Abstract
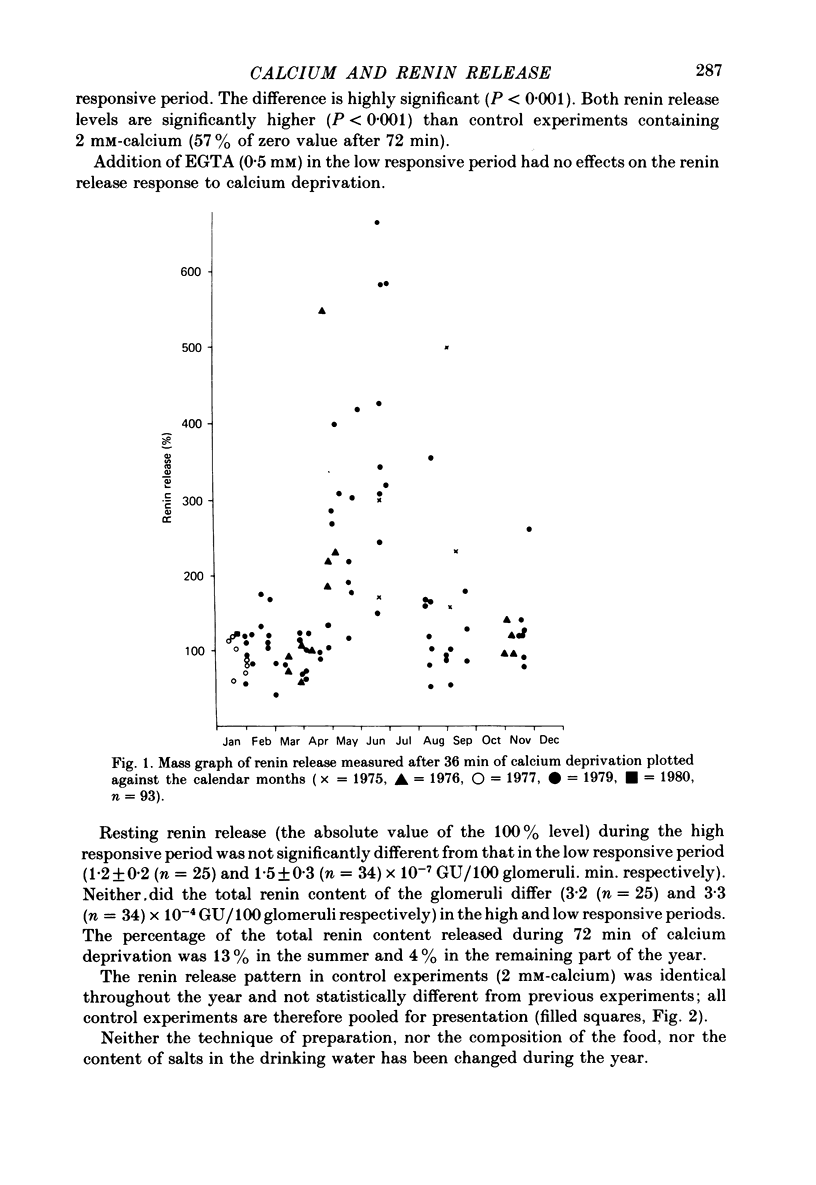
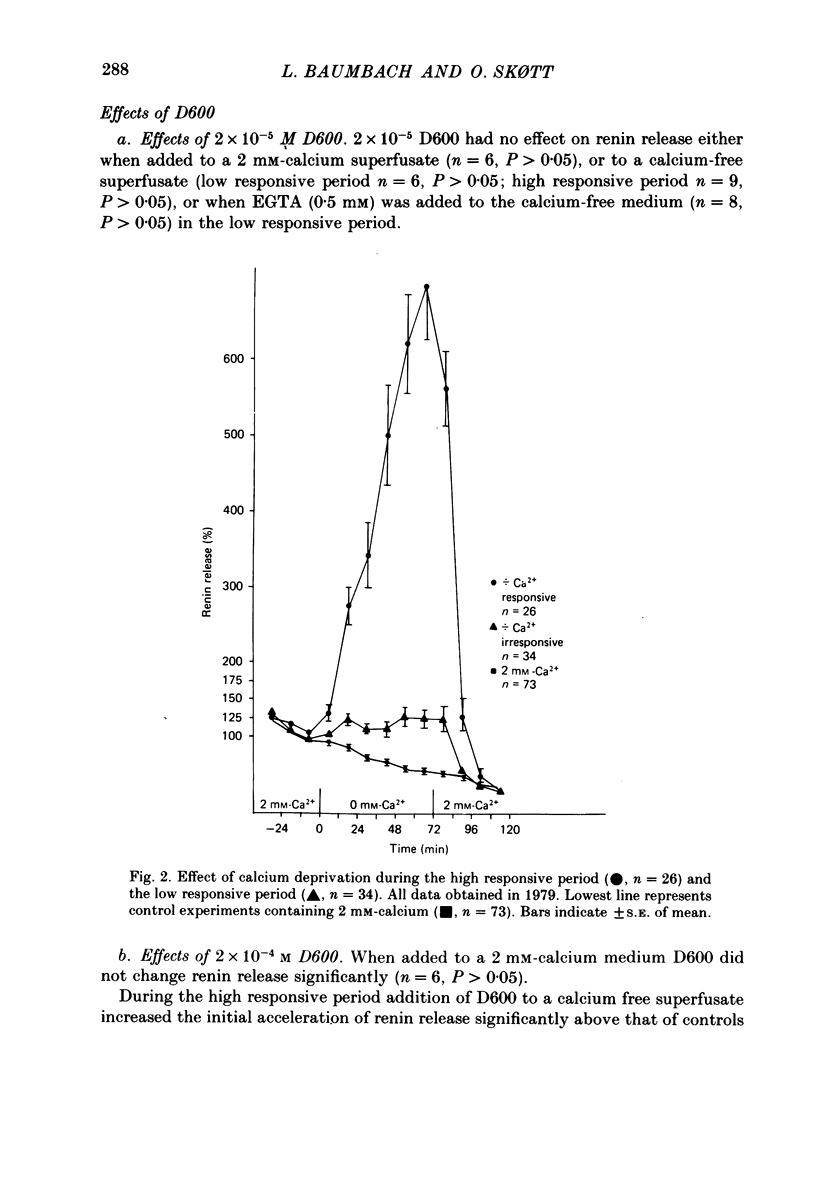
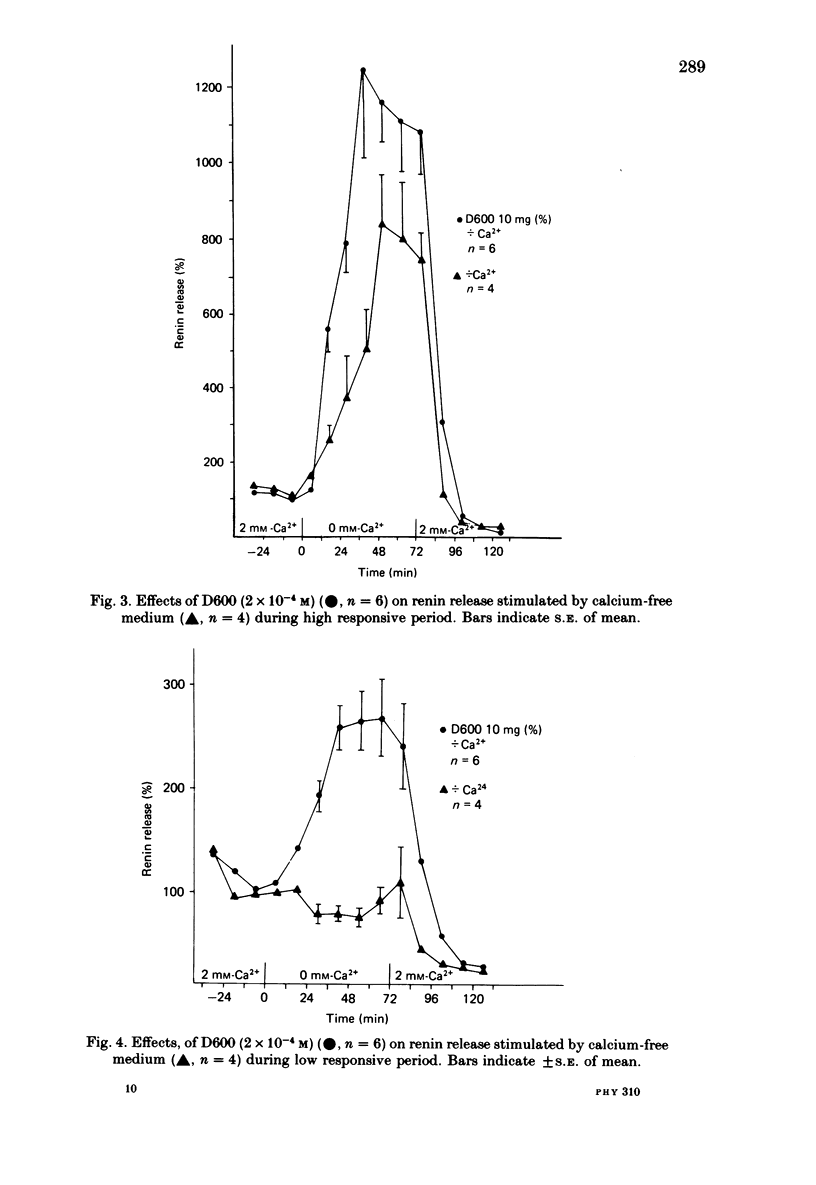
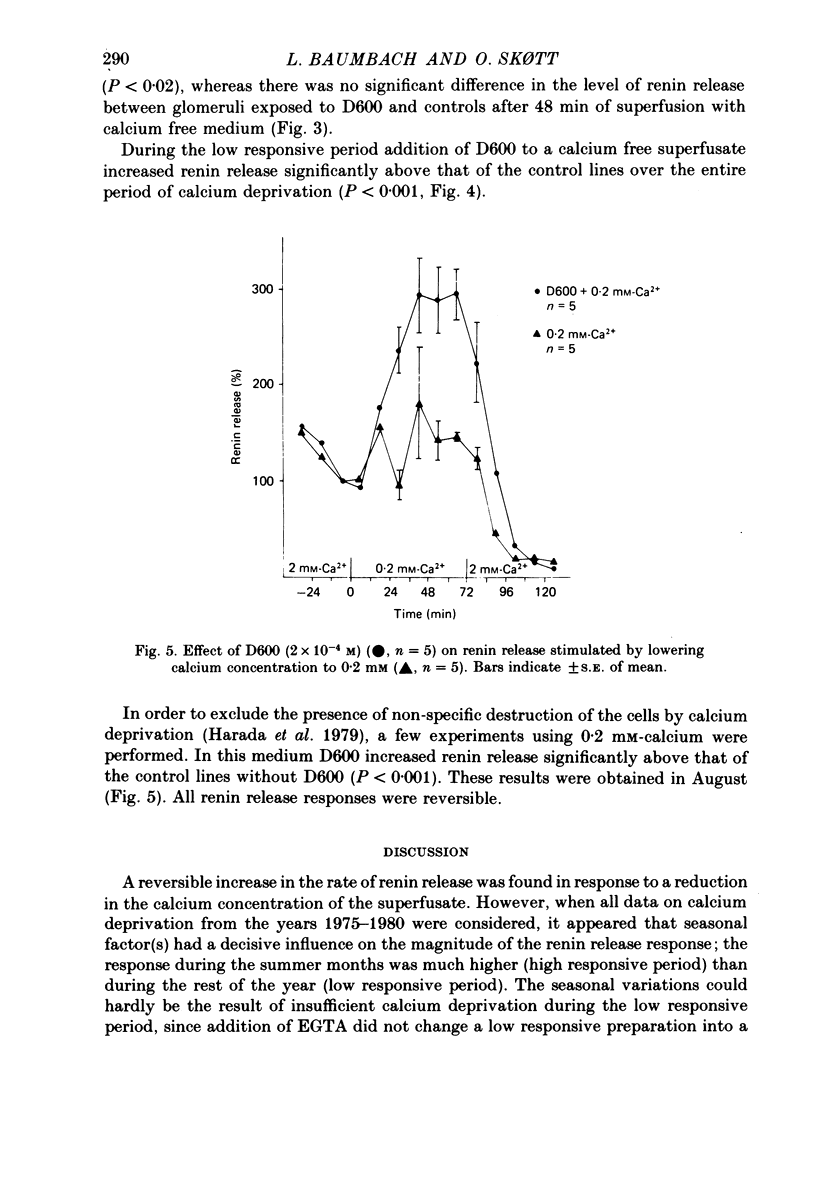
1. The effects of calcium deprivation and D600 on the rate of renin release and seasonal variations in the response were studied on juxtaglomerular cells from a preparation of isolated rat glomeruli superfused in vitro. 2. Reduction of superfusate calcium concentration caused an increase in renin release, which was significantly higher during the summer (May-August) than during the rest of the year. 3. Addition of D600 (2 X 10(-4) M) to a calcium-free medium in the low responsive period caused a markedly increased renin release. In the high responsive period renin release increased more rapidly and to a higher level initially than observed in the control lines without D600. 4. It is suggested that the effect of calcium on renin release predominantly is mediated by changes in calcium bound to the plasma membrane of the juxtaglomerular cell. The sensitivity of this cell to changes in the extracellular calcium concentration seems to be regulated and varies with season, possibly due to regulation of the amount of calcium bound to the membrane.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumbach L., Leyssac P. P. Studies on the mechanism of renin release from isolated superfused rat glomeruli: effects of calcium, calcium ionophore and lanthanum. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):745–764. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendstrup K., Leyssac P. P., Poulsen K., Skinner S. L. Characteristics of renin release from isolated superfused glomeruli in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK W. F., PICKERING G. W. The location of renin in the rabbit kidney. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:526–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. S. Stimulation of renin release in perfused kidney by low calcium and high magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F377–F382. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAS H., HAERTFELDER G. [(N-methyl-N-homoveratryl)-gamma-aminopropyl]-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl-acetonitrile, a substance with coronary vasodilating properties]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1962 Jun;12:549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada E., Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. Stimulation of renin secretion from the intact kidney and from isolated glomeruli by the calcium ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 19;583(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in renin secretion from the isolated perfused cat kidney. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):93–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler W. G., Dunnet J., Sullivan A. Drug-induced changes in the superficially located stores of calcium in heart sarcolemma. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct Metab. 1976;9:53–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S. Renin 1978. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978 Dec;143(6):193–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens S., Haeusler G. Effects of some vasodilators on calcium translocation in intact and fractionated vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen R., Peart W. S. Calcium dependence of the inhibitory effect of angiotensin on renin secretion in the isolated perfused kidney of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09599.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


