Abstract
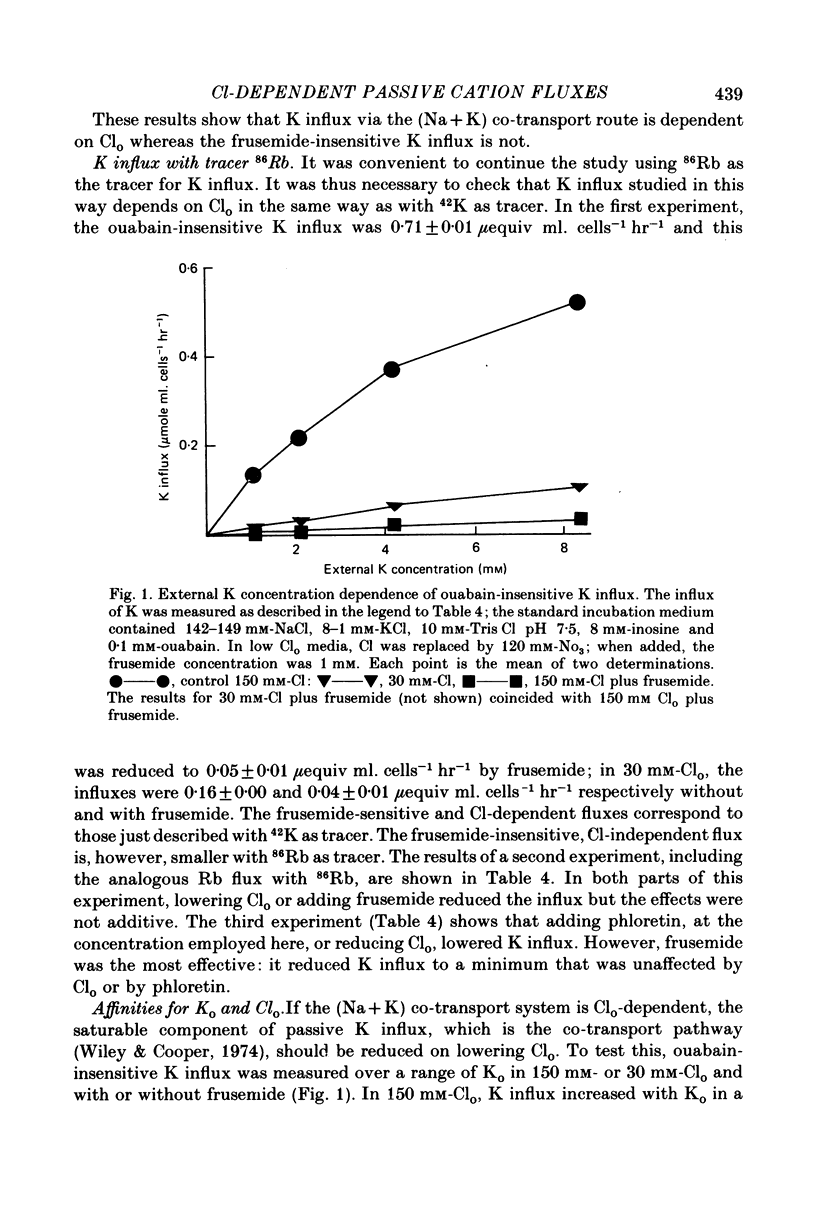
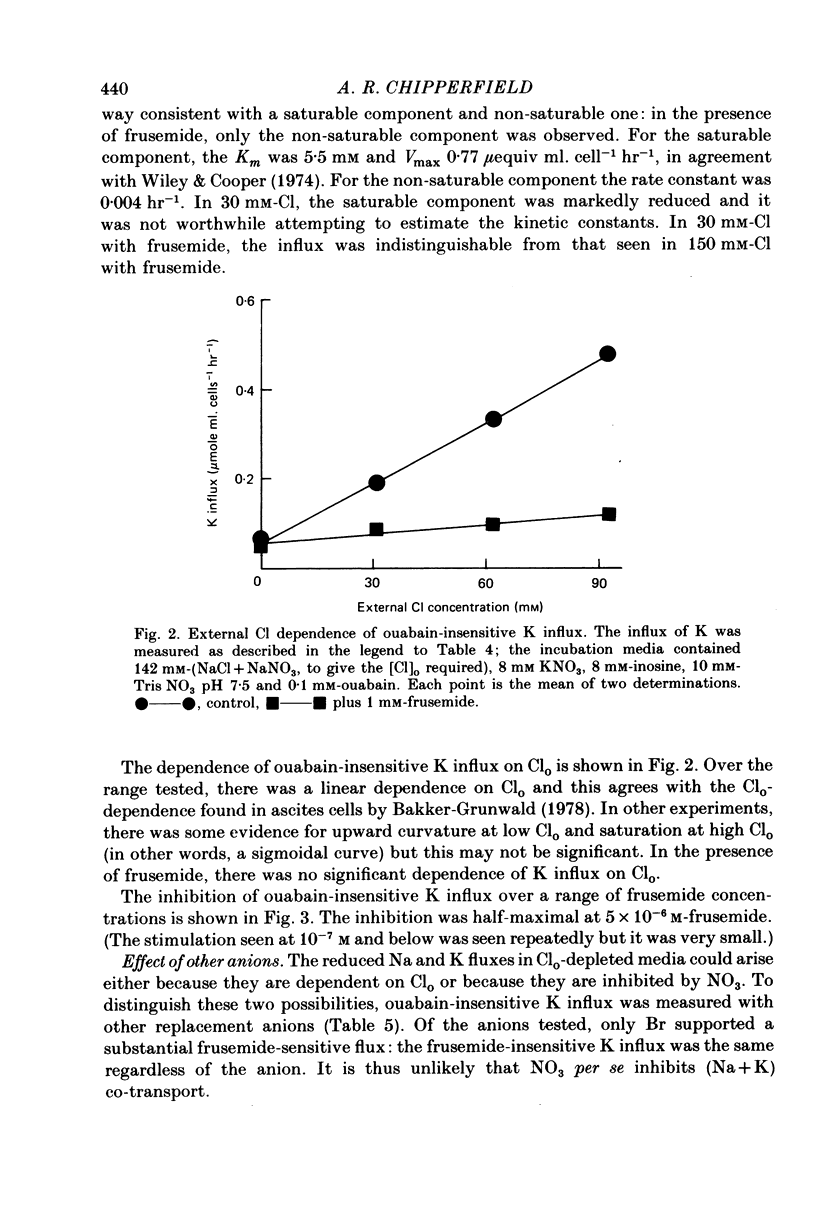
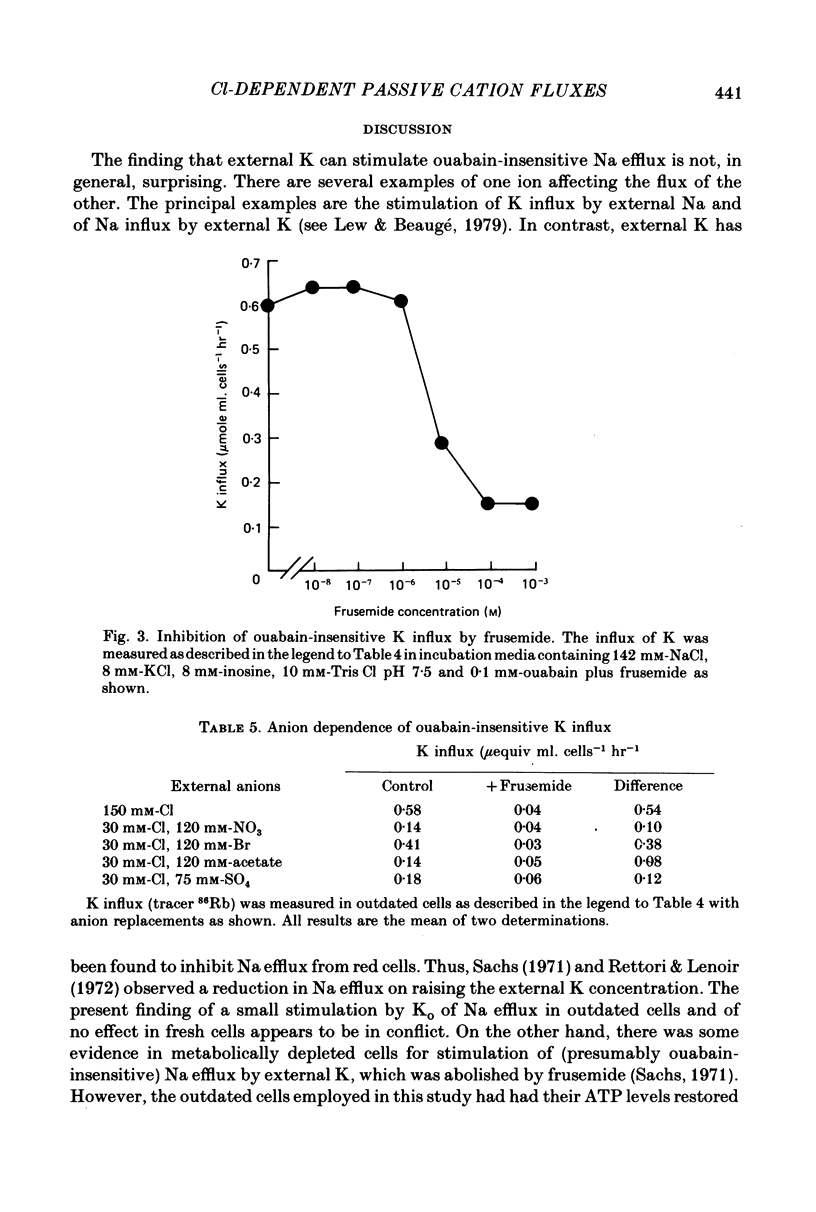
1. In outdated human red blood cells, there was a Ko-dependent, ouabain-insensitive efflux of Na that was inhibited by frusemide and phloretin. 2. It was reduced or absent (a) in media containing Ca or Mg, (b) in fresh cells. 3. In media with Cl partly replaced by NO3, Na efflux, and its sensitivity to Ko and frusemide, were reduced. 4. The saturable component of ouabain-insensitive K influx was dependent on Cl and inhibited by frusemide and by phloretin. 5. Bromide also supported a frusemide-sensitive, ouabain-insensitive K influx but acetate and SO4 (like NO3) did not.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker-Grunwald T. Effect of anions of potassium self-exchange in ascites tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 2;513(2):292–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. Non-pumped sodium fluxes in human red blood cells. Evidence for facilitated diffusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R. An effect of chloride on (Na+K) co-transport in human red blood cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):281–282. doi: 10.1038/286281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R., Whittam R. The connexion between the ion-binding sites of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):371–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhm J., Becker B. F. Studies on lithium transport across the red cell membrane. V. On the nature of the Na+-dependent Li+ countertransport system of mammalian erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1979 Dec 31;51(3-4):263–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01869087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Stewart G. W., Ellory J. C. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J., Wieth J. O. Effects of some monovalent anions on fluxes of Na and K, and on glucose metabolism of ouabain treated human red cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Oct-Nov;71(2):168–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):278–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. The action of cardiac glycosides on sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):148–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. J. Human erythrocyte anion permeabilities measured under conditions of net charge transfer. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):35–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey G. N., Sarkadi B., Haas M., Gunn R. B., Davis J. M., Tosteson D. C. Lithium transport pathways in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Aug;72(2):233–247. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestland R. N., Whittam R. The influence of external sodium ions on the sodium pump in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1090369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettori O., Lenoir J. P. Ouabain-insensitive active socium transport in erythrocytes: effect of external cation. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):880–884. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Ouabain-insensitive sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):259–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The role of bicarbonate, chloride and sodium ions in the regulation of intracellular pH in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R., Wiley J. S. Some aspects of adenosine triphosphate synthesis from adenine and adenosine in human red blood cells. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):485–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Cooper R. A. A furosemide-sensitive cotransport of sodium plus potassium in the human red cell. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):745–755. doi: 10.1172/JCI107613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


