Abstract
1. A glycerol teichoic acid has been extracted from cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus B65 and its structure examined. 2. Trichloroacetic acid-extractable teichoic acid accounted for 68% of the total cell-wall phosphorus and residual material could be hydrolysed to a mixture of products including those characteristic of glycerol teichoic acids. 3. The extracted polymer is composed of glycerol, phosphoric acid, d-glucose and d-alanine. 4. Hydrolysis of the polymer with alkali gave glycerol, 1-O-α-d-glucopyranosylglycerol and its monophosphates, glycerol mono- and di-phosphate, as well as traces of a glucosyldiglycerol triphosphate and a glucosylglycerol diphosphate. 5. The teichoic acid is a polymer of 18 or 19 glycerol phosphate units having α-d-glucopyranosyl residues attached to position 1 of 14 or 15 of the glycerol residues. 6. The glycerol residues are joined by phosphodiester linkages involving positions 2 and 3 in each glycerol. 7. d-Alanine is in ester linkage to the hydroxyl group at position 6 of approximately half of the glucose residues. 8. One in every 13 or 12 polymer molecules bears a phosphomonoester group on position 3 of a glucose residue, the possible significance of which in linkage of the polymer to other wall constituents is discussed.
Full text
PDF


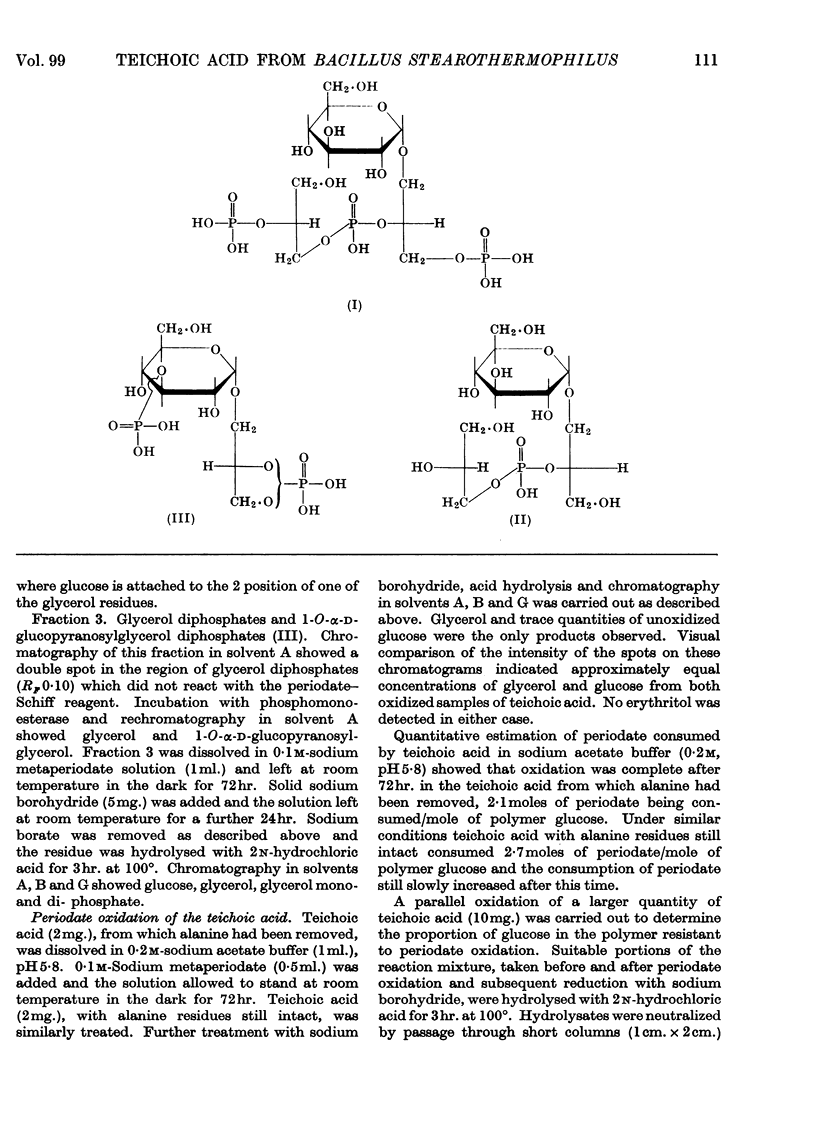

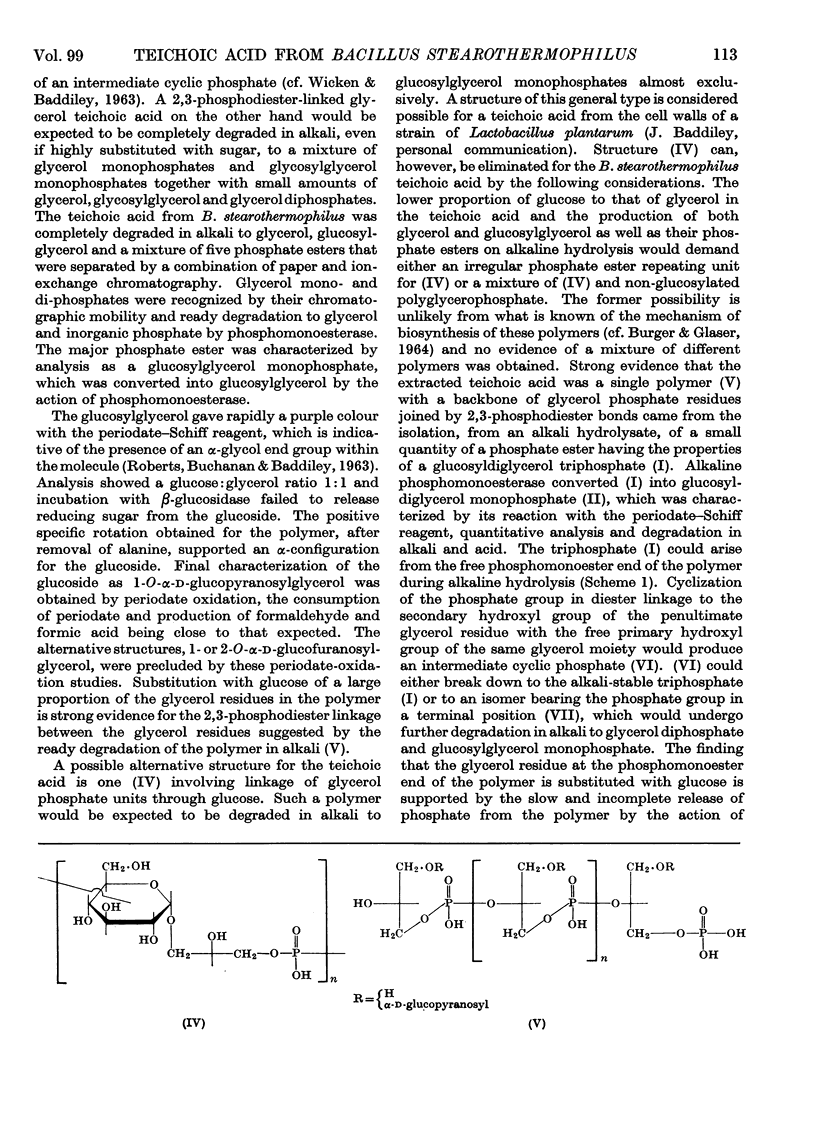
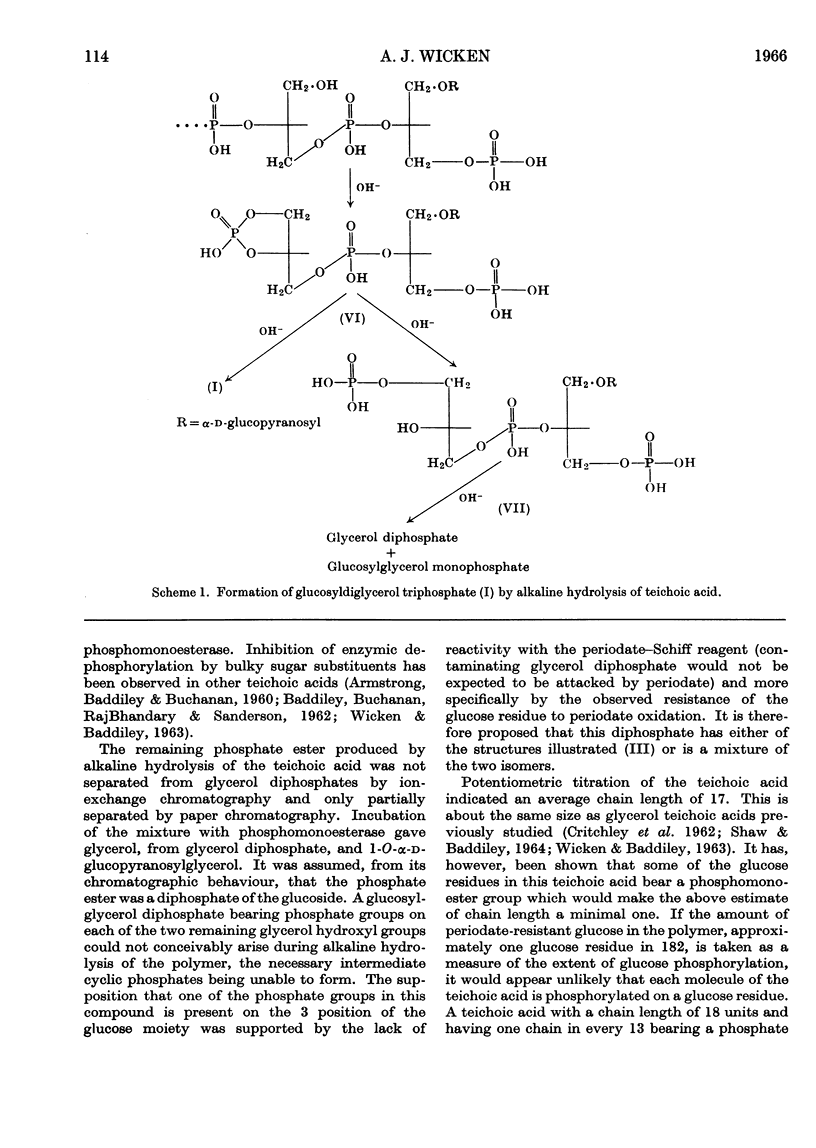


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHIBALD A. R., ARMSTRONG J. J., BADDILEY J., HAY J. B. Teichoic acids and the structure of bacterial walls. Nature. 1961 Aug 5;191:570–572. doi: 10.1038/191570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG J. J., BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G. Further studies on the teichoic acid from Bacillus subtilis walls. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:254–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0800254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG J. J., BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G. Structure of the ribitol teichoic acid from the walls of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:610–621. doi: 10.1042/bj0760610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G., RAJBHANDARY U. L., SANDERSON A. R. Teichoic acid from the walls of Staphylococcus aureus H. Structure of the N-acetylglucosaminyl-ribitol residues. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:439–448. doi: 10.1042/bj0820439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. I. POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3168–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M. M. The enzymic glucosylation of polyglycerophosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:495–497. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRITCHLEY P., ARCHIBALD A. R., BADDILEY J. The intracellular teichoic acid from Lactobacillus arabinosus 17-5. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:420–431. doi: 10.1042/bj0850420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Kelemen M. V., Baddiley J. The glycerol teichoic acid from the walls of Staphylococcus albus N.T.C.C. 7944. Biochem J. 1963 Feb;86(2):213–225. doi: 10.1042/bj0860213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAHAN D. J., OLLEY J. N. Chemical nature of monophosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):813–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELEMEN M. V., BADDILEY J. Structure of the intracellular glycerol teichoic acid from Lactobacillus casei A.T.C.C. 7469. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:246–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0800246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J., GARRETT A. J. THE INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MUCOPEPTIDE AND RIBITOL TEICHOIC ACID FORMATION AS SHOWN BY THE EFFECT OF INHIBITORS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:231–243. doi: 10.1042/bj0960231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Buchanan J. G., Baddiley J. The specific substance from Pneumococcus type 34 (41). The structure of a phosphorus-free repeating unit. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):1–7. doi: 10.1042/bj0880001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., GHUYSEN J. M. ON THE LINKAGE BETWEEN TEICHOIC ACID AND THE GLYCOPEPTIDE IN THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:418–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Baddiley J. The teichoic acid from the walls of Lactobacillus buchneri N.C.I.B. 8007. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj0930317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKEN A. J., BADDILEY J. Structure of intracellular teichoic acids from group D streptococci. Biochem J. 1963 Apr;87:54–62. doi: 10.1042/bj0870054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG F. E., TIPPER D. J., STROMINGER J. L. AUTOLYSIS OF CELL WALLS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. MECHANISM AND POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP TO COMPETENCE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:PC3600–PC3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


