Abstract
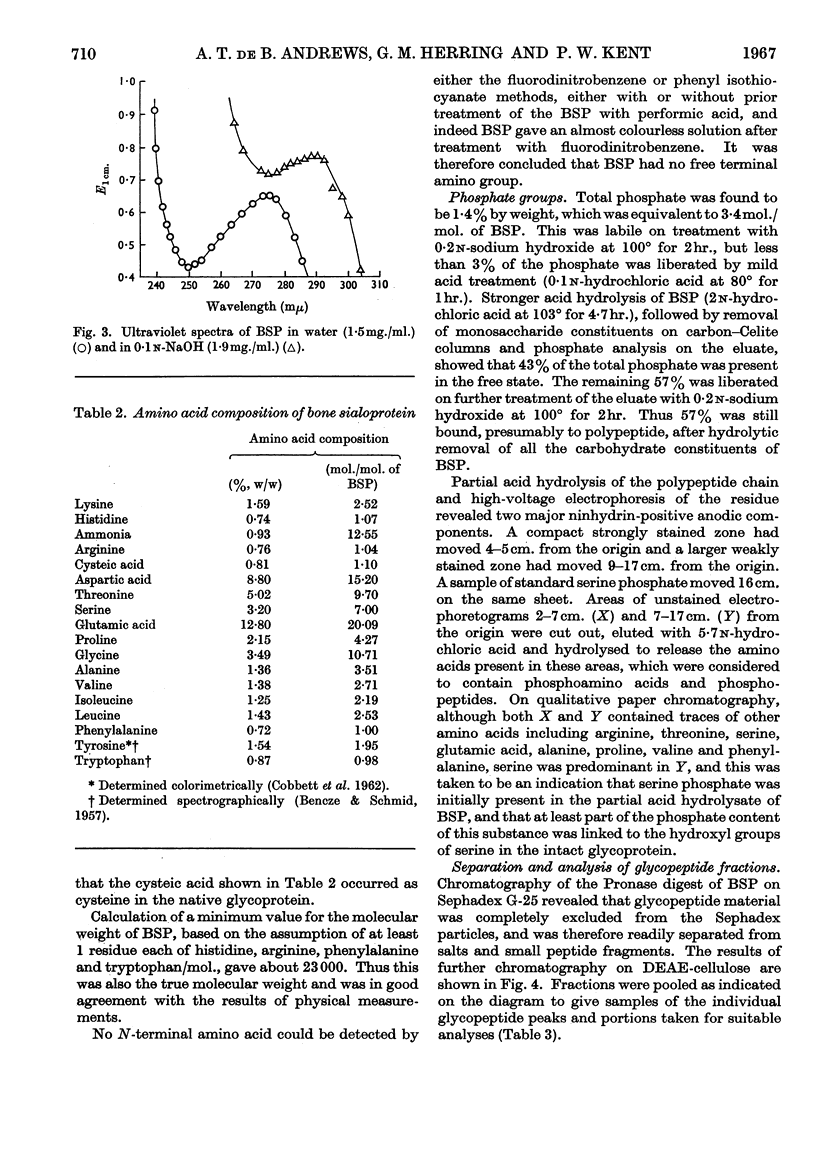
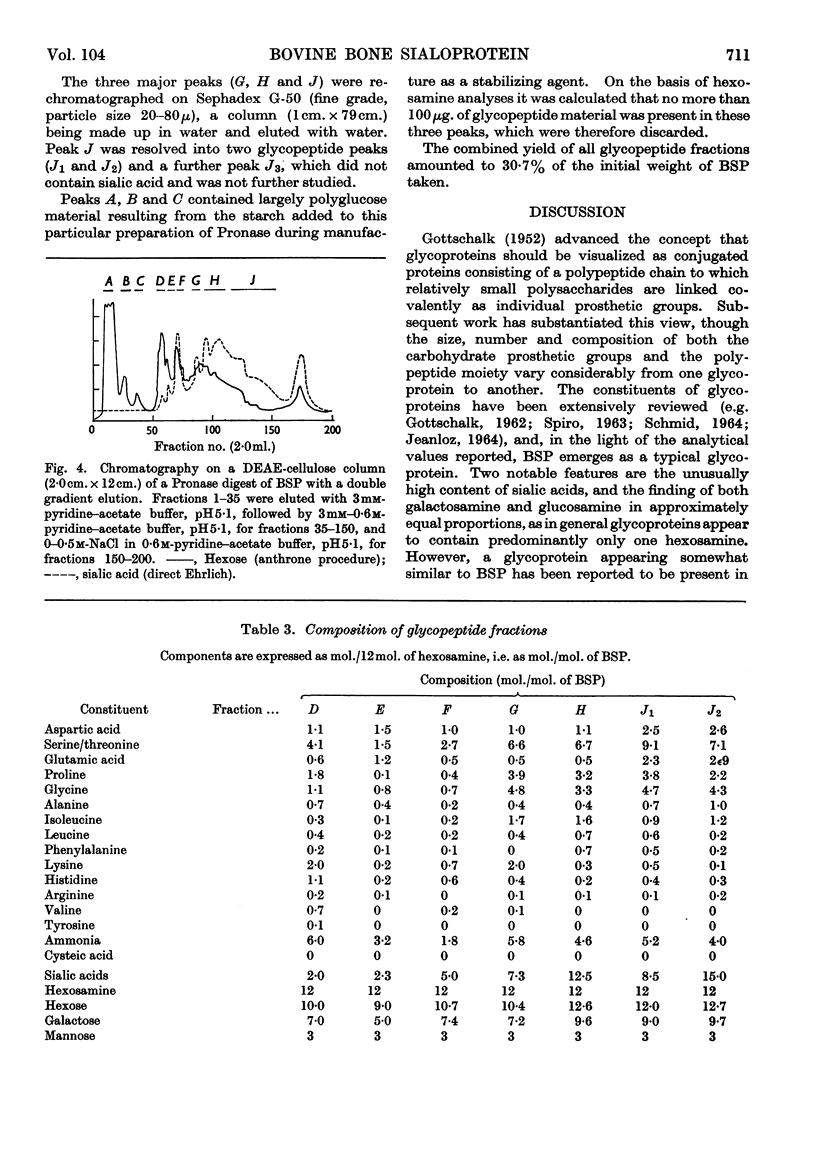
1. An analysis of bovine bone sialoprotein, a homogeneous glycoprotein isolated from cortical bone, is presented. 2. Analytical results agree with earlier physical measurements indicating a molecular weight of about 23000. 3. Mild acid hydrolysis and treatment with neuraminidase showed that fucose and sialic acid occupy terminal positions on oligosaccharide chains. 4. Treatment of the sialic acid-free glycoprotein with β-galactosidase showed that much of the galactose occupies a sub-terminal location in the intact glycoprotein. 5. The polypeptide chain is rich in aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, threonine and glycine, and has no detectable free terminal amino group. 6. Glycopeptides were studied after proteolytic digestion. 7. It is considered that the carbohydrate moiety is highly branched and is probably linked by an acid- and alkali-stable glycosylamine bond involving aspartic acid.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKBURN S., LOWTHER A. G. The separation of N-2:4-dinitrophenly amino-acids on paper chromatograms. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0480126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOAS N. F. Method for the determination of hexosamines in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):553–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURRILLON R., GOT R., BOUGUEREAU J., MARCY R. Sur une alpha 1 mucoprotéine du sérum de jument gravide et son rôle de transport de l'hormone gonadotrope. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1957 Sep 26;39(9-10):1119–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Buddecke E., Carubelli R., Gottschalk A. The complete enzymic degradation of glycopeptides containing O-seryl and O-threonyl linked carbohydrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Jul 1;16(4):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourrillon R., Meyer D. M., Dabat M. T. Isolement et structure d'un acetylpeptide de l'orosomucoide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 15;111(1):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBBETT W. G., KENCHINGTON A. W., WARD A. G. The determination of the tyrosine content of gelatins. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:468–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0840468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGE H. On the structure of ganglioside 2 from ox-brain of some acid oligosaccharides from human milk and a new method of methylation. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1960;42:1429–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT D. F., PEART W. S. The amino acid sequence in a hypertensin. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):246–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0650246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAILLARD H. [The effect of neuraminidase on different forms of cattle submaxillary mucin]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;317:257–268. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.317.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLK J. E., GLADNER J. A. The amino acid sequence of peptide B of co-fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 4;44:383–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAILLARD B. D. Use of unneutralized hydrolysates in paper chromatography of sugars. Nature. 1953 Jun 27;171(4365):1160–1160. doi: 10.1038/1711160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. A. THE SENSITIVITY OF THE NEURAMINOSIDIC LINKAGE IN MUCOSUBSTANCES TOWARDS ACID AND TOWARDS NEURAMINIDASE. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:380–391. doi: 10.1042/bj0890380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLIMCHER M. J., FRANCOIS C. J., RICHARDS L., KRANE S. M. THE PRESENCE OF ORGANIC PHOSPHORUS IN COLLAGENS AND GELATINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 9;93:585–602. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLIMCHER M. J., KRANE S. M. THE IDENTIFICATION OF SERINE PHOSPHATE IN ENAMEL PROTEINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 4;90:477–483. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK A. Carbohydrate residue of a urine mucoprotein inhibiting influenza virus haemagglutination. Nature. 1952 Oct 18;170(4329):662–663. doi: 10.1038/170662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK A., GRAHAM E. R. 6-alpha-D-Sialyl-N-acetyl-galactosamine: the neuraminidase-susceptible prosthetic group of bovine salivary mucoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:380–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. I., ROOS P. Studies on pituitary polypeptide hormones. II. The action of pepsin and subtilisin on beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):445–451. doi: 10.1042/bj0710445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRING G. M., KENT P. W. SOME STUDIES ON MUCOSUBSTANCES OF BOVINE CORTICAL BONE. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:405–414. doi: 10.1042/bj0890405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRING G. M., VAUGHAN J., WILLIAMSON M. Preliminary report on the site of localization and possible binding agent for yttrium, americium and plutonium in cortical bone. Health Phys. 1962 Dec;8:717–724. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196212000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMIESON G. A. STUDIES ON GLYCOPROTEINS. I. THE CARBOHYDRATE PORTION OF HUMAN CERULOPLASMIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2019–2027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANLOZ R. W. STUDY OF THE ALPHA-1-ACID GLYCOPROTEIN OF HUMAN PLASMA, A MEMBER OF A CLASS OF COMPLEX BIOCHEMICAL COMPOUNDS. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 May;43:363–369. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196405000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRANE S., STONE M. J., GLIMCHER M. J. THE PRESENCE OF PROTEIN PHOSPHOKINASE IN CONNECTIVE TISSUES AND THE PHOSPHORYLATION OF ENAMEL PROTEINS IN VITRO. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 4;97:77–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN G. E. The nature of phosphorus linkages in phosphoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1955;10:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPENOE E. A. The linkage neuraminic acid in orosomucoid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:584–585. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90651-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacocke A. R., Williams P. A. Binding of calcium, yttrium and thorium to a glycoprotein from bovine cortical bone. Nature. 1966 Sep 10;211(5054):1140–1141. doi: 10.1038/2111140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., HOCQUARD E. Formation of dephospho-ovalbumin as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ovalbumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 27;62:606–607. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOQUIST J. Determination of amino acids as phenyl thiohydantoin derivatives. III. Quantitative determination of 3-phenyl-2-thiohydantoins from paper chromatograms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:20–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO R. G. GLYCOPROTEINS: STRUCTURE, METABOLISM AND BIOLOGY. N Engl J Med. 1963 Sep 12;269:566–CONTD. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196309122691107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUGITA A. Studies on the N-terminal sequence of tobaccomosaic-virus protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 12;38:145–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. Thiobarbituric acid spray reaction for deoxy sugars and sialic acids. Nature. 1960 Apr 16;186:237–237. doi: 10.1038/186237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINFELD H., TUNIS M. The cleavage of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein by pepsin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1668–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J., SANGER F. The grouping of serine phosphate residues in phosvitin and casein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 May;33(1):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Peacocke A. R. The physical properties of a glycoprotein from bovine cortical bone (bone sialoprotein). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 1;101(3):327–335. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


