Abstract
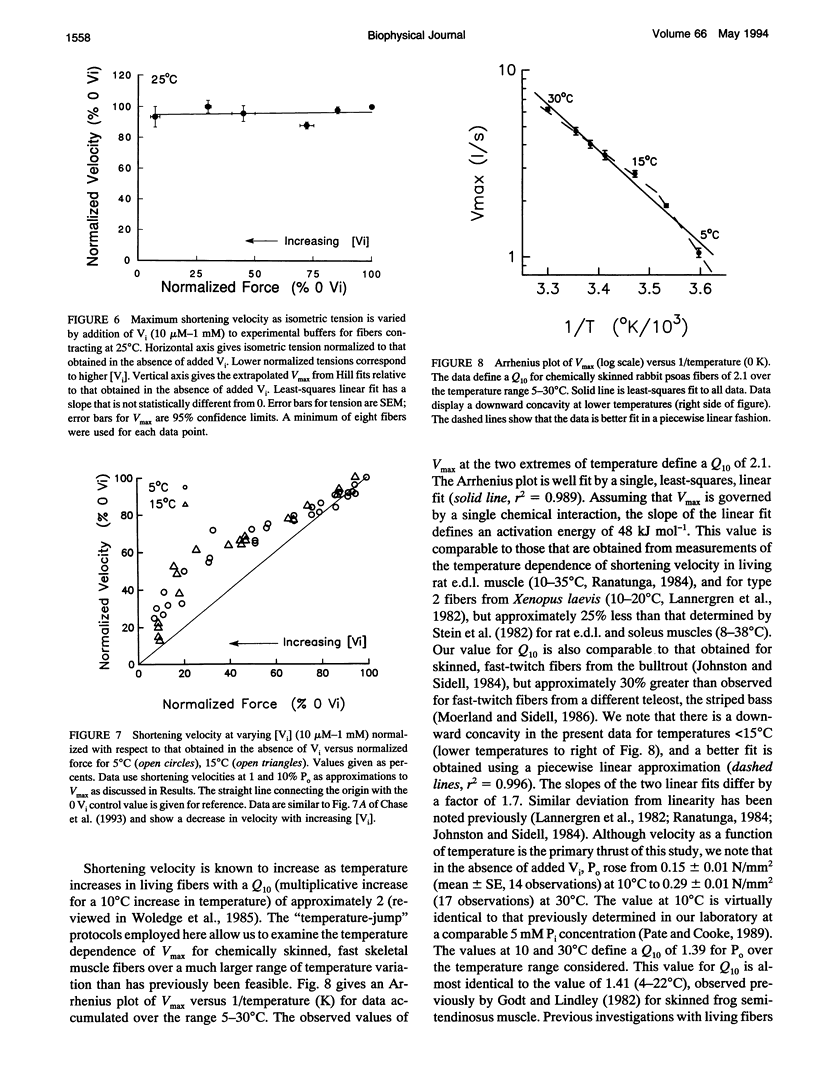
We have investigated the effects of the orthophosphate (P(i)) analog orthovanadate (Vi) on maximum shortening velocity (Vmax) in activated, chemically skinned, vertebrate skeletal muscle fibers. Using new "temperature-jump" protocols, reproducible data can be obtained from activated fibers at high temperatures, and we have examined the effect of increased [Vi] on Vmax for temperatures in the range 5-30 degrees C. We find that for temperatures < or = 20 degrees C, increasing [Vi] inhibits Vmax; for temperatures > or = 25 degrees C, increasing [Vi] does not inhibit Vmax. Attached cross-bridges bound to Vi are thought to be an analog of the weakly bound actin-myosin.ADP-P(i) state. The data suggest that the weakly bound Vi state can inhibit velocity at low temperature, but not at high temperature, with the transition occurring over a narrow temperature range of < 5 degrees C. This suggests a highly cooperative interaction. The data also define a Q10 for Vmax of 2.1 for chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers over the temperature range of 5-30 degrees C.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altringham J. D., Johnston I. A. Effects of phosphate on the contractile properties of fast and slow muscle fibres from an Antarctic fish. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:491–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bershitsky S. Y., Tsaturyan A. K. Tension responses to joule temperature jump in skinned rabbit muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:425–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozovich F. V., Yates L. D., Gordon A. M. Muscle force and stiffness during activation and relaxation. Implications for the actomyosin ATPase. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):399–420. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Crosslinked myosin subfragment 1: a stable analogue of the subfragment-1.ATP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4909–4913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Kushmerick M. J. Effects of pH on contraction of rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83174-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Effects of inorganic phosphate analogues on stiffness and unloaded shortening of skinned muscle fibres from rabbit. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:231–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Bialek W. Contraction of glycerinated muscle fibers as a function of the ATP concentration. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85174-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Franks K., Luciani G. B., Pate E. The inhibition of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction by hydrogen ions and phosphate. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:77–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Pate E. The effects of ADP and phosphate on the contraction of muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):789–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83837-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):53–118. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E., Millar N. C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E. Suppression of muscle contraction by vanadate. Mechanical and ligand binding studies on glycerol-extracted rabbit fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Sep;86(3):305–327. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.3.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Harrington W. F. A single order-disorder transition generates tension during the Huxley-Simmons phase 2 in muscle. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1886–1898. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81259-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Lindley B. D. Influence of temperature upon contractile activation and isometric force production in mechanically skinned muscle fibers of the frog. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E. Kinetics of the actomyosin ATPase in muscle fibers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:637–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
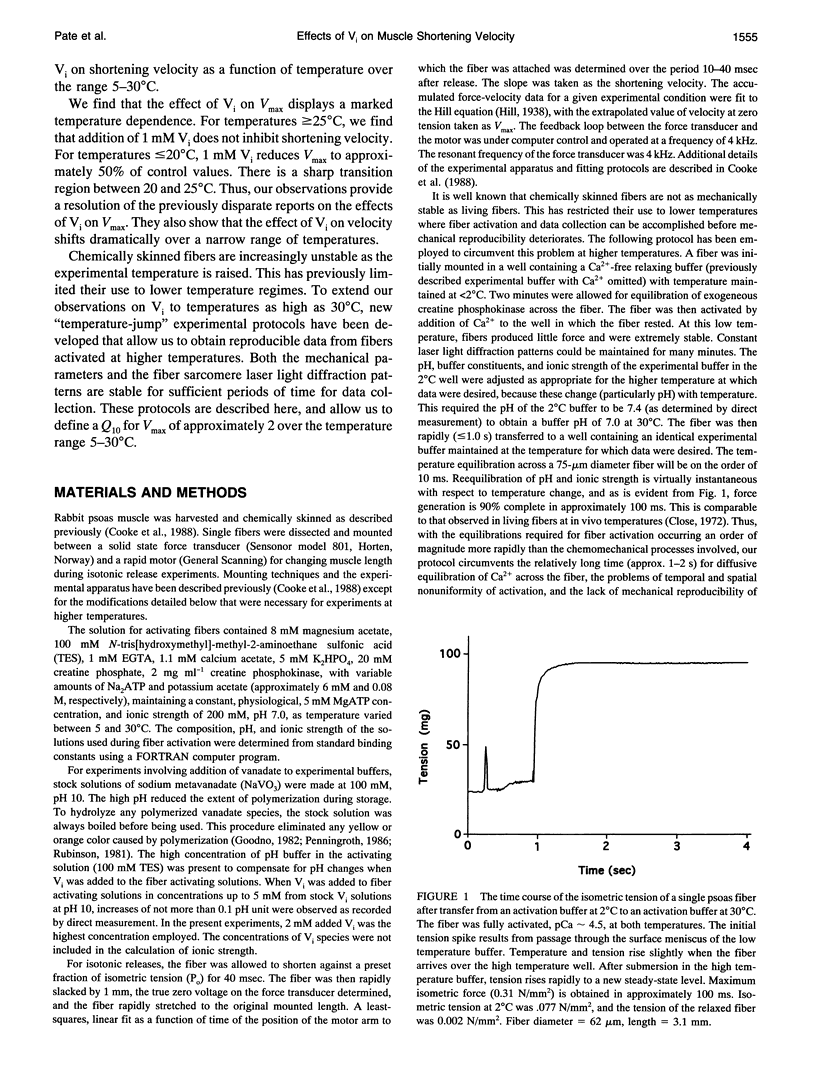
- Goldman Y. E., McCray J. A., Ranatunga K. W. Transient tension changes initiated by laser temperature jumps in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:71–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C. Myosin active-site trapping with vanadate ion. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
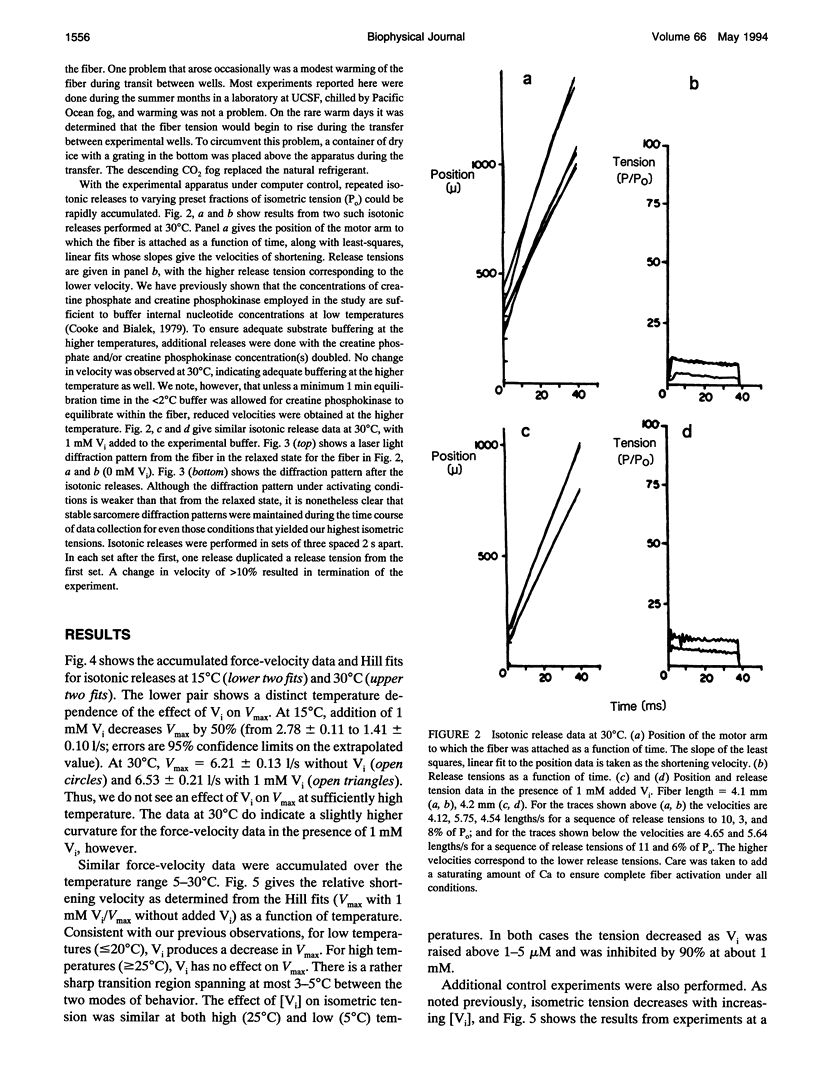
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cooperative binding of myosin subfragment-1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The heat of activation and the heat of shortening in a muscle twitch. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1949 Jun 23;136(883):195–211. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1949.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Dantzig J. A., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Phosphate release and force generation in skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.3159090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
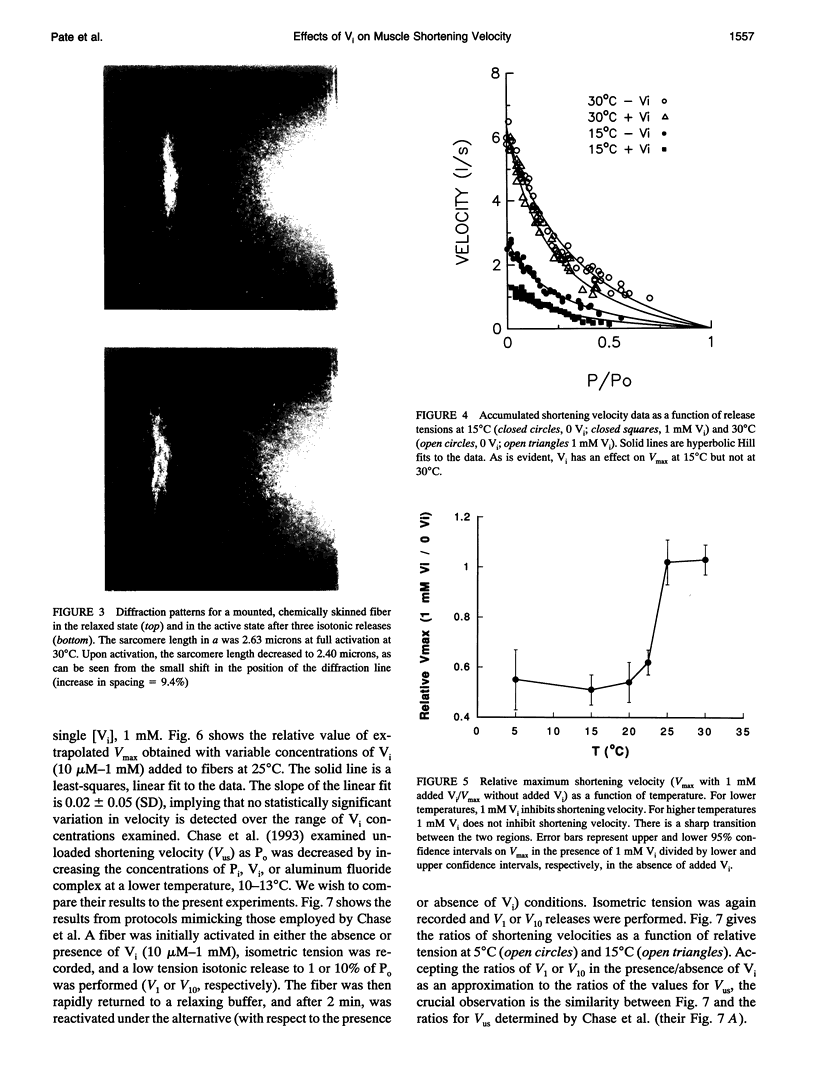
- Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relationships between chemical and mechanical events during muscular contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:119–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I. A., Sidell B. D. Differences in temperature dependence of muscle contractile properties and myofibrillar ATPase activity in a cold-temperature fish. J Exp Biol. 1984 Jul;111:179–189. doi: 10.1242/jeb.111.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Chantler P. D., Kensler R. W., Woodhead J. L. Effects of phosphorylation by myosin light chain kinase on the structure of Limulus thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):563–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lännergren J., Lindblom P., Johansson B. Contractile properties of two varieties of twitch muscle fibres in Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Apr;114(4):523–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M. Force and stiffness in glycerinated rabbit psoas fibers. Effects of calcium and elevated phosphate. J Gen Physiol. 1992 May;99(5):795–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. Addition of phosphate to active muscle fibers probes actomyosin states within the powerstroke. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00585629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. Simulation of stochastic processes in motile crossbridge systems. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Aug;12(4):376–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01738593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penningroth S. M. Erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)]adenine and vanadate as probes for microtubule-based cytoskeletal mechanochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:477–487. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranatunga K. W. The force-velocity relation of rat fast- and slow-twitch muscles examined at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:517–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinson K. A. Concerning the form of biochemically active vanadium. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 May 7;212(1186):65–84. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Spudich J. A., Sheetz M. P. Light chain phosphorylation regulates the movement of smooth muscle myosin on actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1897–1902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. B., Gordon T., Shriver J. Temperature dependence of mammalian muscle contractions and ATPase activities. Biophys J. 1982 Nov;40(2):97–107. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84464-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Lu Z., Moss R. L. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetics of phosphate release in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2459–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Pate E., Cooke R., Yount R. Synthesis of non-nucleotide ATP analogues and characterization of their chemomechanical interaction with muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1993 Oct;14(5):484–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00297211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw D. M., Desrosiers J. M., Work S. S., Trybus K. M. Smooth muscle myosin cross-bridge interactions modulate actin filament sliding velocity in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):453–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zot A. S., Potter J. D. Structural aspects of troponin-tropomyosin regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:535–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]