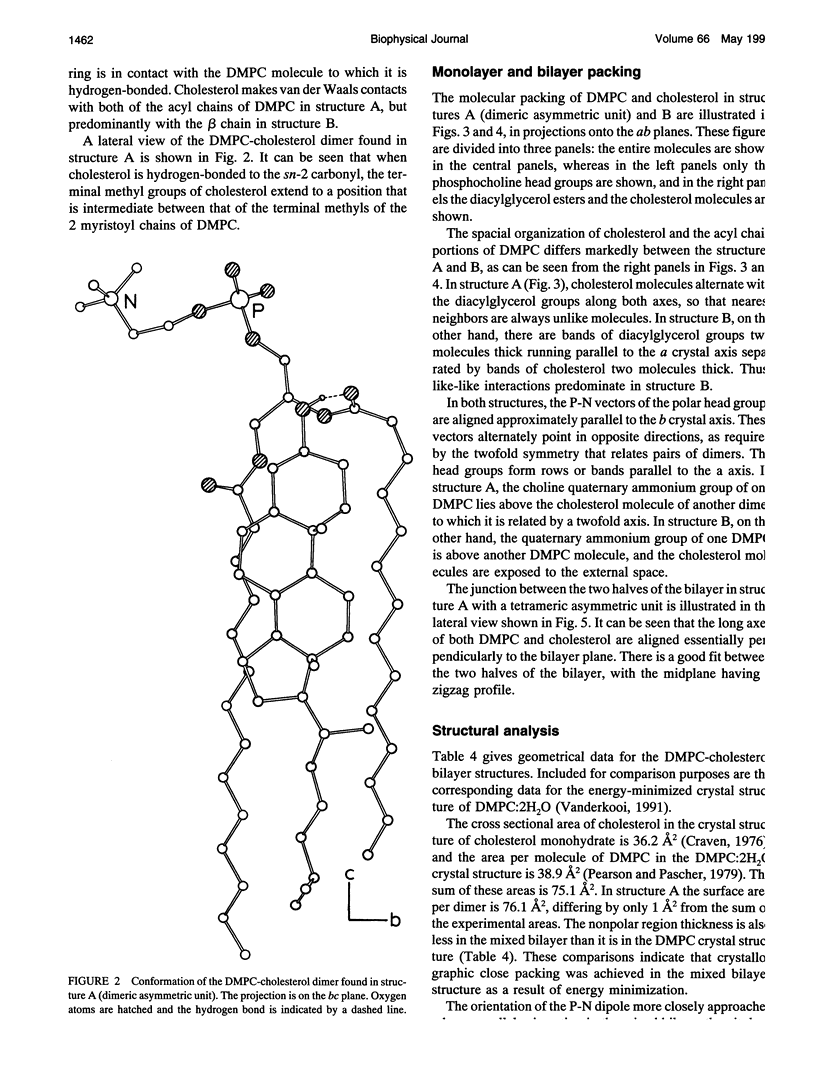
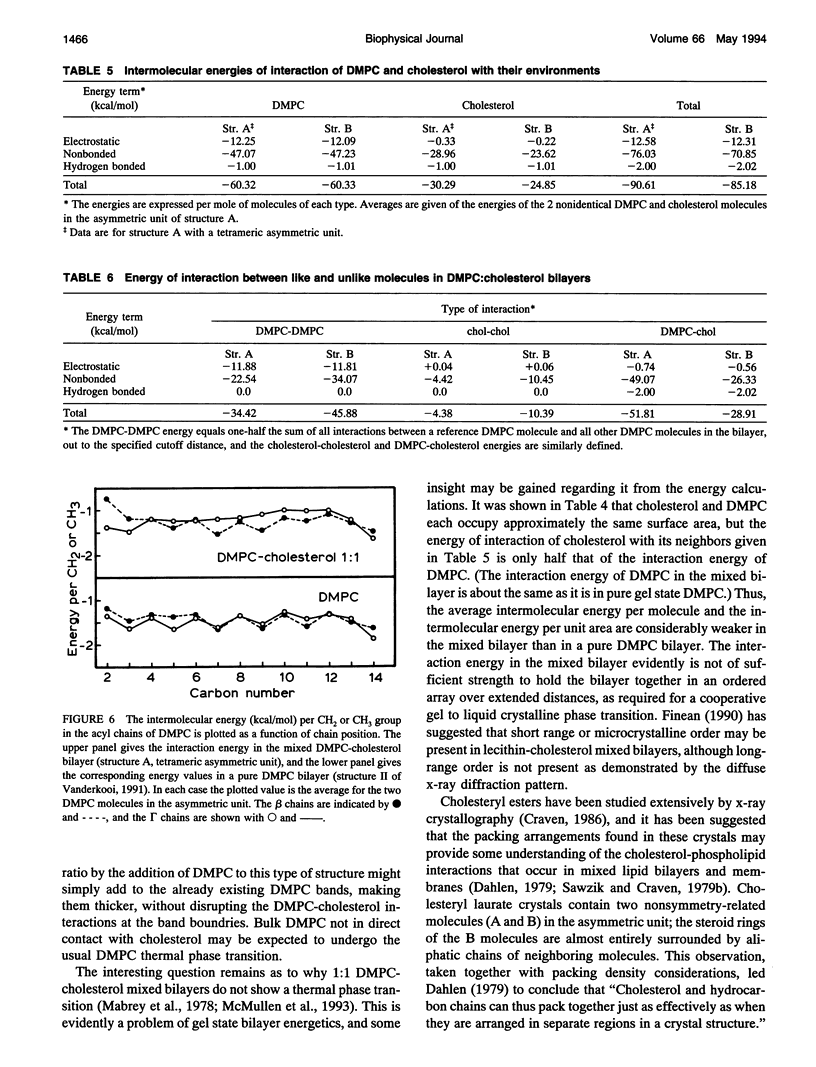
Abstract
The energetically preferred structures of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC)-cholesterol bilayers were determined at a 1:1 mole ratio. Crystallographic symmetry operations were used to generate planar bilayers of cholesterol and DMPC. Energy minimization was carried out with respect to bond rotations, rigid body motions, and the two-dimensional lattice constants. The lowest energy structures had a hydrogen bond between the cholesterol hydroxyl and the carbonyl oxygen of the sn-2 acyl chain, but the largest contribution to the intermolecular energy was from the nonbonded interactions between the flat alpha surface of cholesterol and the acyl chains of DMPC. Two modes of packing in the bilayer were found; in structure A (the global minimum), unlike molecules are nearest neighbors, whereas in structure B (second lowest energy) like-like intermolecular interactions predominate. Crystallographic close packing of the molecules in the bilayer was achieved, as judged from the molecular areas and the bilayer thickness. These energy-minimized structures are consistent with the available experimental data on mixed bilayers of lecithin and cholesterol, and may be used as starting points for molecular dynamics or other calculations on bilayers.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brockerhoff H. Model of interaction of polar lipids, cholesterol, and proteins in biological membranes. Lipids. 1974 Sep;9(9):645–650. doi: 10.1007/BF02532169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Phillips M. C. The stability and structure of cholesterol-rich codispersions of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine. J Lipid Res. 1982 Feb;23(2):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven B. M. Crystal structure of cholesterol monohydrate. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):727–729. doi: 10.1038/260727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darke A., Finer E. G., Flook A. G., Phillips M. C. Complex and cluster formation in mixed lecithincholesterol bilayers. Cooperativity of motion in lipid systems. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80478-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. Structural requirements of sterols for the interaction with lecithin at the air water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. The effect of sterol structure on the permeability of lipomes to glucose, glycerol and Rb + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Jansen J. W., van Dijck P. W., van Deenen L. L. The preferential interaction of cholesterol with different classes of phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 14;465(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Rothman J. E. The planar organization of lecithin-cholesterol bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3694–3697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B. Phospholipid-cholesterol complex in the structure of myelin. Experientia. 1953 Jan 15;9(1):17–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02147697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finean J. B. X-ray diffraction studies of lipid phase transitions in hydrated mixtures of cholesterol and diacylphosphatidylcholines and their relevance to the structure of biological membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Mar;49(4):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. H. A structural model for the cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine complexes in bilayer membranes. Lipids. 1977 Apr;12(4):348–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02533637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Configurations of fatty acyl chains in egg phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1977 Jun;19(2):150–158. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(77)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. B., Yeagle P. L. Models for lipid organization in cholesterol-phospholipid bilayers including cholesterol dimer formation. Lipids. 1978 Sep;13(9):594–597. doi: 10.1007/BF02535821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. The effect of cholesterol on the structure of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):43–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen T. P., Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N. Differential scanning calorimetric study of the effect of cholesterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of a homologous series of linear saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):516–522. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior D. L., Scavitto F. J., Steim J. M. Dilatometry of dipalmitoyllecithin-cholesterol bilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4828–4834. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. H., Pascher I. The molecular structure of lecithin dihydrate. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):499–501. doi: 10.1038/281499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presti F. T., Pace R. J., Chan S. I. Cholesterol-phospholipid interaction in membranes. 2. Stoichiometry and molecular packing of cholesterol-rich domains. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3831–3835. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijck P. W., De Kruijff B., Van Deenen L. L., De Gier J., Demel R. A. The preference of cholesterol for phosphatidylcholine in mixed phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):576–587. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi G. Comparison of energy-minimized crystal structures of 2,3-dilauroyl-D-glycerol, 3-palmitoyl-DL-glycerol-1-phosphorylethanolamine and 1,2-dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine:acetic acid. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Sep;55(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90163-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi G. Multibilayer structure of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine dihydrate as determined by energy minimization. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10760–10768. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma S. P., Wallach D. F. Effects of cholesterol on the infrared dichroism of phosphatide multibilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 13;330(2):122–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Capes S. E., Mantsch H. H. Hydrogen bonding between anhydrous cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines: an infrared spectroscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 27;980(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):267–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Hutton W. C., Huang C. H., Martin R. B. Headgroup conformation and lipid--cholesterol association in phosphatidylcholine vesicles: a 31P(1H) nuclear Overhauser effect study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3477–3481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Martin R. B. Hydrogen-bonding of the ester carbonyls in phosphatidycholine bilayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):775–780. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90942-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Martin R. B., Lala A. K., Lin H. K., Bloch K. Differential effects of cholesterol and lanosterol on artificial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4924–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C., Vanderkooi G. Molecular origin of the internal dipole potential in lipid bilayers: calculation of the electrostatic potential. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):935–941. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81673-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruyff B., Demel R. A., Slotboom A. J., van Deenen L. L., Rosenthal A. F. The effect of the polar headgroup on the lipid-cholesterol interaction: a monolayer and differential scanning calorimetry study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 25;307(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


