Abstract
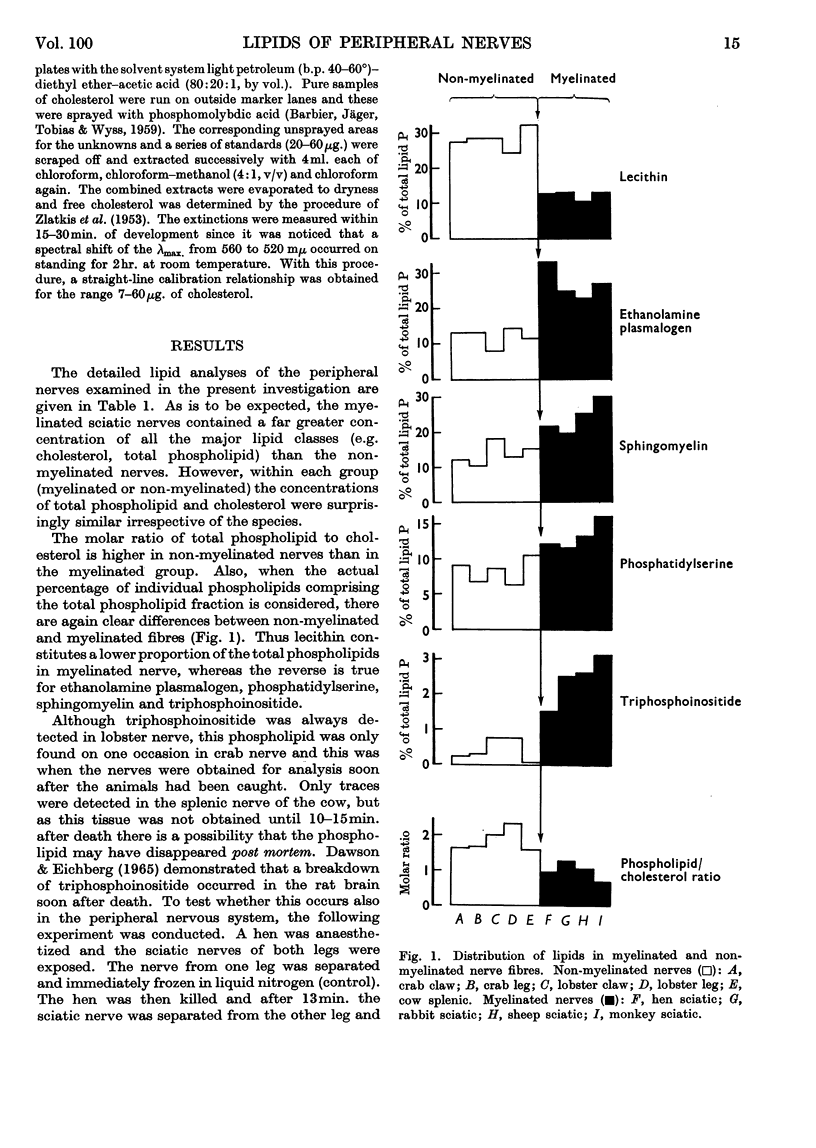
1. A detailed lipid analysis of the peripheral nerves of the crab (claw, leg), lobster (claw, leg), cow (splenic), hen, rabbit, sheep and monkey (sciatic) is presented. 2. The so-called `myelinic lipids', cholesterol, sphingomyelin, ethanolamine plasmalogen and phosphatidylserine, occurred in the highest proportion in the lipids of vertebrate myelinated nerves, whereas the percentage of lecithin was greatest in the lipids of non-myelinated nerve fibres of both vertebrates and invertebrates. 3. Triphosphoinositide was found in all nerves examined and its concentration in the extracted lipids supports the concept that it is predominantly localized in the myelin sheath. 4. In crustacean nerve 12–14% of the phospholipids was in the form of alkyl ether phospholipids, which in the lobster were approximately half choline-containing and half ethanolamine-containing.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADUCCI L., PAZZAGLI A., PESSINA G. The relation of proteolipids and phosphatidopeptides to tissue elements in the bovine nervous system. J Neurochem. 1962 Sep-Oct;9:509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANSELL G. B., SPANNER S. The occurence of a long-chain ether analogue of phosphatidylethanolamine in brain tissue. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:56–64. doi: 10.1042/bj0880056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D. PHYSICAL STRUCTURE AND BEHAVIOR OF LIPIDS AND LIPID ENZYMES. Adv Lipid Res. 1963;1:65–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9937-5.50008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLEY W., SOBRINHO-SIMOES M., NOTTON B. M., MONTESI G. The anaerobic metabolism of citrate in rat liver. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):26–32. doi: 10.1042/bj0710026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY J. F., CEVALLOS W. H., WADE R. R., Jr LIPID CLASS AND FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF INTACT PERIPHERAL NERVE AND DURING WALLERIAN DEGENERATION. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jun;42:492–500. doi: 10.1007/BF02540090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKERHOFF H. BREAKDOWN OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN MILD ALKALINE HYDROLYSIS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS F. D. STUDIES ON PHOSPHOLIPIDS. 9. THE COMPOSITION OF RAT-LIVER LECITHINS. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:319–324. doi: 10.1042/bj0880319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUZNER M. L., DAVISON A. N., GREGSON N. A. CHEMICAL AND METABOLIC STUDIES OF RAT MYELIN OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:86–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAS M. L., MYERS D. E., CRANE F. L. PROTEOLIPIDS. II. ISOLATION OF A PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE REQUIRED FOR LIPID-CYTOCHROME C FORMATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 2;84:618–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., LINDSAY D. B. The phospholipids of the erythrocyte 'ghosts' of various species. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:226–230. doi: 10.1042/bj0770226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. 'Phosphatido-peptide'-like complexes formed by the interaction of calcium triphosphoinositide with protein. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):134–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0970134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Eichberg J. Diphosphoinositide and triphosphoinositide in animal tissues. Extraction, estimation and changes post mortem. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):634–643. doi: 10.1042/bj0960634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Dawson R. M. Polyphosphoinositides in myelin. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):644–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0960644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Whittaker V. P., Dawson R. M. Distribution of lipids in subcellular particles of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):91–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0920091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Finean J. B. The lipid composition of myelin from brain and peripheral nerve. J Neurochem. 1965 Aug;12(8):729–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., CASALS J., POPE A., MEATH J. A., LEBARON F. N., LEES M. Chemistry of myelin development. Prog Neurobiol. 1959;4:122–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geren B. B., Schmitt F. O. THE STRUCTURE OF THE SCHWANN CELL AND ITS RELATION TO THE AXON IN CERTAIN INVERTEBRATE NERVE FIBERS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Sep;40(9):863–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.9.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACK M. H. Analysis of lipids by spot tests on filter-paper disk chromatograms. Biochem J. 1953 Jul;54(4):602–605. doi: 10.1042/bj0540602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORHAMMER L., WAGNER H., RICHTER G. Zur papierchromatographischen Auftrennung von Phosphatiden. I. Biochem Z. 1959;331(3):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., McNabb A. R., Rossiter R. J. Concentration of lipids in the brain of infants and adults. Biochem J. 1949;44(4):494–498. doi: 10.1042/bj0440494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., McNabb A. R., Rossiter R. J. Lipids of normal brain. Biochem J. 1948;43(4):573–577. doi: 10.1042/bj0430573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., McNabb A. R., Rossiter R. J. Lipids of peripheral nerve. Biochem J. 1948;43(4):578–580. doi: 10.1042/bj0430578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERR S. E., KFOURY G. A., HADDAD F. S. A COMPARISON OF THE POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDE IN HUMAN AND OX BRAIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 5;84:461–463. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N., MCDONALD C. P., RAMARAO B. S. THE AMOUNTS AND DISTRIBUTION OF FREE INOSITOL AND FREE AND PROTEIN-BOUND PHOSPHOINOSITIDES IN BRAIN TISSUES. J Neurochem. 1963 Oct;10:677–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWDEN J. A., WOLFE L. S. STUDIES ON BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. 3. EVIDENCE FOR THE LOCATION OF GANGLIOSIDES SPECIFICALLY IN NEURONES. Can J Biochem. 1964 Nov;42:1587–1594. doi: 10.1139/o64-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Staples D. A. Chromatographic separation of brain lipids: cerebroside and sulphatide. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78(1):179–185. doi: 10.1042/bj0780179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON W. T., AUTILIO L. A. THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF BOVINE CNS MYELIN. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:77–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. O., SCHULMAN J. H. BINDING OF METAL IONS TO MONOLAYERS OF LECITHINS, PLASMALOGEN, CARDIOLIPIN, AND DICETYL PHOSPHATE. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L., THORIN H. Isolation of "kepalin B" from cerebral lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:371–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone W. E. The effects of anaesthetics and of convulsants on the lactic acid content of the brain. Biochem J. 1938 Nov;32(11):1908–1918. doi: 10.1042/bj0321908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON G. A., Jr, HANAHAN D. J. IDENTIFICATION OF ALPHA-GLYCERYL ETHER PHOSPHOLIPIDS AS MAJOR LIPID CONSTITUENTS IN TWO SPECIES OF TERRESTRIAL SLUG. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2628–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLATKIS A., ZAK B., BOYLE A. J. A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de GIER, VAN DEENEN L. Some lipid characteristics of red cell membranes of various animal species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 May 13;49:286–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


