Full text
PDF

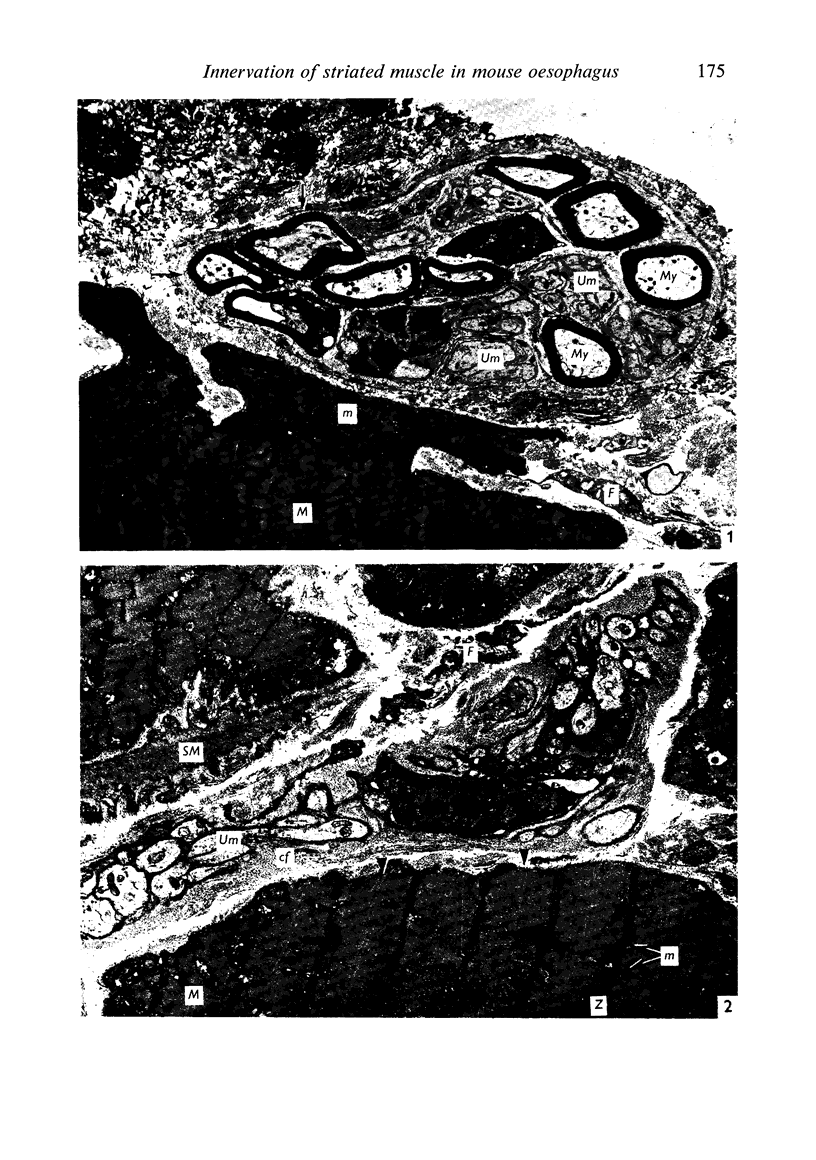

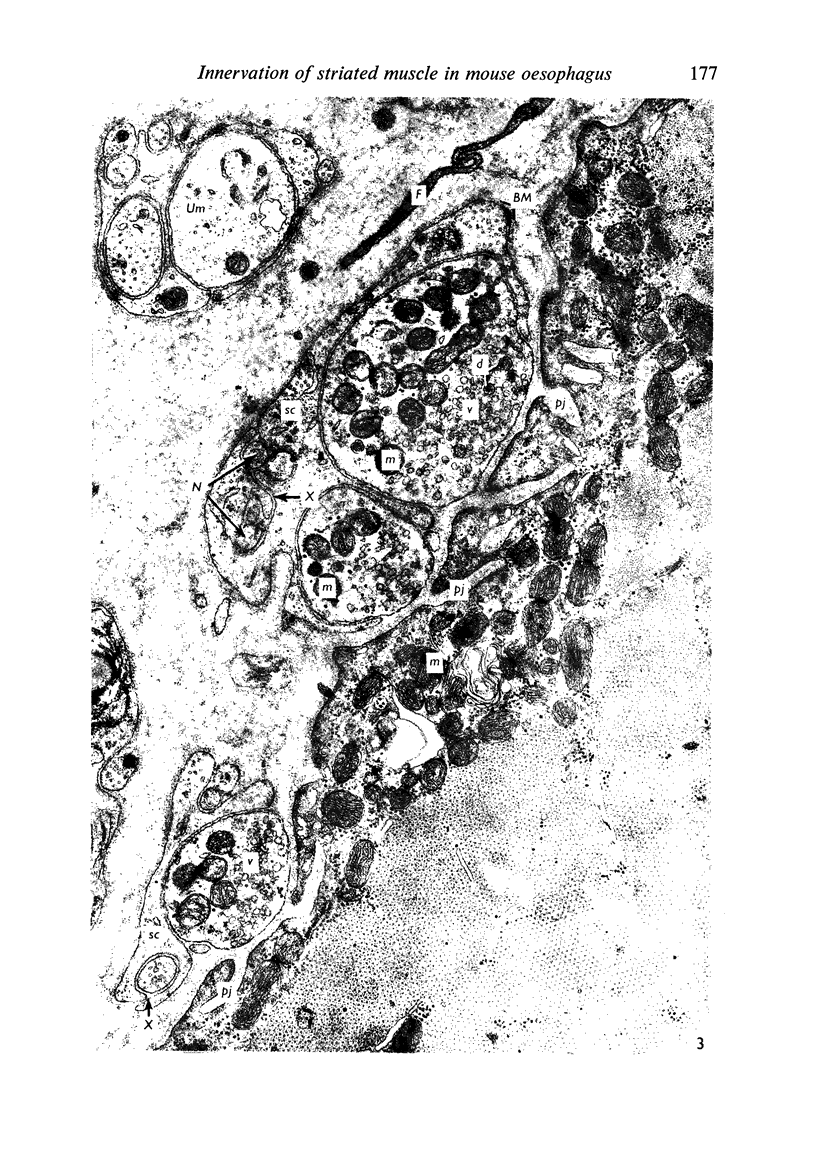

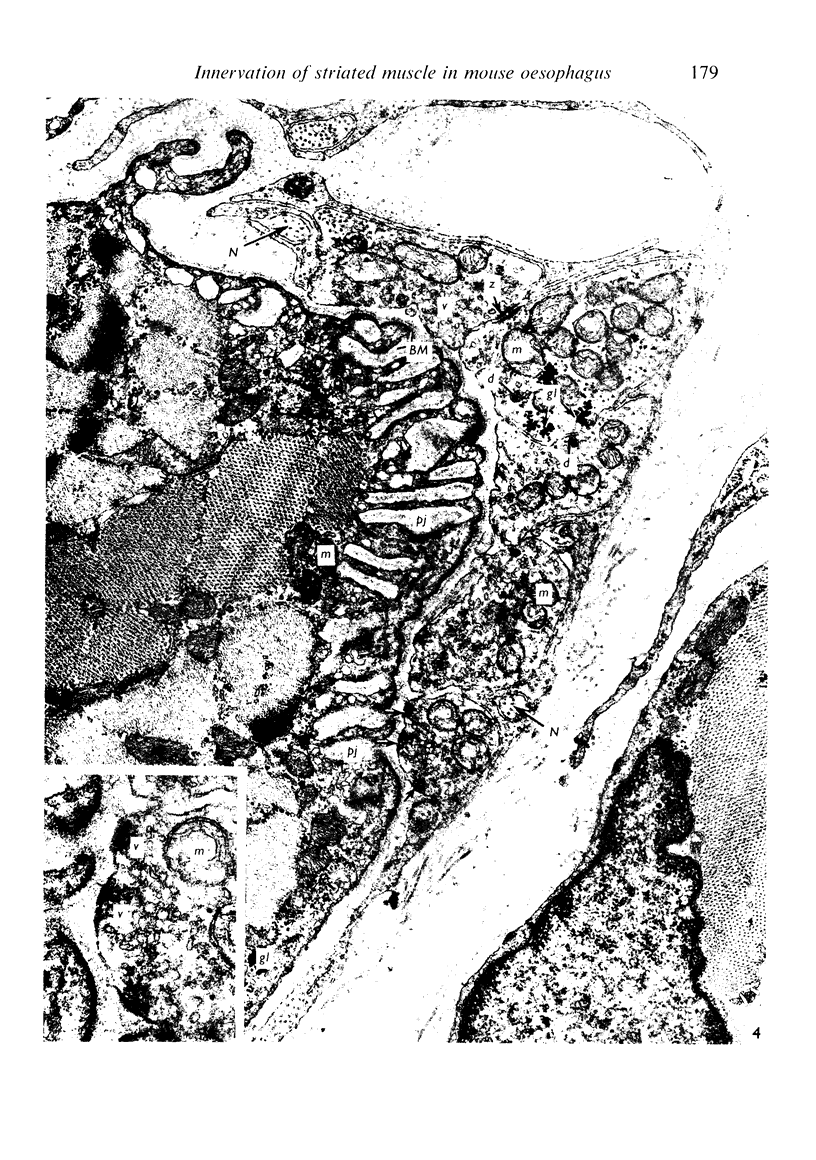





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. E., Johnson A. G., Woolf A. L. The intramuscular nerve endings in dystrophia myotonica--a biopsy study by vital staining and electron microscopy. J Anat. 1969 Jul;105(Pt 1):1–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio S. R., Marsden P. A rapid methylene blue-basic fuchsin stain for semi-thin sections of peripheral nerve and other tissues. J Microsc. 1969;89(1):139–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKS R., HUXLEY H. E., KATZ B. The fine structure of the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:134–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlet A. L. An atypical action of acetylcholine on the striped muscle of the guinea-pig oesophagus. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Apr;53(2):175–180. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlet A. L. The effect of vagal stimulation and eserine on isolated guinea-pig oesophagus. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Apr;53(2):170–174. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE W. V. Structural variations of nerve endings in the striated muscles of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1957 Dec;108(3):445–463. doi: 10.1002/cne.901080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecio A., Califano G. Neurohistological observations on the oesophageal innervation of rabbit. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;83(1):30–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00334736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coërs C. Structure and organization of the myoneural junction. Int Rev Cytol. 1967;22:239–267. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61837-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber H. Uber Struktur und Innervation der quergestreiften Muskulatur des Oesophagus der Ratte. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;91(2):236–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Vertebrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):40–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz P. A., Siegel C. I. Strong MJ, Hendrix TR: Response of the human oesophagus to d-tubocurarine and atropine. Gut. 1970 Jan;11(1):47–50. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWN A. M. THE LOCALIZATION, BY MEANS OF ELECTRICAL STIMULATION, OF THE ORIGIN AND PATH IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF THE MOTOR NERVE FIBRES OF THE RABBITS OESOPHAGUS. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:232–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. The localization, in the nucleus ambiguus of the rabbit, of the cells of origin of motor nerve fibers in the glossopharyngeal nerve and various branches of the vagus nerve by means of retrograde degeneration. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jun;127(2):293–306. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. The nucleus ambiguus of the rabbit. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jun;127(2):307–320. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Scott J. A., Navaratnam V. Localization in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in the rat. J Anat. 1970 Sep;107(Pt 2):197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padykula H. A., Gauthier G. F. The ultrastructure of the neuromuscular junctions of mammalian red, white, and intermediate skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):27–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGER J. F. Electron microscopy of the motor end-plate in rat intercostal muscle. Anat Rec. 1955 May;122(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091220102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGER J. F. The fine structure of neuromuscular synapses of gastrocnemii from mouse and frog. Anat Rec. 1958 Jan;130(1):7–23. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091300103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of a reptilian myoneural junction. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4):381–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROHEN J. Uber den funktionellen Zusammenhang zwischen glatter und quergestreifter Muskulatur im menschlichen Oesophagus. Oesophagusstudien I. Anat Anz. 1955 Nov 23;102(9-14):210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Zacks S. I. Ultrastructure of Schwann and perineural sheaths at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Anat Rec. 1969 Aug;164(4):379–390. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091640401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIEGS O. W. Innervation of voluntary muscle. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jan;33(1):90–144. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACKS S. I., BLUMBERG J. M. Observations on the fine structure and cytochemistry of mouse and human intercostal neuromuscular junctions. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10:517–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]