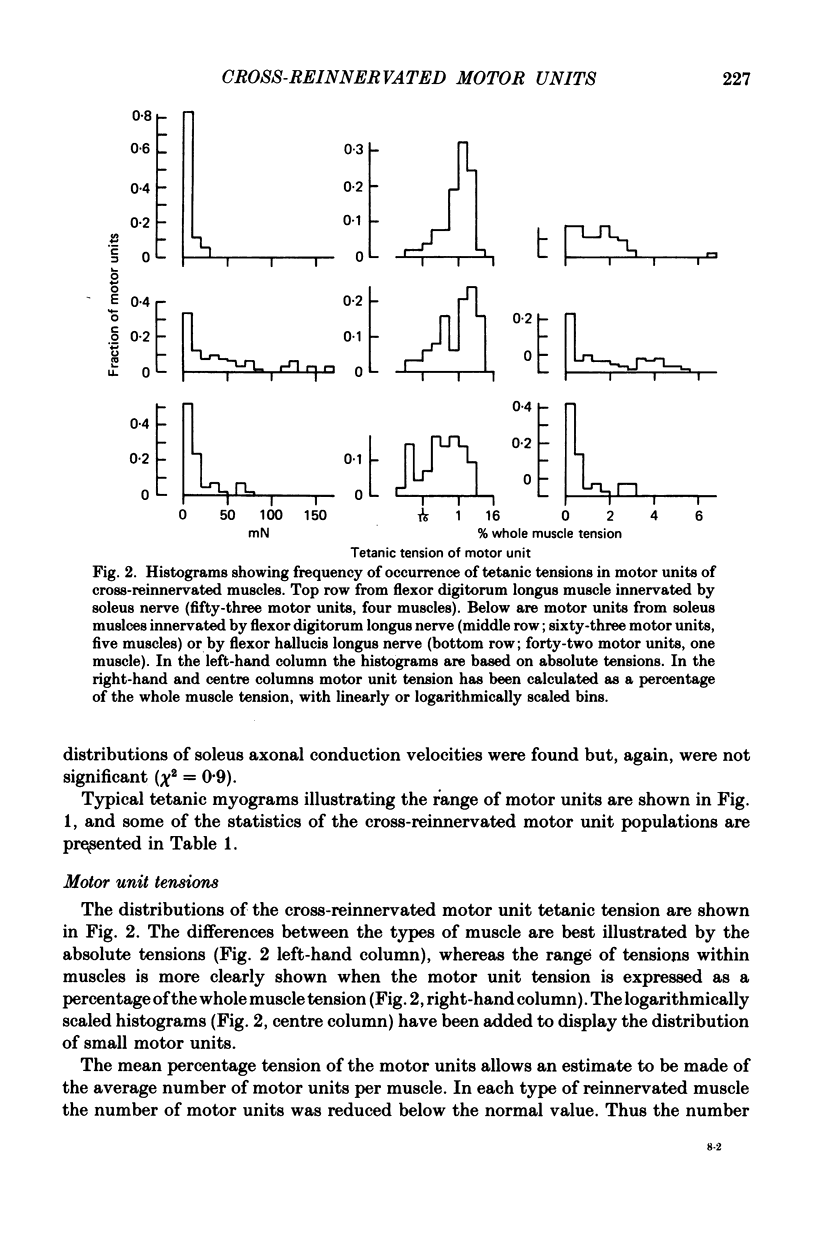
Abstract
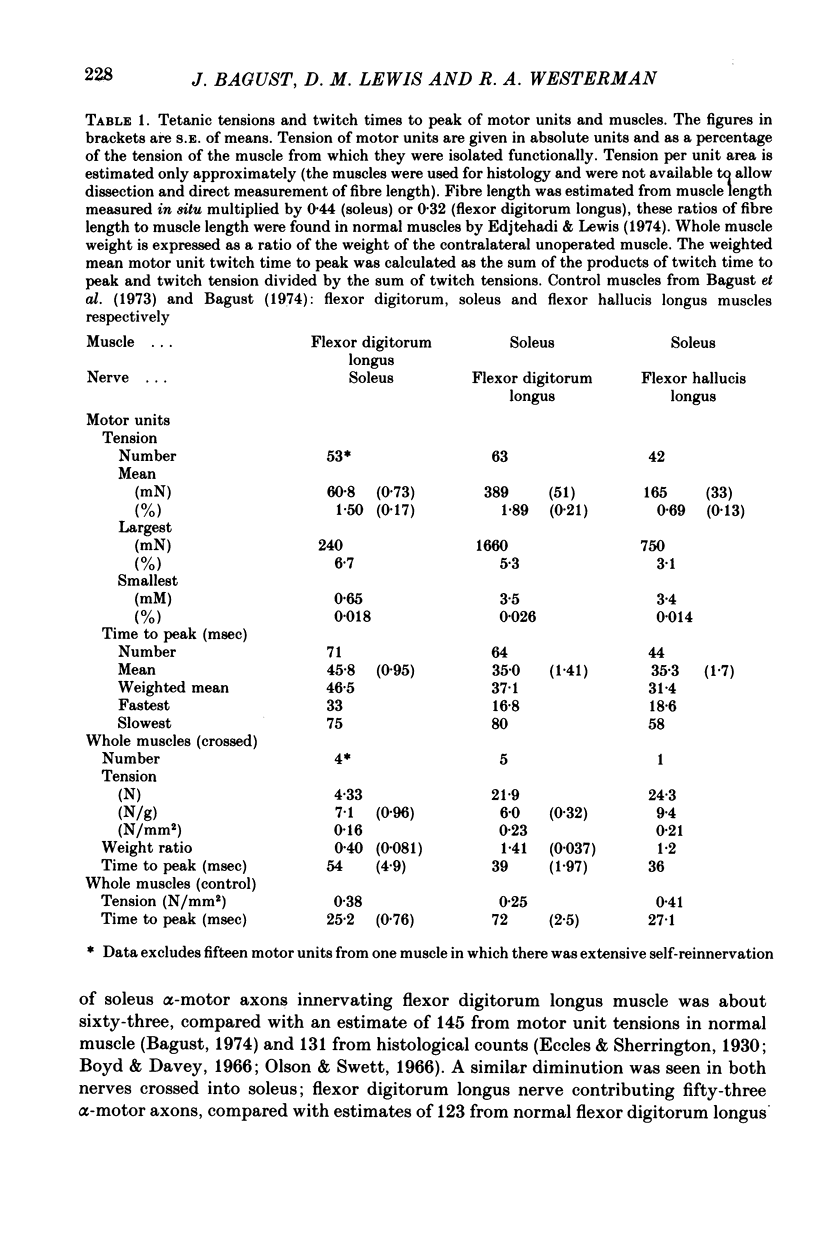
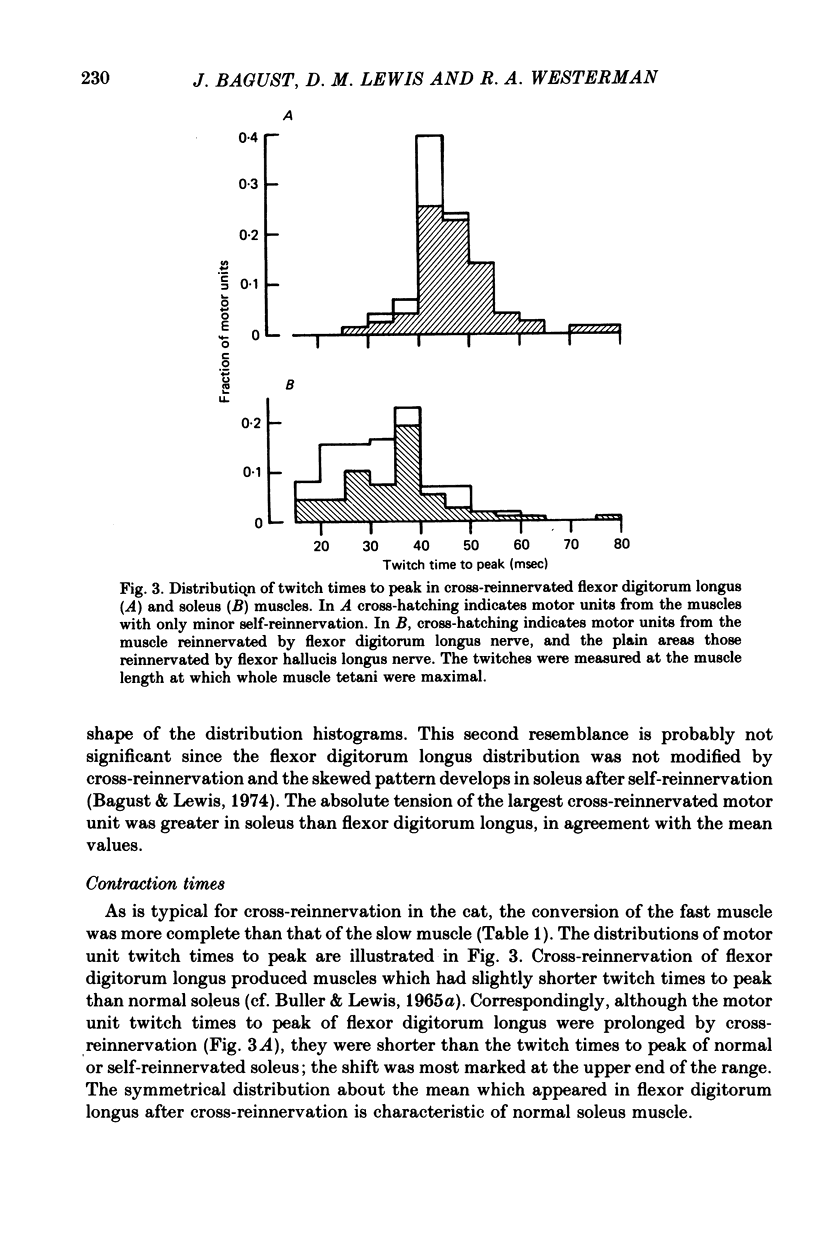
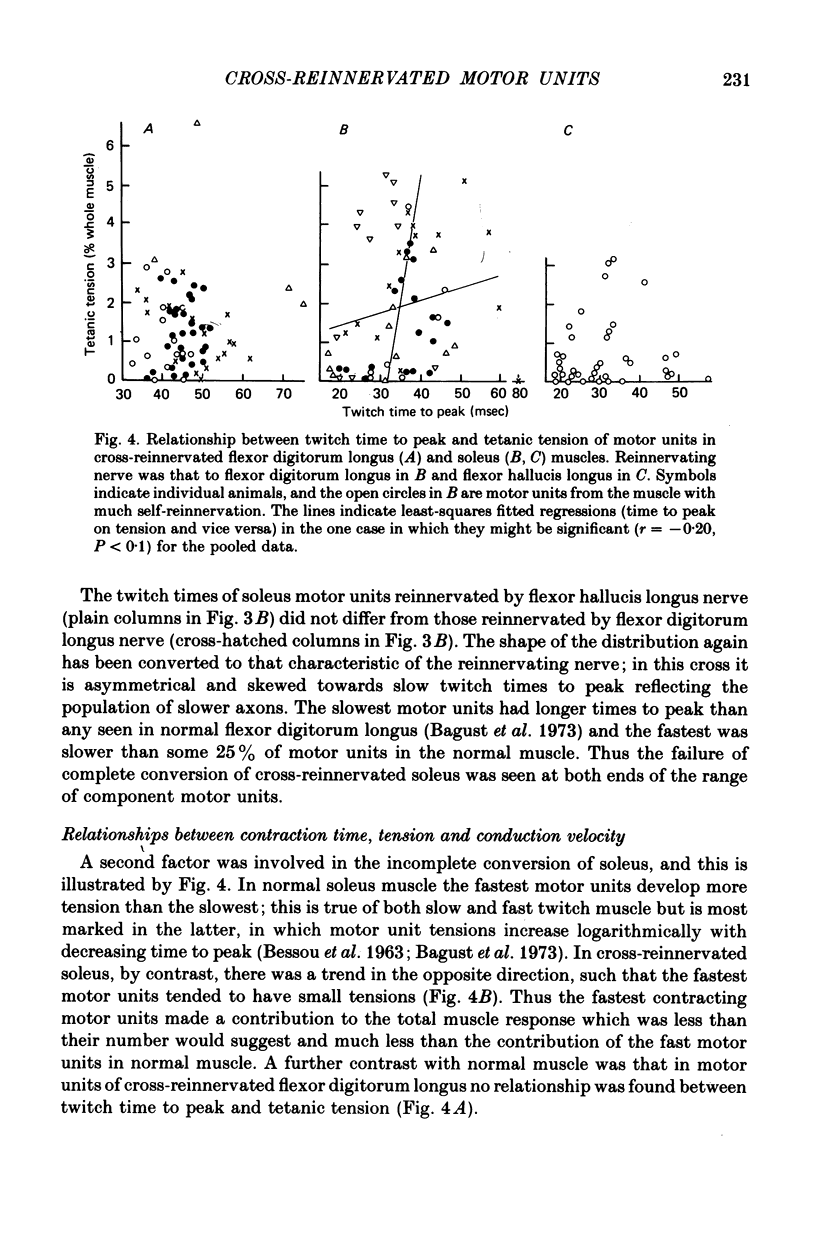
1. Isometric contractile properties of motor units were measured in cross-reinnervated fast (flexor digitorum longus) and slow (soleus) twitch muscles of the cat. All but one cross was at least 95% pure. 2. There was a reduction in the number of motor units in all muscles, but totals remained about equal in cross-reinnervated soleus and flexor digitorum longus. 3. Motor unit tensions (mean and maximum values) were higher in cross-reinnervated soleus than in cross-reinnervated flexor digitorum longus, reversing the differences between normal muscles. This was due to increases in muscle mass and in the tension developed per unit cross-sectional area. There were motor unit tensions larger and smaller than those seen in normal muscle, but the range was comparable with that seen in self-reinnervated muscle. 4. The changes in twitch time to peak of whole muscle following cross-reinnervations resulted from a change over the whole range of motor units. The conversion of soleus was less complete than that of flexor digitorum longus, and the time to peak of its fastest motor unit was twice as long as any seen in normal flexor digitorum longus. 5. In neither of the cross-reinnervated muscles were the fast contracting motor units larger than the slow contracting ones, and in cross-reinnervated soleus they were smaller. 6. Axonal conduction velocity was correlated with motor unit tension in both muscles and with twitch time to peak in cross-reinnervated flexor digitorum longus, but in all cases less clearly than in normal muscles. 7. The ratio of twitch to tetanic tension increased with increasing twitch time to peak, as in normal muscles.
Full text
PDF




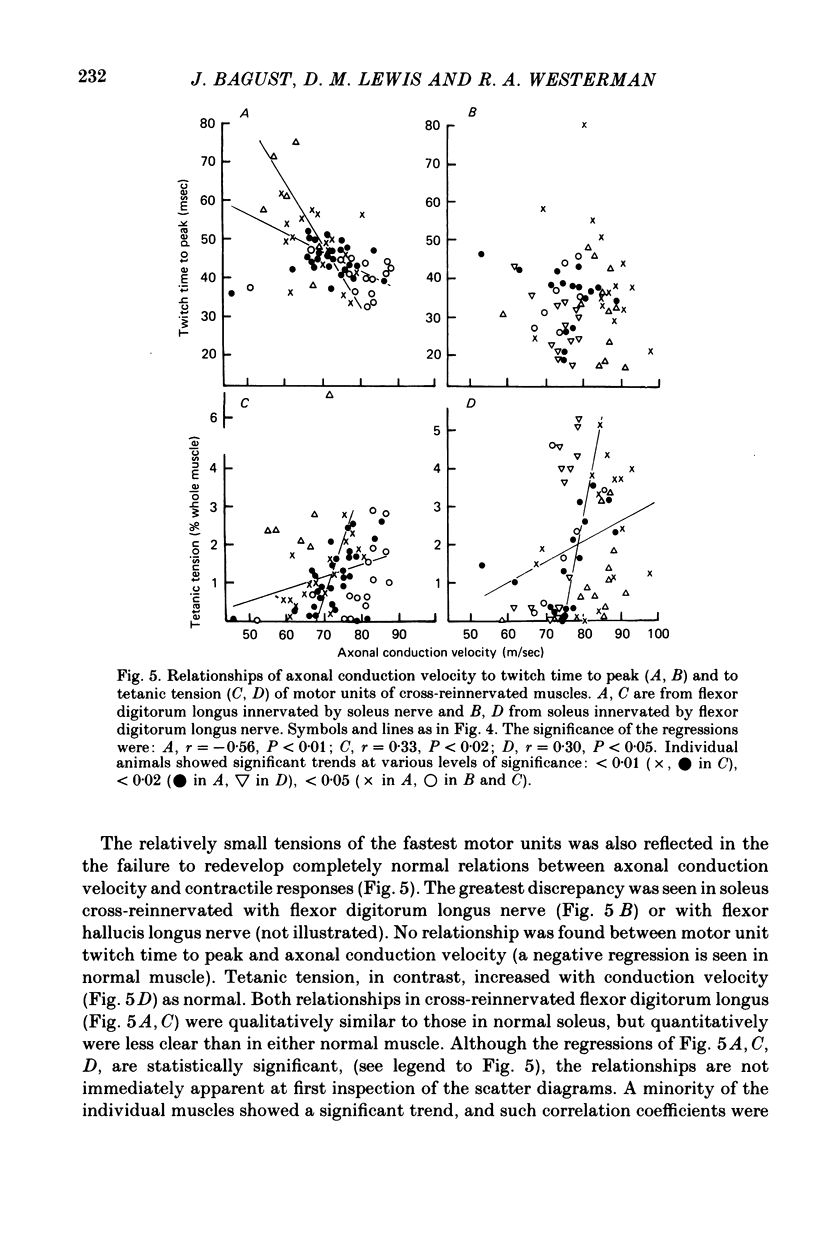
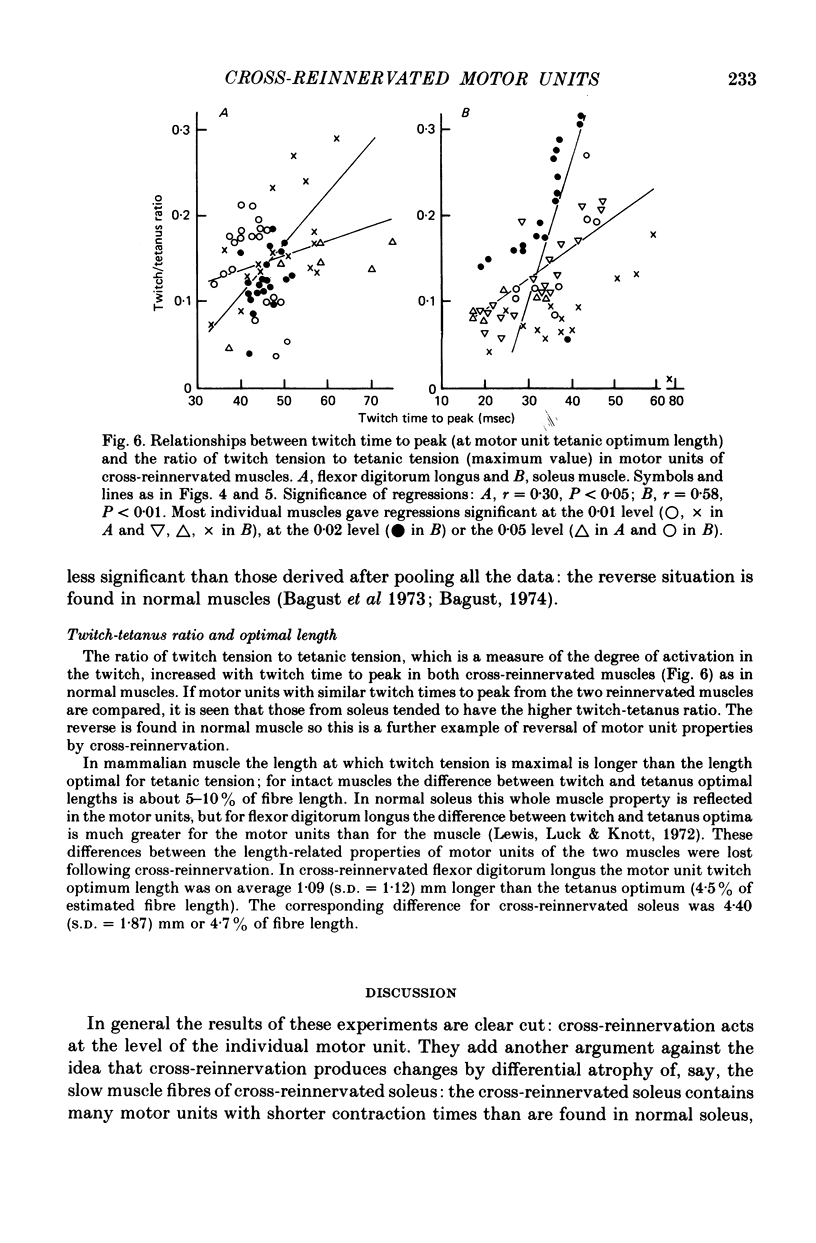


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSOU P., EMONET-DENAND F., LAPORTE Y. [Relation between the conduction rate of motor nerve fibers and the contraction time of their motor units]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 24;256:5625–5627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON MAMMALIAN CROSS-INNERVATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:343–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE DIFFERENTIATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLES IN THE KITTEN HIND LIMB. J Physiol. 1965 Feb;176:355–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Finol H. J., Lewis D. M., Webb S., Westerman R. A. Proceedings: Motor units of cross-reinnervated fast and slow twitch muscles. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Knott S., Lewis D. M., Luck J. C., Westerman R. A. Isometric contractions of motor units in a fast twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M. Isometric contractions of motor units in self-reinnervated fast and slow twitch muscles of the cat. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):91–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. The properties of motor units in a fast and a slow twitch muscle during post-natal development in the kitten. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):75–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J. Relationships between motor nerve conduction velocities and motor unit contraction characteristics in a slow twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):269–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller A. J., Kean C. J. Further observations on the force velocity characteristics of cross-innervated cat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):24P–25P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edjtehadi G. D., Lewis D. M. Histochemical reactions of fibres in a fast twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:439–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edjtehadi G., Lewis D. M. Structural features of muscle fibres from a fast and a slow twitch muscle in the kitten during postnatal development. J Anat. 1974 Nov;118(Pt 2):253–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J., Albers R. W. The neural regulation of some phenotypic differences between the fiber types of mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp Neurol. 1970 Jan;26(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Bagust J., Webb S. N., Westerman R. A., Finol H. J. Axon conduction velocity modified by reinnervation of mammalian muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):745–746. doi: 10.1038/270745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Luck J. C., Knott S. A comparison of isometric contractions of the whole muscle with those of motor units in a fast-twitch muscle of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1972 Oct;37(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCPHEDRAN A. M., WUERKER R. B., HENNEMAN E. PROPERTIES OF MOTOR UNITS IN A HOMOGENEOUS RED MUSCLE (SOLEUS) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:71–84. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt M. A., Salafsky B. Enzymic and histochemical changes in fast and slow muscles after cross innervation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):69–74. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


