Abstract
1. Interactions of proteins with neutral polysaccharides and such polyacids as polygalacturonic acid, chondroitin sulphate, RNA and DNA in a two-phase system composed of phenol and aqueous buffers in the pH range 1·5–10 were studied. 2. Analysis of the products of the interaction was facilitated by the absolute preference of the proteins studied for the phenol-rich phase at all pH values. 3. The polyacids, on the other hand, in the absence of interactions were recovered mainly from the aqueous phases. 4. The interaction, the extent of which was mainly determined by the pH-dependent ionization state of the reacting partners, followed the patterns of antigen–antibody interactions with a well-defined equivalence point (maximum point of precipitation) and with the formation of soluble complexes. 5. The soluble complexes formed below the equivalence point were composed of proteins with small amounts of polyacids attached, and so passed into the phenol-rich phase; those formed above the maximum precipitation point were polyacidic in character and found in the aqueous phases. 6. Glycoproteins, with small amounts of covalently linked sugar residues, passed quantitatively into the phenol-rich phases. 7. The possibilities of developing a method for the analysis of glycoproteins and other applications are discussed.
Full text
PDF

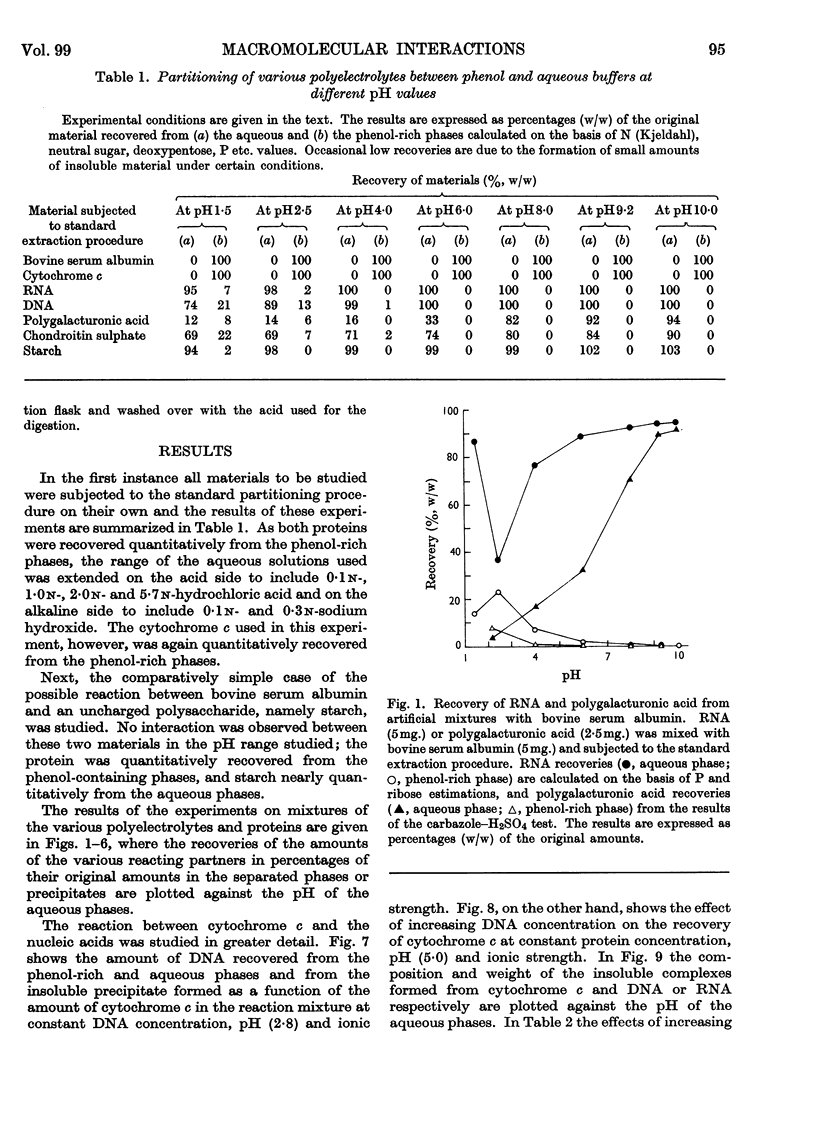
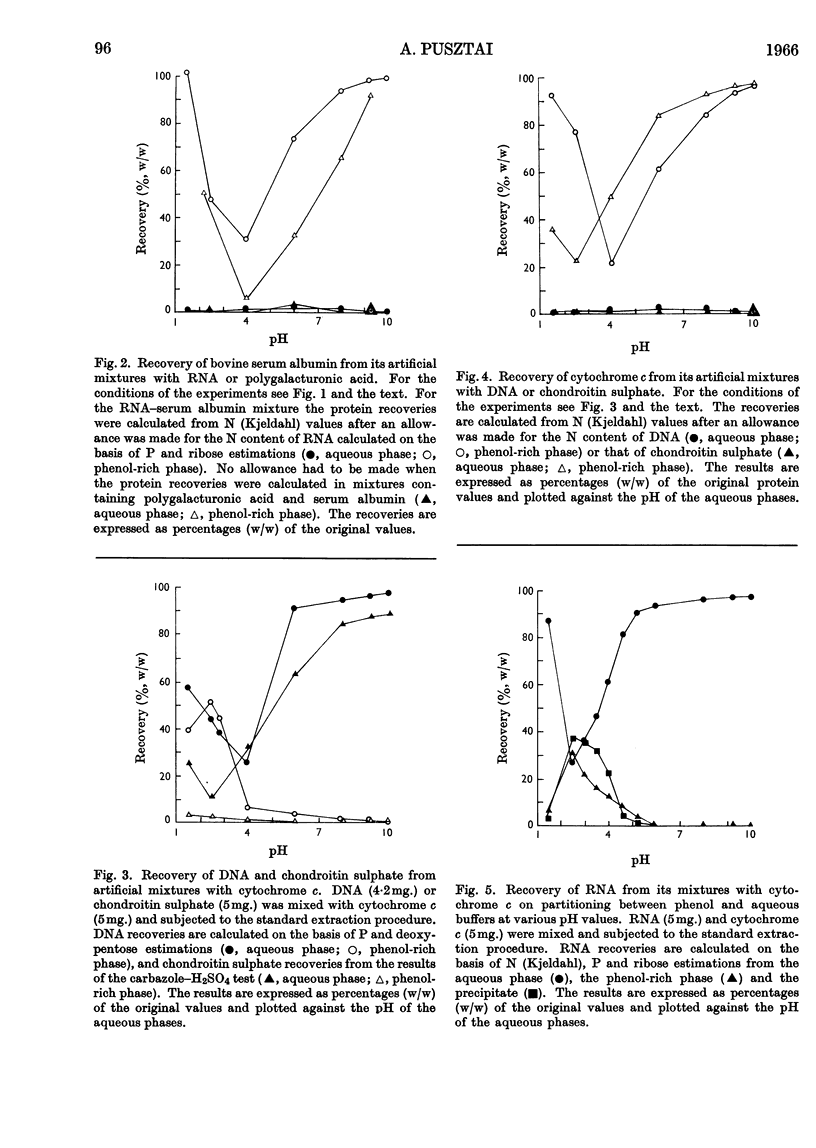
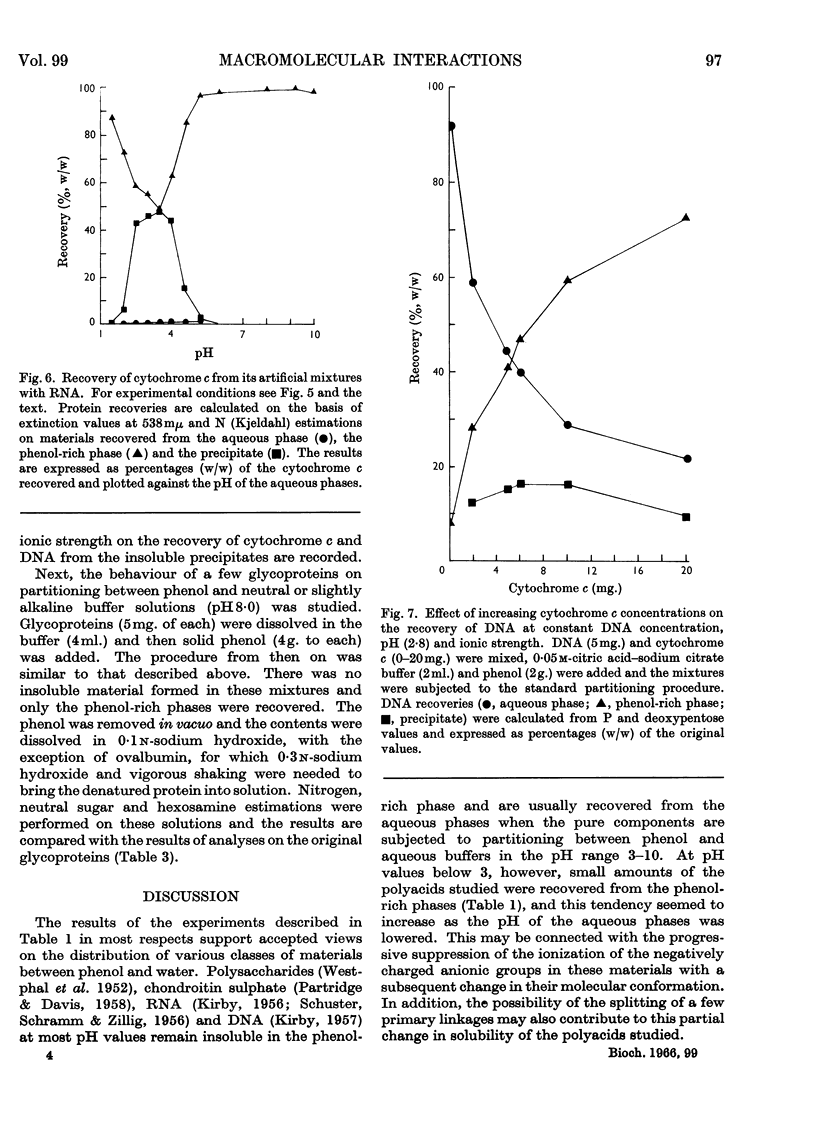
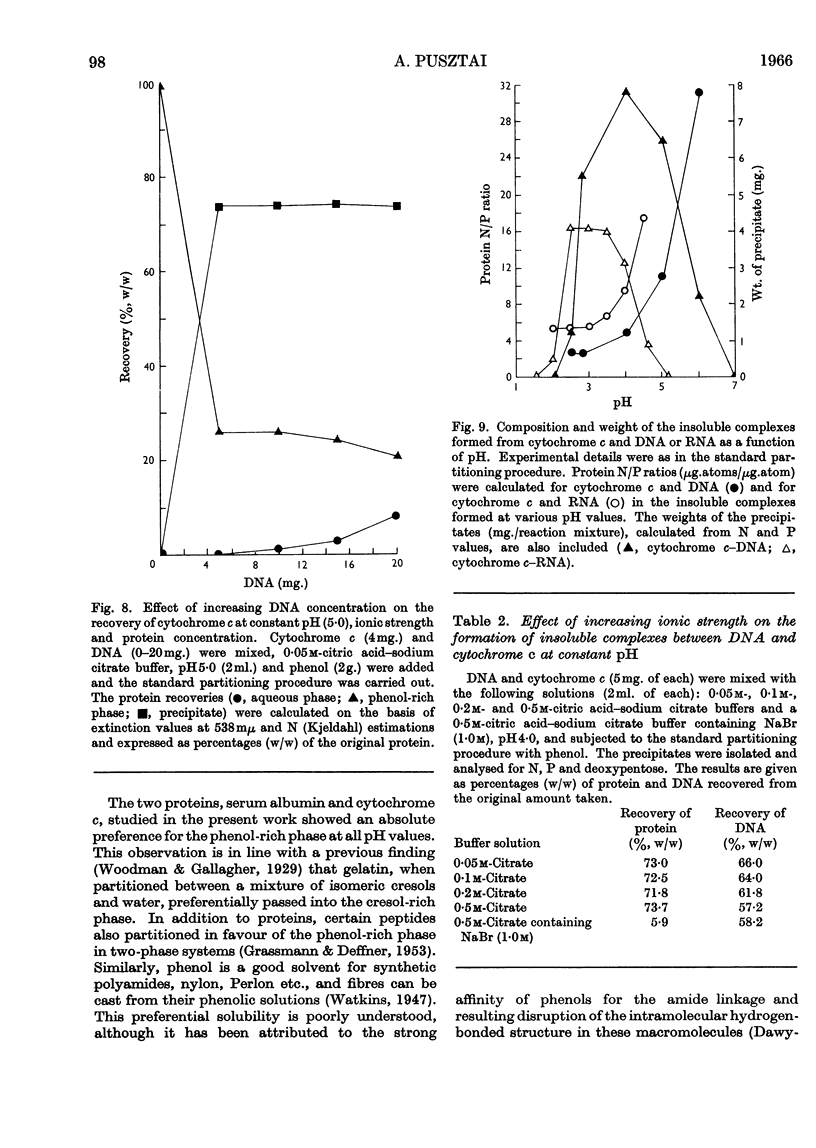


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON A. J. Some studies on the occurrence of sialic acid in human cartilage. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:399–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0780399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON A. J. Some studies on the relationship between sialic acid and the mucopolysaccharide-protein complexes in human cartilage. Biochem J. 1962 Feb;82:372–381. doi: 10.1042/bj0820372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON A. J. THE EFFECT OF CHONDROMUCOPROTEIN ON THE SOLUBILITY AND PEROXIDATIC PROPERTIES OF HAEMOGLOBIN AND METHAEMALBUMIN IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION AND BLOOD. Biochem J. 1965 Feb;94:401–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0940401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON A. J. THE FORMATION OF CHONDROMUCOPROTEIN-FIBRINOGEN AND CHONDROMUCOPROTEIN-BETA-LIPOPROTEIN COMPLEXES. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:460–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0880460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Matheson N. A., Synge R. L., Youngson M. A. New procedures for isolating polypeptides and proteins from tissues. Metabolic incorporation of L-[14C]valine into fractions of intermediate molecular weight in broad-bean (Vicia faba L.) leaves. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):91–105. doi: 10.1042/bj0910091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattsten I., Synge R. L., Watt W. B. A search for O-polypeptidyl-ribonucleic acids in rabbit-reticulocyte ribosomes by electrophoresis in phenol-acetic acid-water systems. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):678–688. doi: 10.1042/bj0970678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAMP J. R., BERNIER G. M., PUTNAM F. W. THE SOURCE OF THE APPARENT CARBOHYDRATE CONTENT OF BENCE-JONES PROTEINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:149–155. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper E. A. On the Relations of Phenol and Meta-Cresol to Proteins; A Contribution to our knowledge of the Mechanism of Disinfection. Biochem J. 1912;6(4):362–387. doi: 10.1042/bj0060362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A., SCHRAMM G. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid from tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1956 Apr 14;177(4511):702–703. doi: 10.1038/177702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acids; evidence on the nature of bonds between deoxyribonucleic acid and protein. Biochem J. 1957 Jul;66(3):495–504. doi: 10.1042/bj0660495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of ribonucleic acids from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):405–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0640405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., FROHWIRT N., WIENER E. A study of the cytochrome c haemochromogen. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):559–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0710559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., King H. K. Studies in immunochemistry: 7. The isolation from hog gastric mucin of the polysaccharide-amino acid complex possessing blood group A specificity. Biochem J. 1943;37(5):640–651. doi: 10.1042/bj0370640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Partridge S. M. Studies in immunochemistry: The fractionation and nature of antigenic material isolated from Bact. dysenteriae (Shiga). Biochem J. 1940 Feb;34(2):169–191. doi: 10.1042/bj0340169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
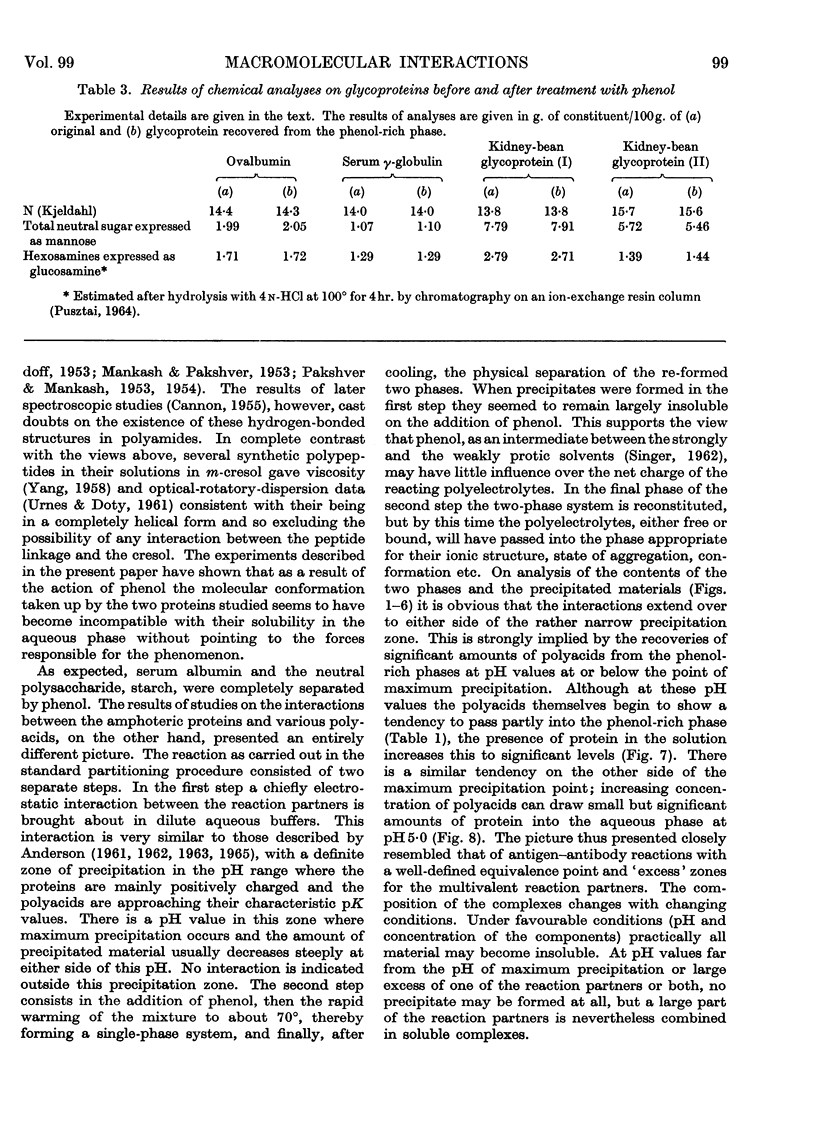
- PUSZTAI A. HEXOSAMINES IN THE SEEDS OF HIGHER PLANTS (SPERMATOPHYTES). Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1328–1329. doi: 10.1038/2011328b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUSZTAI A. STUDIES ON THE EXTRACTION OF NITROGENOUS AND PHOSPHORUS-CONTAINING MATERIALS FROM THE SEEDS OF KIDNEY BEANS (PHASEOLUS VULGARIS). Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:611–616. doi: 10.1042/bj0940611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. W. A SIMPLE METHOD FOR PREPARING ANTIGENIC SUBSTANCES FROM THE TYPHOID BACILLUS. Science. 1940 Aug 16;92(2381):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.92.2381.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGAS D. A., OSGOOD E. E. Purification and properties of the phytohemagglutinin of Phaseolus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1955 Feb;212(2):607–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URNES P., DOTY P. Optical rotation and the conformation of polypeptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1961;16:401–544. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


