Abstract
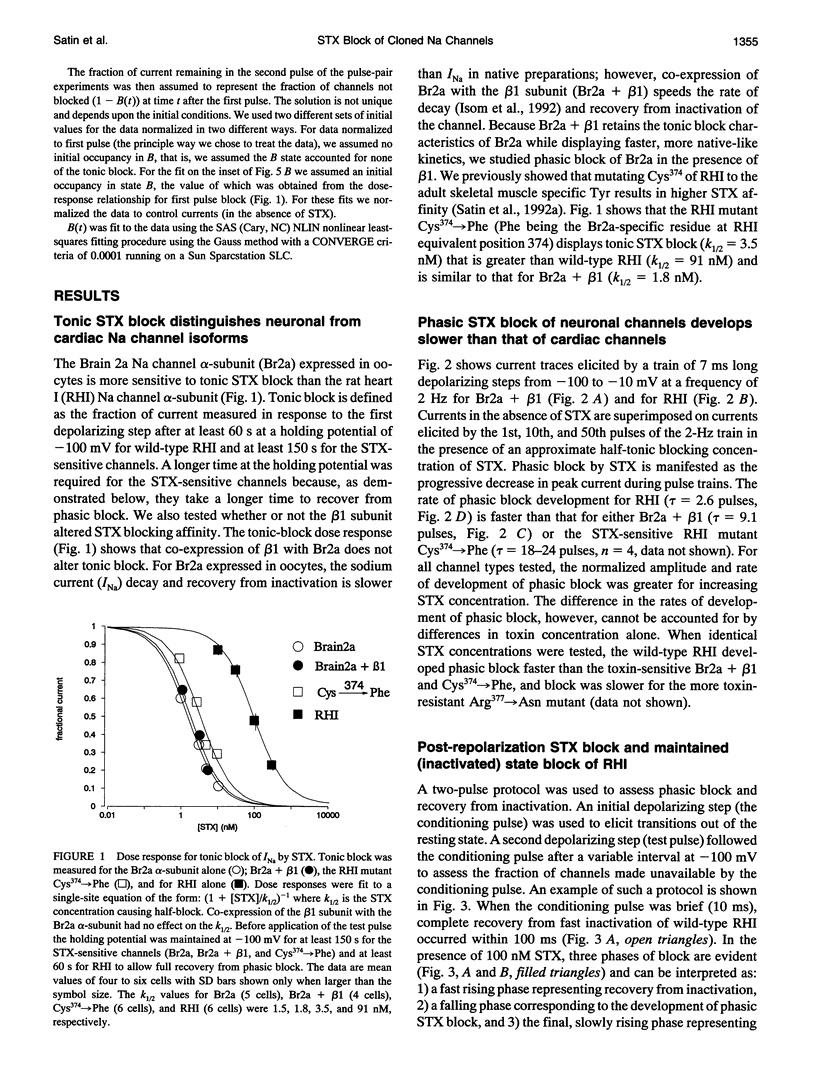
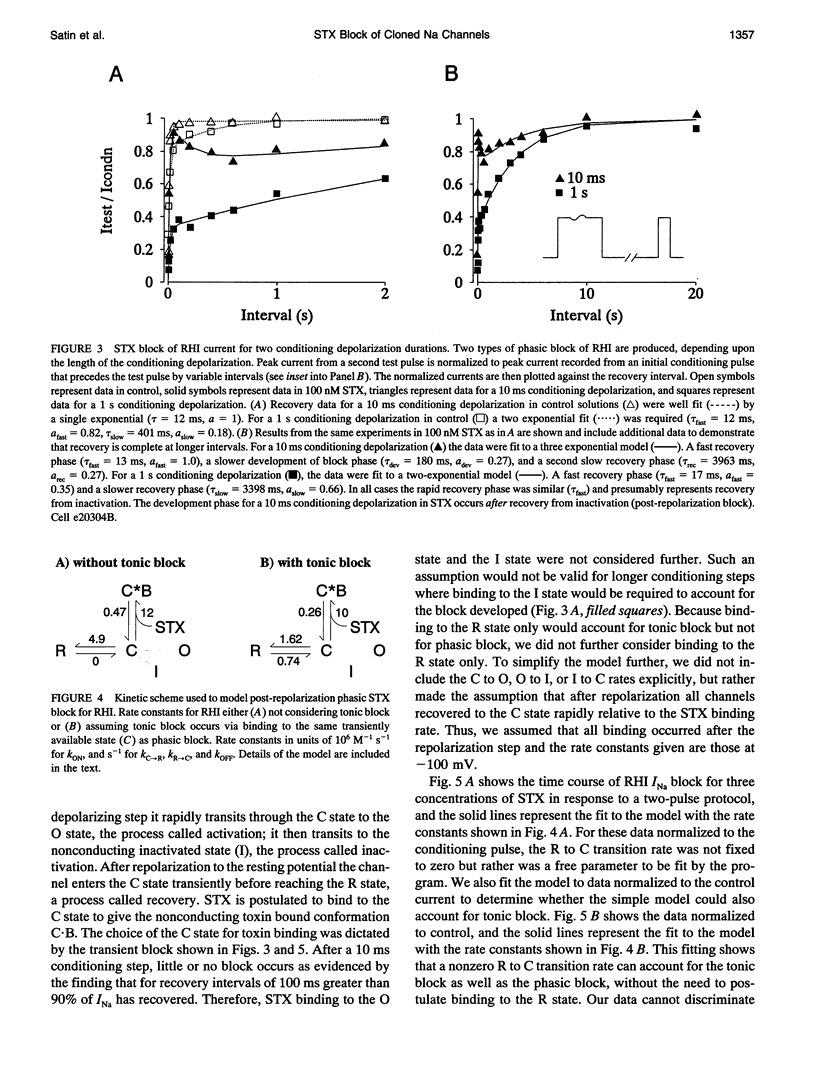
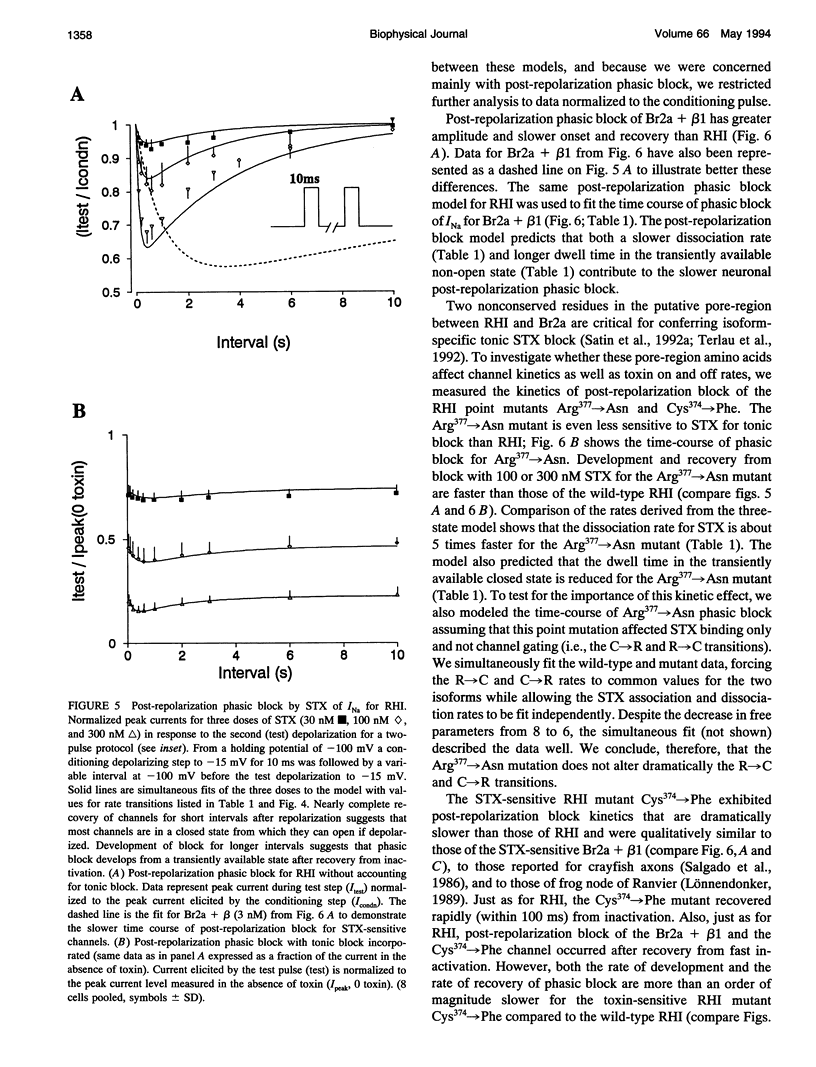
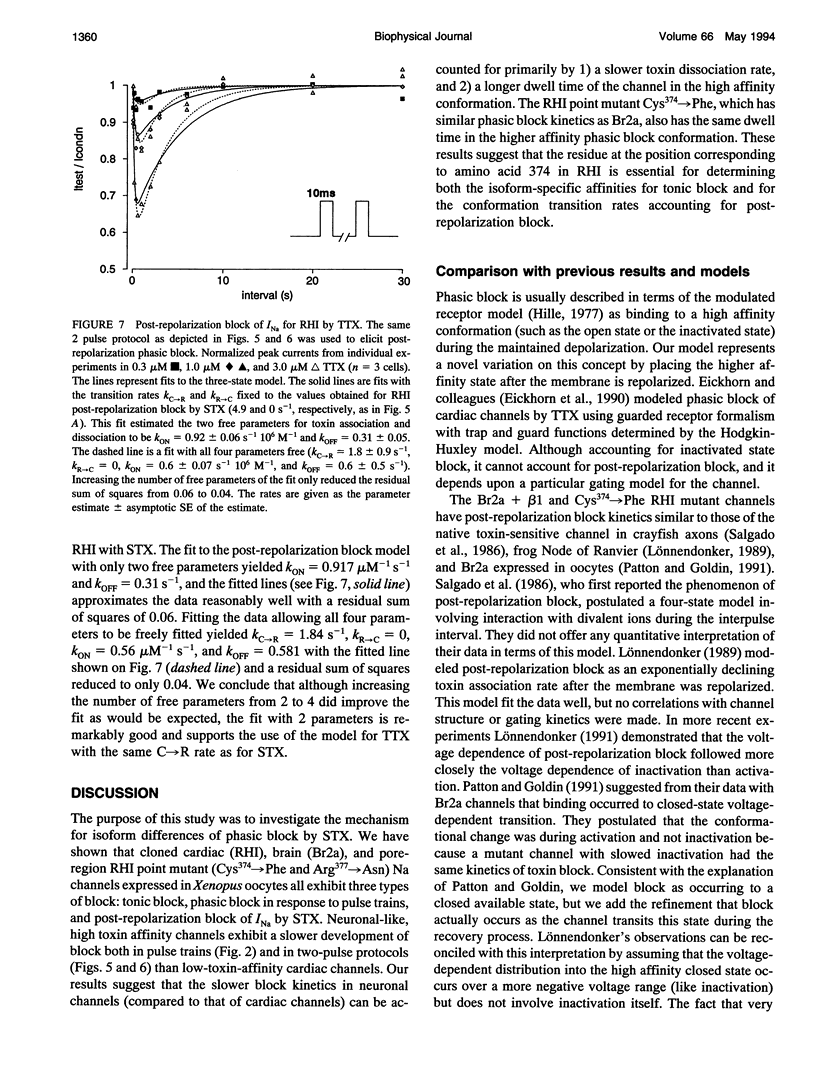
Sodium channels expressed in oocytes exhibited isoform differences in phasic block by saxitoxin (STX). Neuronal channels (rat IIa co-expressed with beta 1 subunit, Br2a + beta 1) had slower kinetics of phasic block for pulse trains than cardiac channels (RHI). After the membrane was repolarized from a single brief depolarizing step, a test pulse at increasing intervals showed first a decrease in current (post-repolarization block) then eventual recovery in the presence of STX. This block/unblock process for Br2a + beta 1 was 10-fold slower than that for RHI. A model accounting for these results predicts a faster toxin dissociation rate and a slower association rate for the cardiac isoform, and it also predicts a shorter dwell time in a putative high STX affinity conformation for the cardiac isoform. The RHI mutation (Cys374-->Phe), which was previously shown to be neuronal-like with respect to high affinity tonic toxin block, was also neuronal-like with respect to the kinetics of post-repolarization block, suggesting that this single amino acid is important for conferring isoform-specific transition rates determining post-repolarization block. Because the same mutation determines both sensitivity for tonic STX block and the kinetics of phasic STX block, the mechanisms accounting for tonic block and phasic block share the same toxin binding site. We conclude that the residue at position 374, in the putative pore-forming region, confers isoform-specific channel kinetics that underlie phasic toxin block.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backx P. H., Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):248–251. doi: 10.1126/science.1321496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer M., Best P. M., Reuter H. Voltage-dependent action of tetrodotoxin in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):344–345. doi: 10.1038/263344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E. A transient calcium-dependent chloride current in the immature Xenopus oocyte. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:309–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth J. F., 4th, Strichartz G. R. Molecular mechanisms of local anesthesia: a review. Anesthesiology. 1990 Apr;72(4):711–734. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199004000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E. Voltage-dependent block by tetrodotoxin of the sodium channel in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jan;51(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83315-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson C. W., Matsubara T., Hondeghem L. M. Evidence for voltage-dependent block of cardiac sodium channels by tetrodotoxin. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Dec;20(12):1119–1131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(88)90592-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., Bean B. P., Colatsky T. J., Tsien R. W. Tetrodotoxin block of sodium channels in rabbit Purkinje fibers. Interactions between toxin binding and channel gating. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Oct;78(4):383–411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs L. L., Satin J., Fozzard H. A., Rogart R. B. Functional expression of the rat heart I Na+ channel isoform. Demonstration of properties characteristic of native cardiac Na+ channels. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle D. D., Guo Y., Lustig S. L., Satin J., Rogart R. B., Fozzard H. A. Divalent cation competition with [3H]saxitoxin binding to tetrodotoxin-resistant and -sensitive sodium channels. A two-site structural model of ion/toxin interaction. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):153–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhorn R., Weirich J., Hornung D., Antoni H. Use dependence of sodium current inhibition by tetrodotoxin in rat cardiac muscle: influence of channel state. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):398–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00370746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X. T., Uehara A., Ravindran A., Bryant S. H., Hall S., Moczydlowski E. Kinetic basis for insensitivity to tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin in sodium channels of canine heart and denervated rat skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7546–7556. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanck D. A., Sheets M. F., Fozzard H. A. Gating currents associated with Na channels in canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):439–457. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Imoto K. Molecular basis for pharmacological differences between brain and cardiac sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Oct;422(1):90–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00381519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue D., Pappano A. J. Block of avian cardiac fast sodium channels by tetrodotoxin is enhanced by repetitive depolarization but not by steady depolarization. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1984 Oct;16(10):943–952. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(84)80030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkind G. M., Fozzard H. A. A structural model of the tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin binding site of the Na+ channel. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80746-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnendonker U. Use-dependent block of sodium channels in frog myelinated nerve by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin at negative holding potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 16;985(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnendonker U. Use-dependent block with tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin at frog Ranvier nodes. II. Extrinsic influence of cations. Eur Biophys J. 1991;20(3):143–149. doi: 10.1007/BF01561136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makielski J. C., Satin J., Fan Z. Post-repolarization block of cardiac sodium channels by saxitoxin. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):790–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81102-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., Stühmer W. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., Goldin A. L. A voltage-dependent gating transition induces use-dependent block by tetrodotoxin of rat IIA sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90376-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. All or none block of single Na+ channels by tetrodotoxin. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 28;54(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgado V. L., Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. Use- and voltage-dependent block of the sodium channel by saxitoxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;479:84–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Bell P., Cribbs L. L., Fozzard H. A., Rogart R. B. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Rogart R. B., Fozzard H. A. The cloned cardiac Na channel alpha-subunit expressed in Xenopus oocytes show gating and blocking properties of native channels. J Membr Biol. 1992 Oct;130(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00233735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanley B. E., Hanck D. A., Chay T., Fozzard H. A. Kinetic analysis of single sodium channels from canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):411–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A., Bezanilla F. Single-channel, macroscopic, and gating currents from sodium channels in the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1499–1510. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82185-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Hadley R. W., Lee K. S., Hume J. R. Voltage-dependent action of tetrodotoxin in mammalian cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):H475–H480. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.2.H475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


