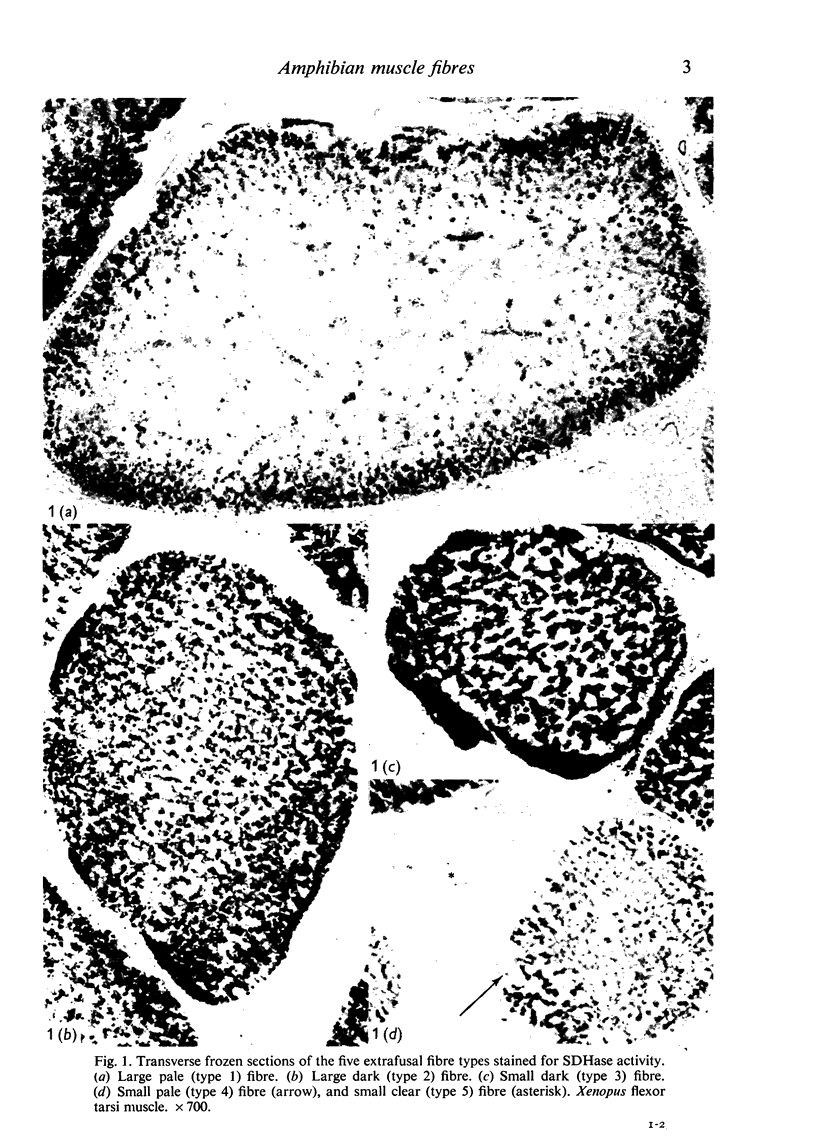
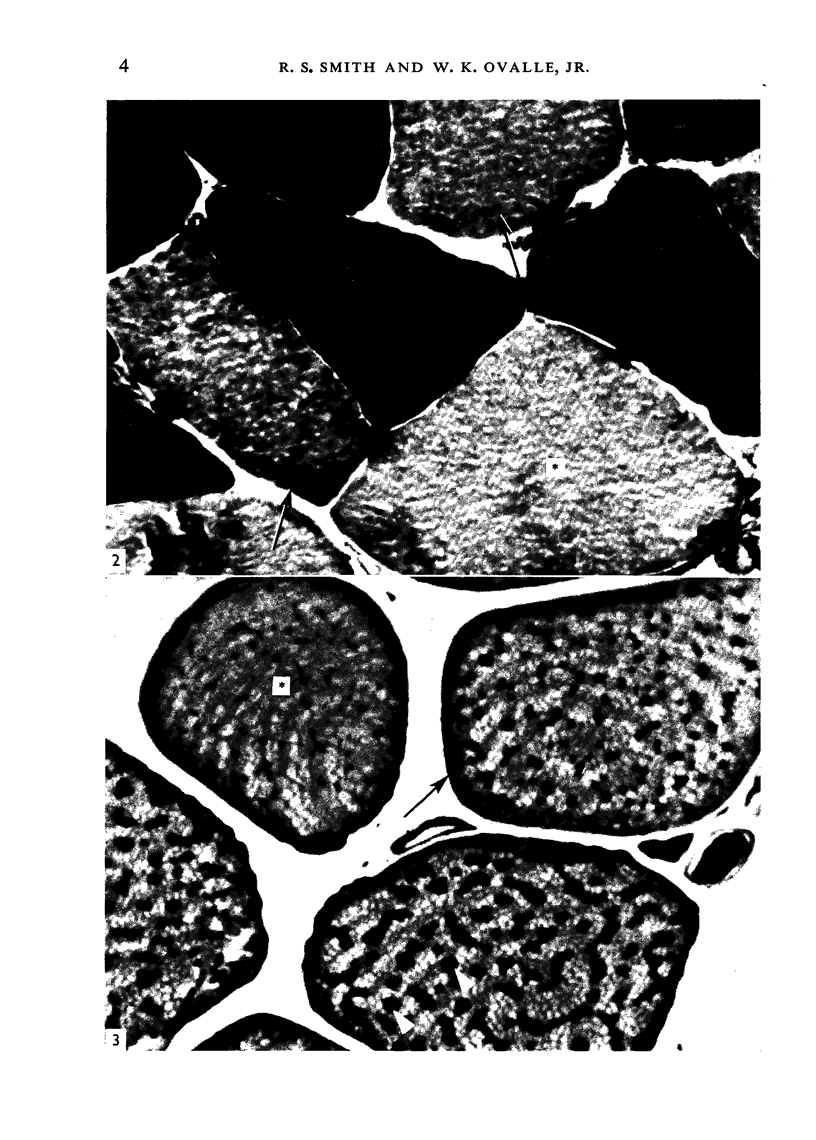
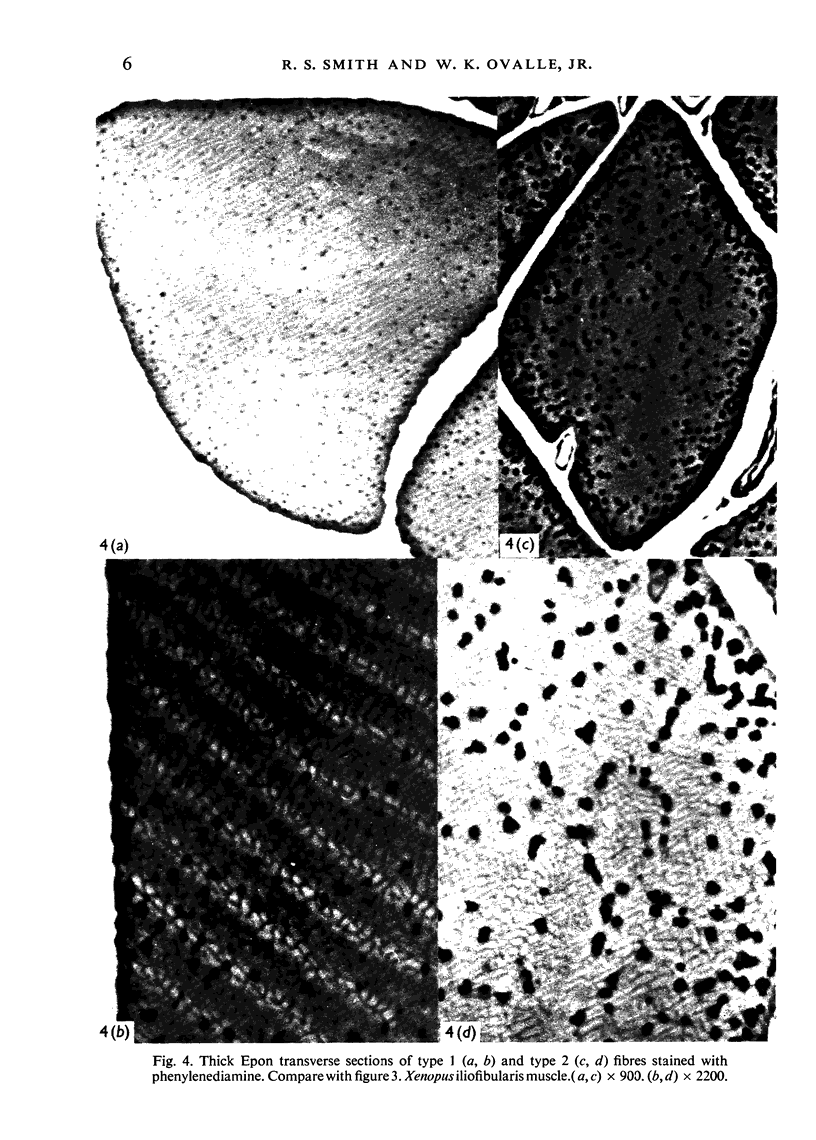
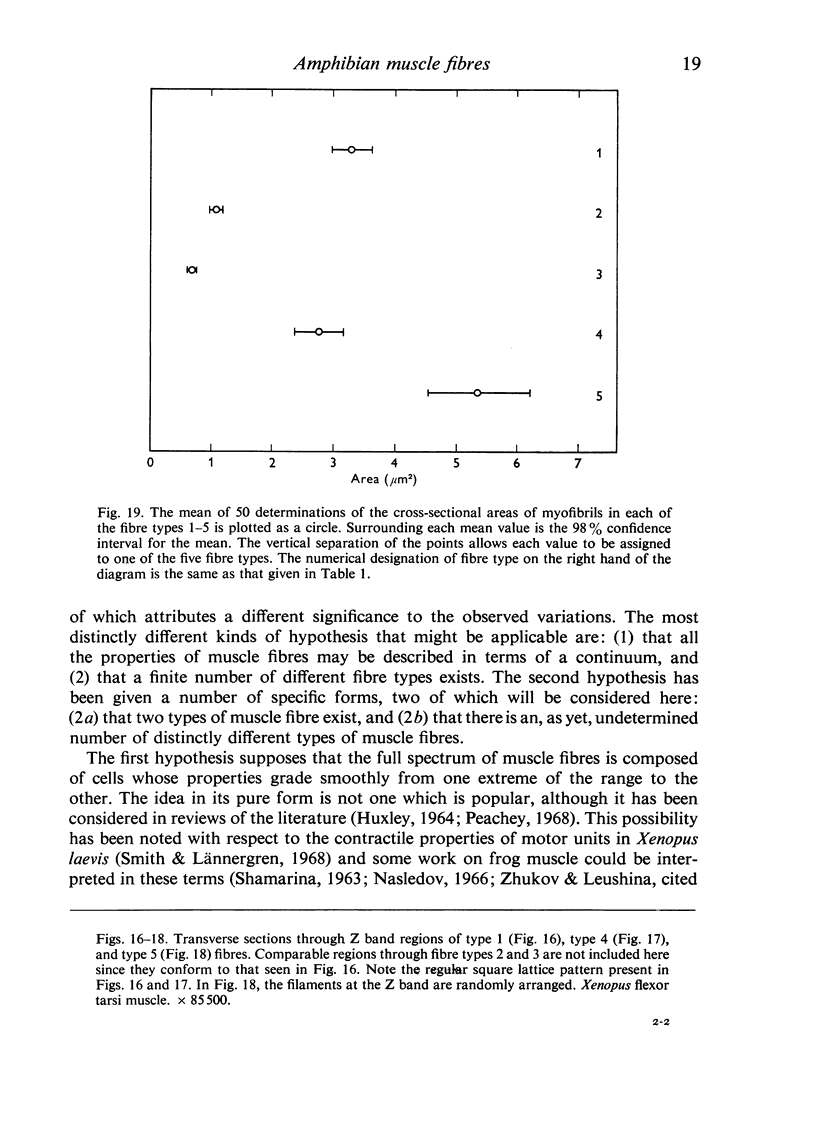
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asmussen G., Kiessling A. Die Muskelfasersorten des Frosches: Ihre Identifikation und die Gesetzmässigkeiten ihrer Anordnung in der Skelettmuskulatur. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1970;24(6):871–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. L'innervation motrice du muscle strié des vertébrés. Actual Neurophysiol (Paris) 1968;8:23–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Zajac F. E., 3rd Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K., Irwin R. L. A histochemical-physiological correlation of frog skeletal muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):511–518. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F. On the relationship of ultrastructural and cytochemical features of color in mammalian skeletal muscle. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;95(3):462–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00995217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J. Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomyosin ATPase. Exp Neurol. 1970 Aug;28(2):365–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., OLSON C. B. RELATIONS BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN THE DESIGN OF SKELETAL MUSCLES. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:581–598. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. MUSCLE. Annu Rev Physiol. 1964;26:131–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.26.030164.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Vertebrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):40–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPPEIS G. G., CARLSEN F. The ultrastructure of the Z disc in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1962 May;13:323–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Small-nerve junctional potentials; the distribution of small motor nerves to frog skeletal muscle, and the membrane characteristics of the fibres they innervate. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):289–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. E., Cahill M. A. Filamentous and matrix components of skeletal muscle Z-disks. Anat Rec. 1972 Apr;172(4):623–642. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091720403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen H. Identification of muscle fiber types in "semithin" sections stained with p-phenylene-diamine. Histochemie. 1972;32(1):95–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00277476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E., Edström L. Differential histochemical effects of muscle contractions on phosphorylase and glycogen in various types of fibres: relation to fatigue. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):415–423. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., TSOU K. C., DE SOUZA E., CHENG C. S., SELIGMAN A. M. Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Jul;5(4):420–436. doi: 10.1177/5.4.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORKAND R. K. A further study of electrical responses in slow and twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:181–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):161–169. doi: 10.1177/3.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACHEY L. D., HUXLEY A. F. Structural identification of twitch and slow striated muscle fibers of the frog. J Cell Biol. 1962 Apr;13:177–180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page S. G. A comparison of the fine structures of frog slow and twitch muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):477–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe R. W. Ultrastructure of the Z line of skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):674–685. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAMARINA N. M. Electric response of 'tonic' muscle fibres of the frog skeletal musculature. Nature. 1962 Feb 24;193:783–784. doi: 10.1038/193783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:87–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Lännergren J. Types of motor units in the skeletal muscle of Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1968 Jan 20;217(5125):281–283. doi: 10.1038/217281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscopic cytology. Int Rev Cytol. 1969;26:235–302. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]