Abstract
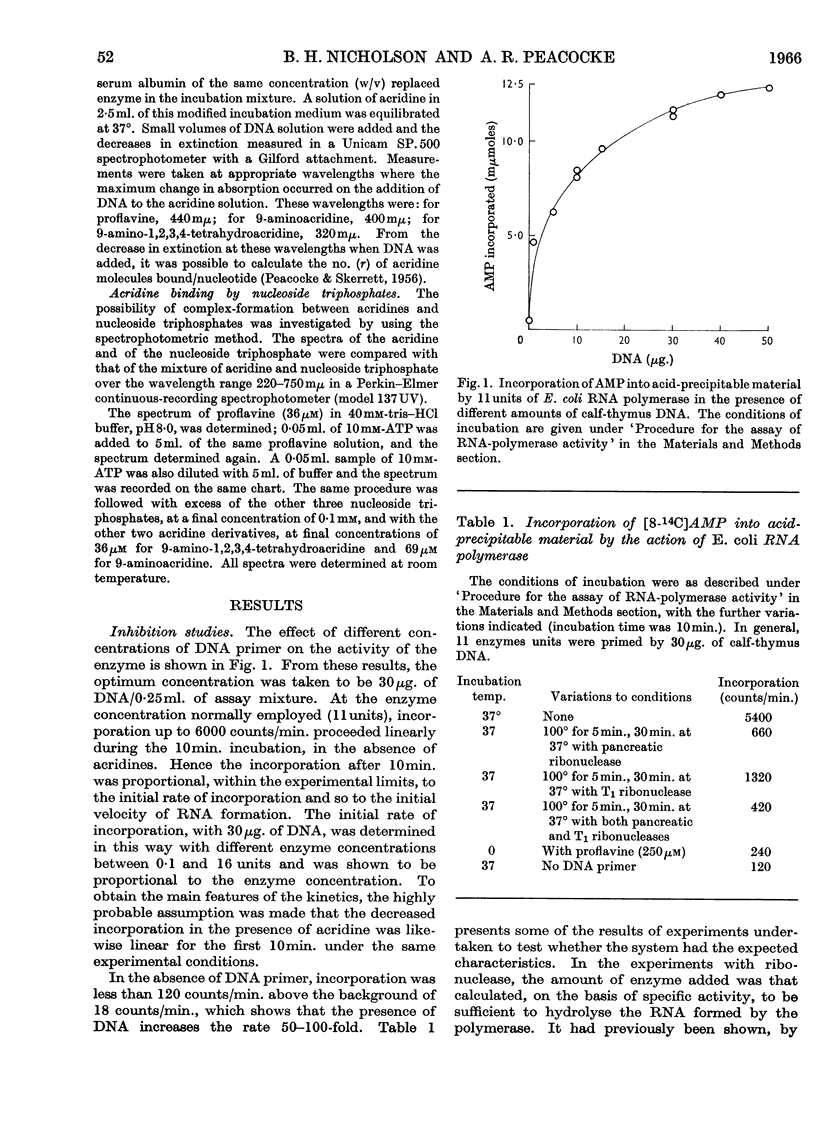
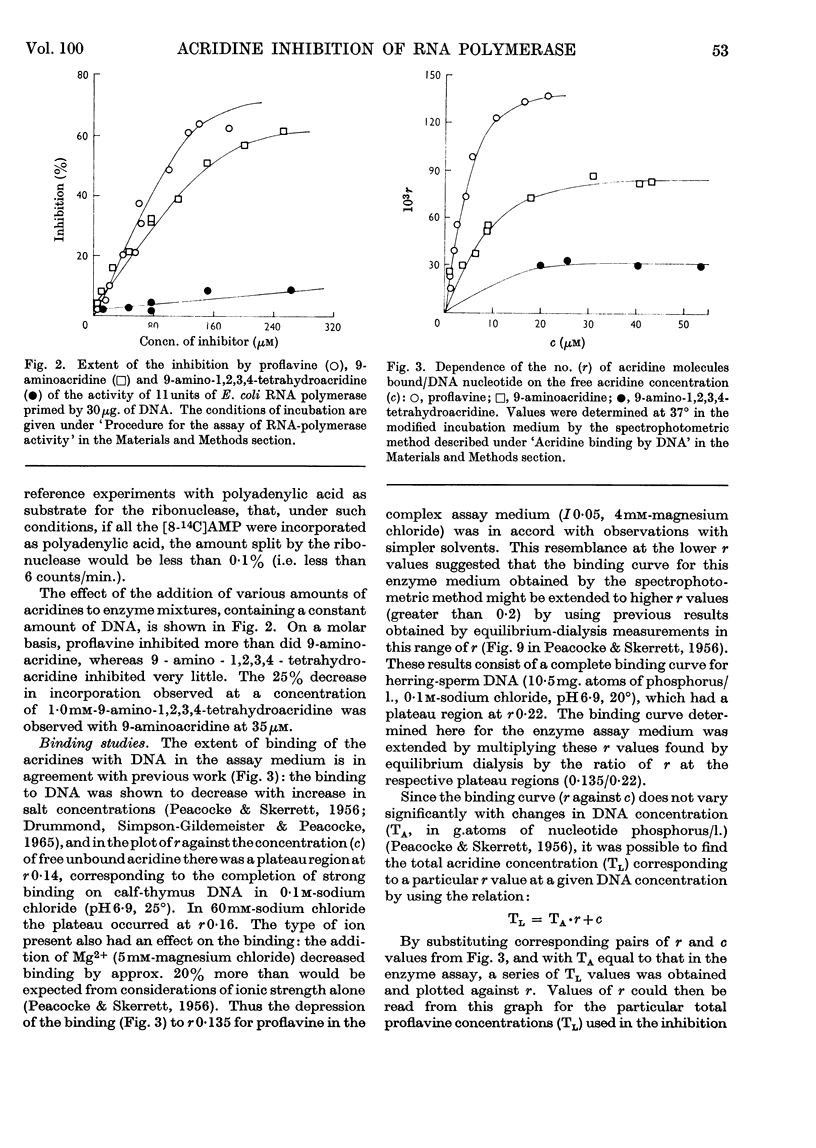
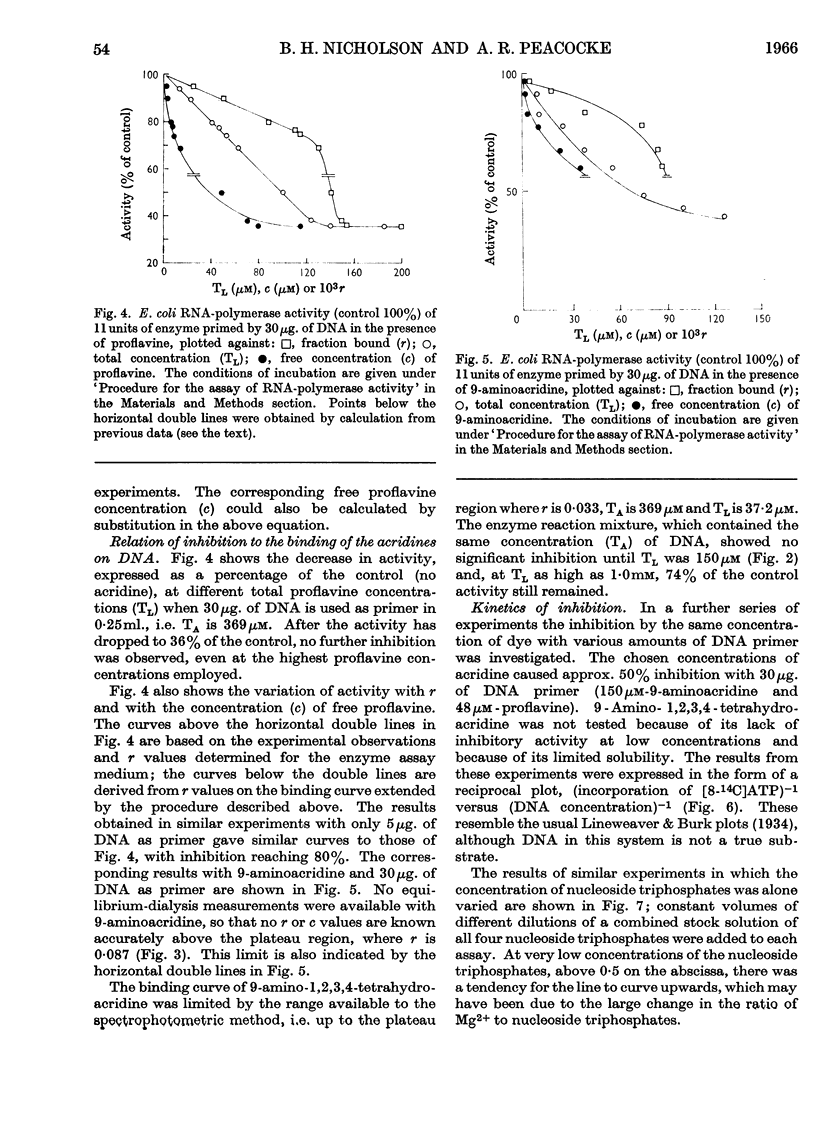
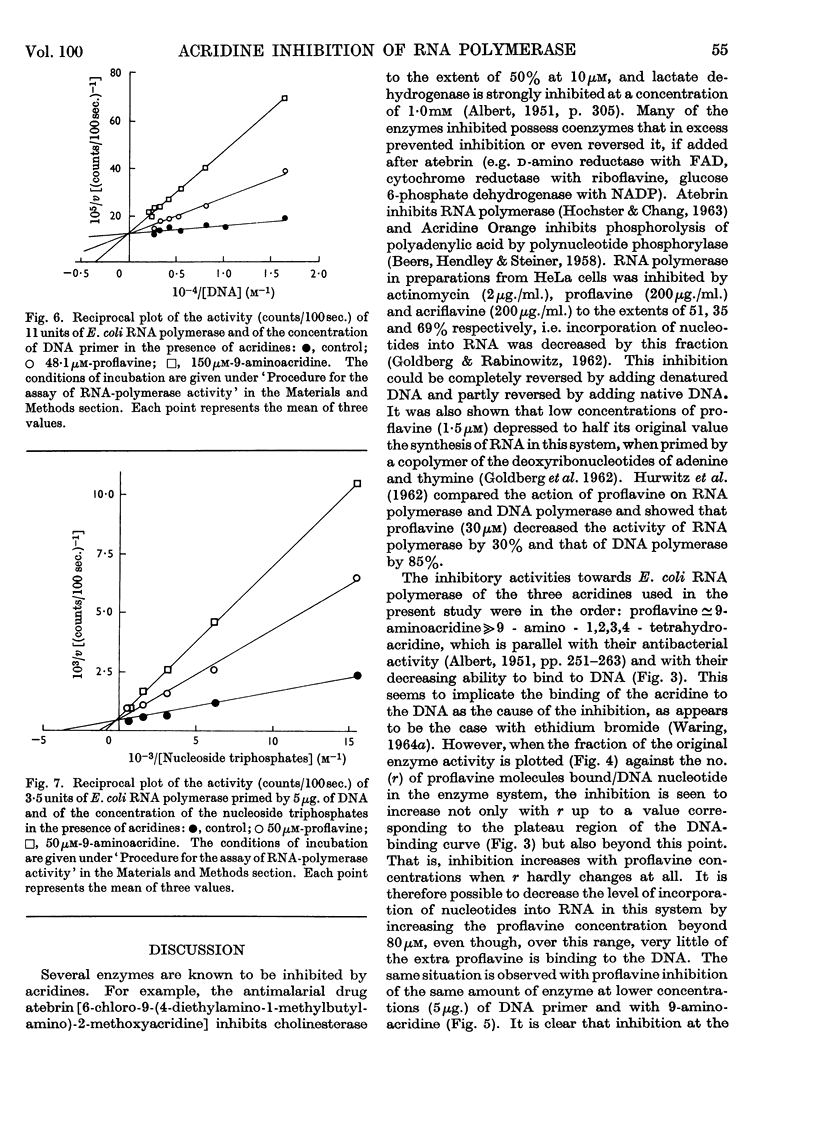
1. The aminoacridines, proflavine (3,6-diaminoacridine) and 9-aminoacridine, and a hydrogenated derivative, 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine, were shown to inhibit in vitro the DNA-primed RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli. The inhibition is strong with both proflavine and 9-aminoacridine, but weak with 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine. 2. The extent to which the three acridines bind to calf-thymus DNA in the enzyme medium was studied spectrophotometrically. The extent of binding decreases in the order: proflavine, 9-aminoacridine, 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine. Some evidence was also obtained for interaction between the nucleoside triphosphate substrates and proflavine or 9-aminoacridine; no such interaction was detectable with 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine. 3. Although the amount of acridine bound to DNA increases with increasing inhibition, a stage is reached where an increase in acridine concentration still causes an increase in inhibition, with practically no increase in the amount bound to DNA. 4. Plots of reciprocal rates against the reciprocal of DNA concentration were linear and had a common intercept when proflavine or 9-aminoacridine was present. Similar relations were obtained when the reciprocal concentration of nucleoside triphosphates was plotted. The observations are interpreted kinetically in terms of a competitive inhibition of the enzyme by proflavine or 9-aminoacridine and of a kinetic role for the DNA analogous to `activation'. 5. This suggests that inhibitory acridine molecules can occupy the sites on the RNA polymerase that are specific for binding the nucleoside triphosphate substrate or the bases of the DNA, when these become accessible during the copying process.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, HENDLEY D. D., STEINER R. F. Inhibition and activation of polynucleotide phosphorylase through the formation of complexes between acridine orange and polynucleotides. Nature. 1958 Jul 26;182(4630):242–244. doi: 10.1038/182242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M. Actionmycin D inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent synthesis of ribonucleic acid. Science. 1962 Apr 27;136(3513):315–316. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3513.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M., REICH E. Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2094–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., FULLER W., REICH E. X-ray diffraction and molecular model building studies of the interaction of actinomycin with nucleic acids. Nature. 1963 May 11;198:538–540. doi: 10.1038/198538b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHSTER R. M., CHANG V. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid synthesis in the crown-gall tumor-inducing organism Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Jul;41:1503–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., FURTH J. J., MALAMY M., ALEXANDER M. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. III. The inhibition of the enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by actinomycin D and proflavin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1222–1230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHIZKY G. W., SOBER H. A. Characterization of the major compounds in ribonuclease TI digests of ribonucleic acid. I. Mono-, di-, and trinucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARING M. J. COMPLEX FORMATION WITH DNA AND INHIBITION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI RNA POLYMERASE BY ETHIDIUM BROMIDE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 22;87:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


