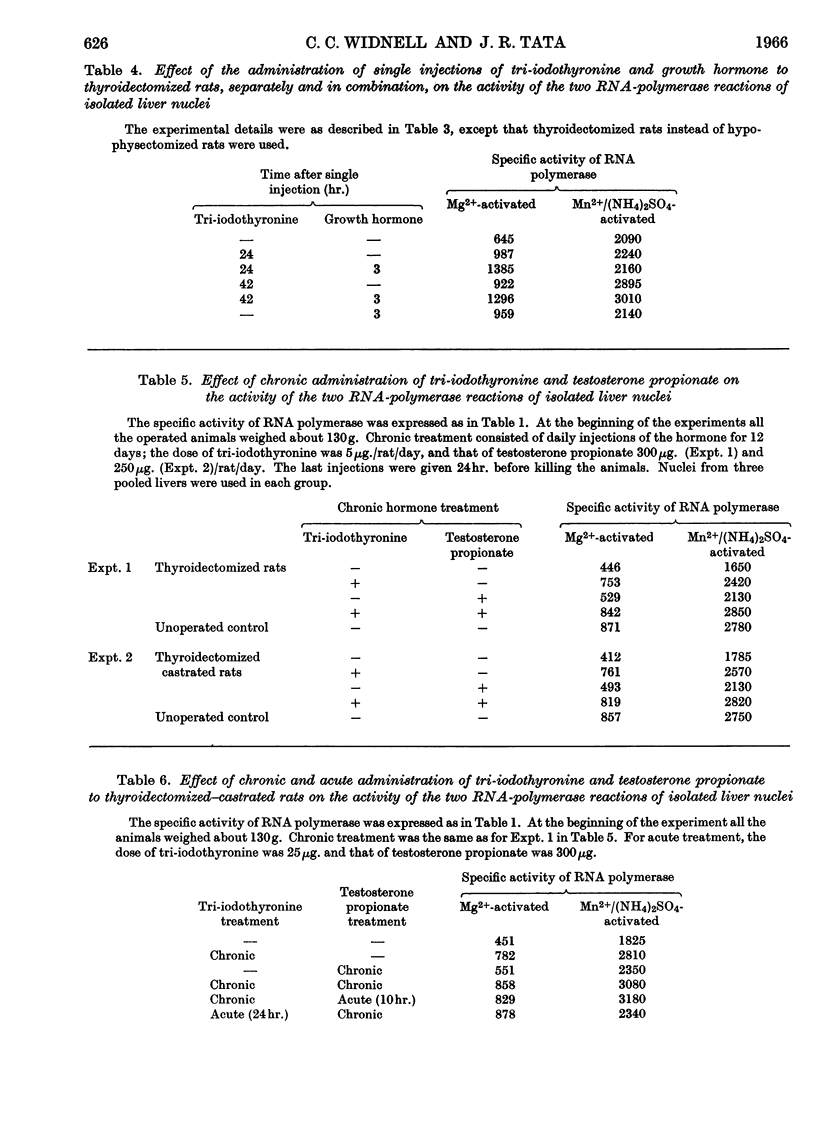
1. The stimulations of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in isolated rat-liver nuclei by thyroid hormone, human growth hormone and testosterone are compared. 2. Single or multiple administrations of growth-promoting doses of tri-iodo-l-thyronine, human growth hormone and testosterone stimulate the Mg2+-activated RNA-polymerase reaction in nuclei from thyroidectomized, hypophysectomized and castrated rats respectively. The magnitude of stimulation was proportional to the degree of enhancement of liver growth by each hormone. After a single injection, the latent period preceding the stimulation was 1, 2 and 10hr. for growth hormone, testosterone and tri-iodothyronine respectively. The time-course of stimulation of enzyme activity and the synthesis of rapidly labelled nuclear RNA in vivo were also different for each hormone. 3. Growth hormone administration failed to stimulate the Mn2+/ammonium sulphate-activated RNA-polymerase reaction. Thyroid hormone and testosterone, however, stimulated it but the effect was less pronounced and occurred several hours later than that observed for the Mg2+-activated RNA-polymerase reaction. 4. In combination experiments, hypophysectomized or the thyroidectomized rats were given growth hormone or tri-iodothyronine in a single or repeated doses at levels that produced the maximum stimulation of Mg2+-activated RNA-polymerase activity. Taking into account the different latent period for each hormone, a single administration of the second hormone caused an additional stimulation of the enzyme activity. Similar additive effects were observed in thyroidectomized–castrated rats after treatment with tri-iodothyronine and testosterone. The magnitude of the additional stimulation caused by the administration of the second hormone was compatible with the capacity of that hormone to promote liver growth in rats deprived of it. 5. It is concluded that, although these hormones have some similar effects, the regulation of nuclear RNA synthesis may be mediated via different routes for each hormone.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANSOME E. D., CHARGAFF E. SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS IN THE ADRENAL CORTEX: EARLY EFFECTS OF ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 11;91:180–182. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSCH S., CHAMBON P., MANDEL P., WEILL J. D. The effect of partial hepatectomy on the ribonucleic acid polymerase of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:255–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTAROW A., WILLIAMS T. L., MELNICK I., PASCHKIS K. E. Influence of acetylaminofluorene, growth hormone, testosterone, and hypothyroidism on incorporation of uracil-2-C14 in liver RNA in the rat. Cancer Res. 1958 Aug;18(7):818–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GESCHWIND I., LI C. H., EVANS H. M. The partition of liver nucleic acids after hypophysectomy and growth hormone treatment. Arch Biochem. 1950 Aug;28(1):73–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORSKI J. EARLY ESTROGEN EFFECTS ON THE ACTIVITY OF UTERINE RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:889–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANCOCK R. L., ZELIS R. F., SHAW M., WILLIAMS-ASHMAN H. G. Incorporation of ribonucleoside triphosphates into ribonucleic acid by nuclei of the prostate gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 22;55:257–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90967-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. H., Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Sequential stimulations by oestrogen of nuclear RNA synthesis and DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activities in rat uterus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 6;108(1):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWAMOTO T., MORIYAMA A., TETSUKA T., MIURA Y. Intracellular transfer of nucleric acids. II. effect of hormones on ribonucleic acid metabolism in rat liver cells. J Biochem. 1963 May;53:408–415. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEY F. T., KULL F. J. HYDROCORTISONE-STIMULATED SYNTHESIS OF NUCLEAR RNA IN ENZYME INDUCTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:493–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCHAKIAN C. D. Comparison of protein anabolic property of various androgens in the castrated rat. Am J Physiol. 1950 Jan;160(1):53–61. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.160.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCHAKIAN C. D., HARRISON D. G. Regulation of nucleic acid synthesis by androgens. Endocrinology. 1962 Jan;70:99–108. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER A. The effect of hyophysectomy and growth-hormone treatment of the rat on the incorporation of amino acids into isolated liver ribosomes. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0810292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER A. The effect of hypophysectomy of the rat and of treatment with growth hormone on the incorporation in vivo of radioactive amino acids into the proteins of subcellular fractions of rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:462–471. doi: 10.1042/bj0740462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER A. The effect of hypophysectomy of the rat and of treatment with growth hormone on the incorporation of amino acids into liver proteins in a cell-free system. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:61–71. doi: 10.1042/bj0730061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner A. Regulation of the rate of synthesis of messenger ribonucleic acid by growth hormone. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0920449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHELS R., CASON J., SOKOLOFF L. Thyroxine: effects on amino acid incorporation into protein in vivo. Science. 1963 Jun 28;140(3574):1417–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3574.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., CHANGEUX J. P., JACOB F. Allosteric proteins and cellular control systems. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:306–329. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE R. J., HAMILTON T. H. ESTROGEN-INDUCED FORMATION OF UTERINE RIBOSOMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:439–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN D. B., FREEMAN K. B., TATA J. R. THE STIMULATION BY TREATMENT IN VIVO WITH TRI-IODOTHYRONINE OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN BY ISOLATED RAT-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:628–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0940628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAFER W. G., MUHLER J. C. Endocrine influences upon the salivary glands. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Mar 29;85:215–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb49960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON M. E., ASLING C. W., EVANS H. M. Some endocrine influences on skeletal growth and differentiation. Yale J Biol Med. 1950 Sep;23(1):1–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALWAR G. P., PANDA N. C., SARIN G. S., TOLANI A. J. Effect of growth hormone on ribonucleic acid metabolism. l. Incorporation of radioactive phosphate into ribonucleic acid fractions of rat liver. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:173–175. doi: 10.1042/bj0820173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R., ERNSTER L., LINDBERG O., ARRHENIUS E., PEDERSEN S., HEDMAN R. The action of thyroid hormones at the cell level. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86:408–428. doi: 10.1042/bj0860408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUKADA K., LIEBERMAN I. SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID BY LIVER NUCLEAR AND NUCLEOLAR PREPARATIONS AFTER PARTIAL HEPATECTOMY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2952–2956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawler G. P., Gupta S. L., Gros F. Effect of growth hormone on ribonucleic acid metabolism. 3. Nature and characteristics of nuclear subfractions stimulated by hormone treatment. Biochem J. 1964 Jun;91(3):565–572. doi: 10.1042/bj0910565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEILL J. D., BUSCH S., CHAMBON P., MANDEL P. The effect of estradiol injections upon chicken liver nuclei ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jan 31;10:122–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKS W. D., KENNEY F. T. RNA SYNTHESIS IN RAT SEMINAL VESICLES: STIMULATION BY TESTOSTERONE. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1346–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDNELL C. C., TATA J. R. EVIDENCE FOR TWO DNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE ACTIVITIES IN ISOLATED RAT-LIVER NUCLEI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:531–533. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS-ASHMAN H. G., LIAO S., HANCOCK R. L., JURKOWITZ L., SILVERMAN D. A. TESTICULAR HORMONES AND THE SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEINS IN THE PROSTATE GLAND. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1964;20:247–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G., MUNRO A. J. AN INFLUENCE OF INSULIN ON THE SYNTHESIS OF A RAPIDLY LABELED RNA BY ISOLATED RAT DIAPHRAGM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:918–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


