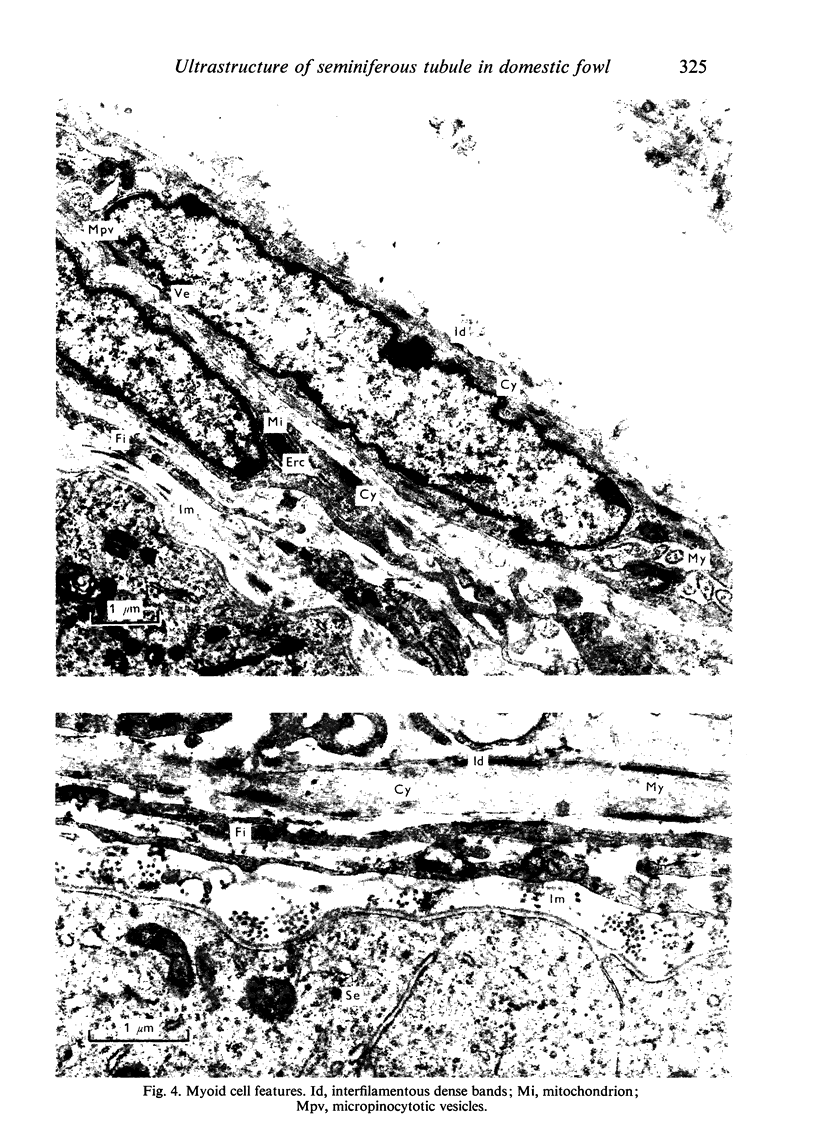
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLERMONT Y. Contractile elements in the limiting membrane of the seminiferous tubules of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Oct;15(2):438–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABO B., GUSTAFSSON B. DISTRIBUTION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM AND ITS RELATION TO SPERM CONCENTRATION IN THE EPIDIDYMAL PLASMA OF THE BULL. J Reprod Fertil. 1964 Jun;7:337–345. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0070337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dym M., Fawcett D. W. The blood-testis barrier in the rat and the physiological compartmentation of the seminiferous epithelium. Biol Reprod. 1970 Dec;3(3):308–326. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/3.3.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Heidger P. M., Leak L. V. Lymph vascular system of the interstitial tissue of the testis as revealed by electron microscopy. J Reprod Fertil. 1969 Jun;19(1):109–119. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0190109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovatta O. Contractility and structure of adult rat seminiferous tubules in organ culture. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;130(2):171–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00306955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormano M., Hovatta O. Contractility and histochemistry of the myoid cell layer of the rat seminiferous tubules during postnatal development. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1972;137(3):239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00519094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACY D., ROTBLAT J. Study of normal and irradiated boundary tissue of the seminiferous tubules of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Oct;21:49–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKE P. E. The male reproductive tract of the fowl. J Anat. 1957 Jan;91(1):116–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEESON C. R., LEESON T. S. THE POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT AND DIFFERENTIATION OF THE BOUNDARY TISSUE OF THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE OF THE RAT. Anat Rec. 1963 Oct;147:243–259. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091470208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON K. E., SHAVER S. L. Some functions of the caput epididymis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Nov 20;55(4):585–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb26578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEMI M., KORMANO M. CONTRACTILITY OF THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE OF THE POSTNATAL RAT TESTIS AND ITS RESPONSE TO OXYTOCIN. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1965;43:40–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H., Long I. R. Contractile cells in human seminiferous tubules. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1271–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H. The fine structure and development of the peritubular contractile cell component in the seminiferous tubules of the mouse. Am J Anat. 1967 Nov;121(3):523–557. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suvanto O., Kormano M. The relation between in vitro contractions of the rat seminiferous tubules and the cyclic stage of the seminiferous epithelium. J Reprod Fertil. 1970 Mar;21(2):227–232. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0210227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingari M. D., Lake P. E. Ultrastructural evidence for resorption of spermatozoa and testicular fluid in the excurrent ducts of the testis of the domestic fowl, Gallus domesticus. J Reprod Fertil. 1972 Dec;31(3):373–381. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0310373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]