Abstract
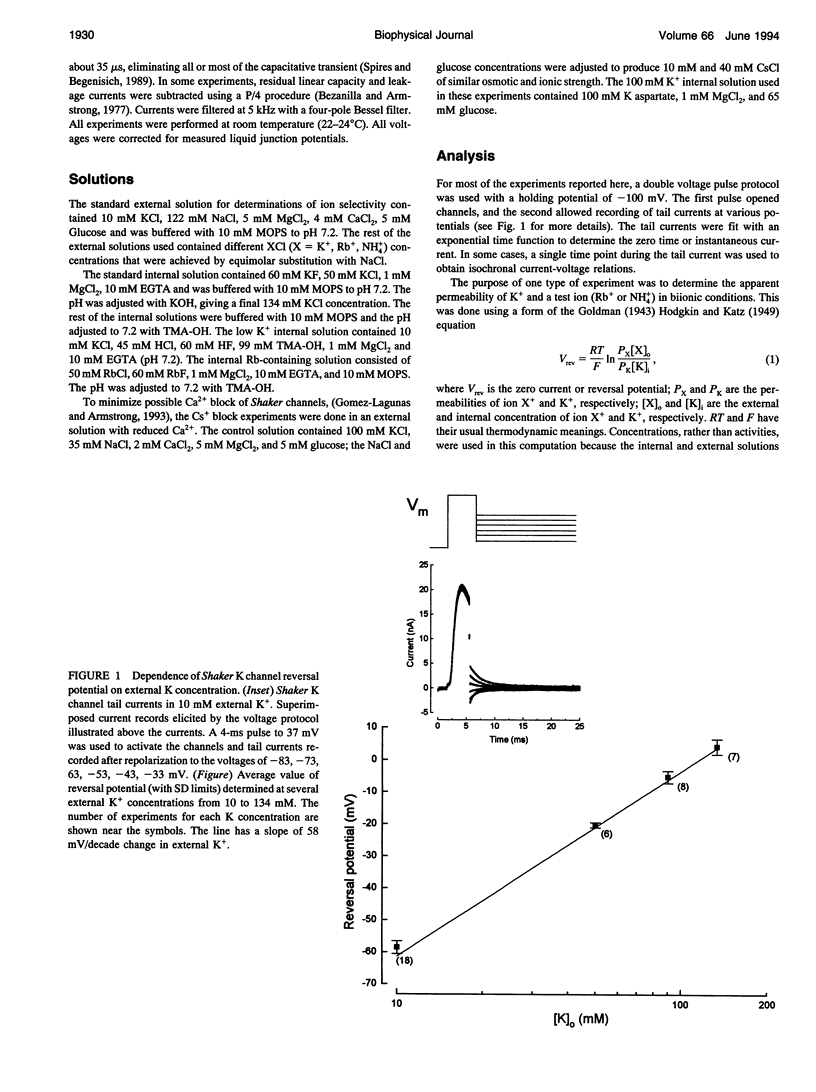
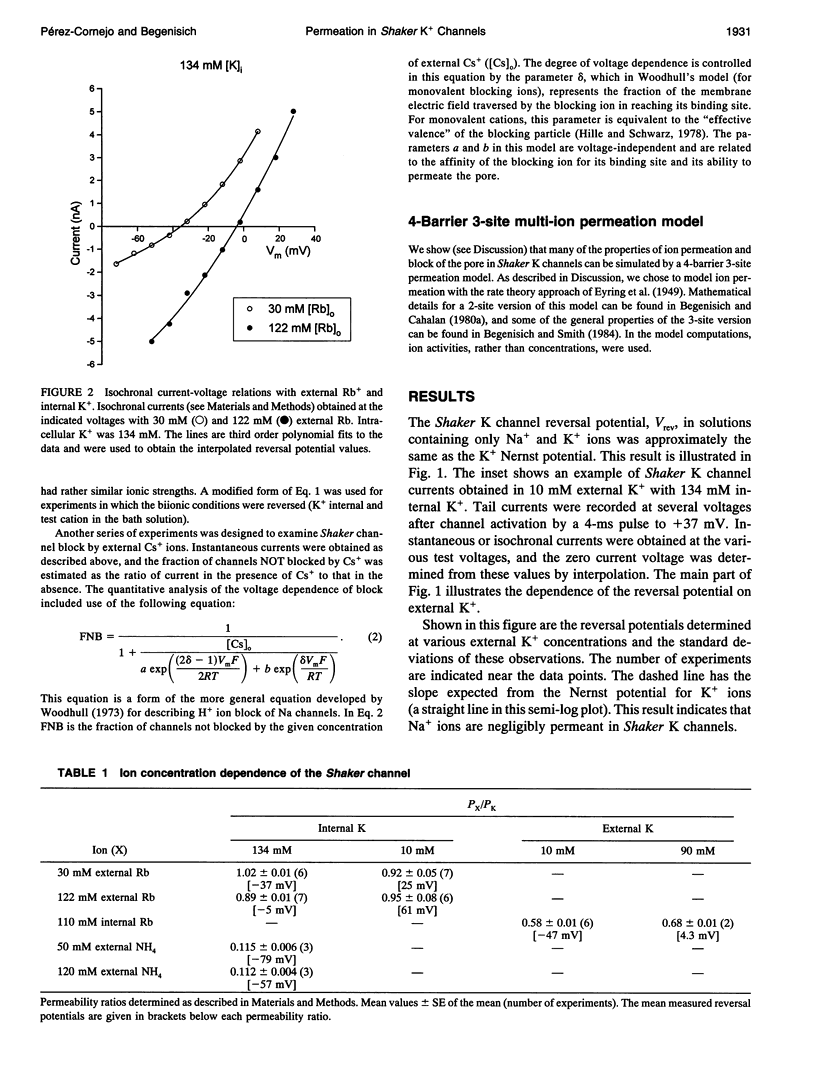
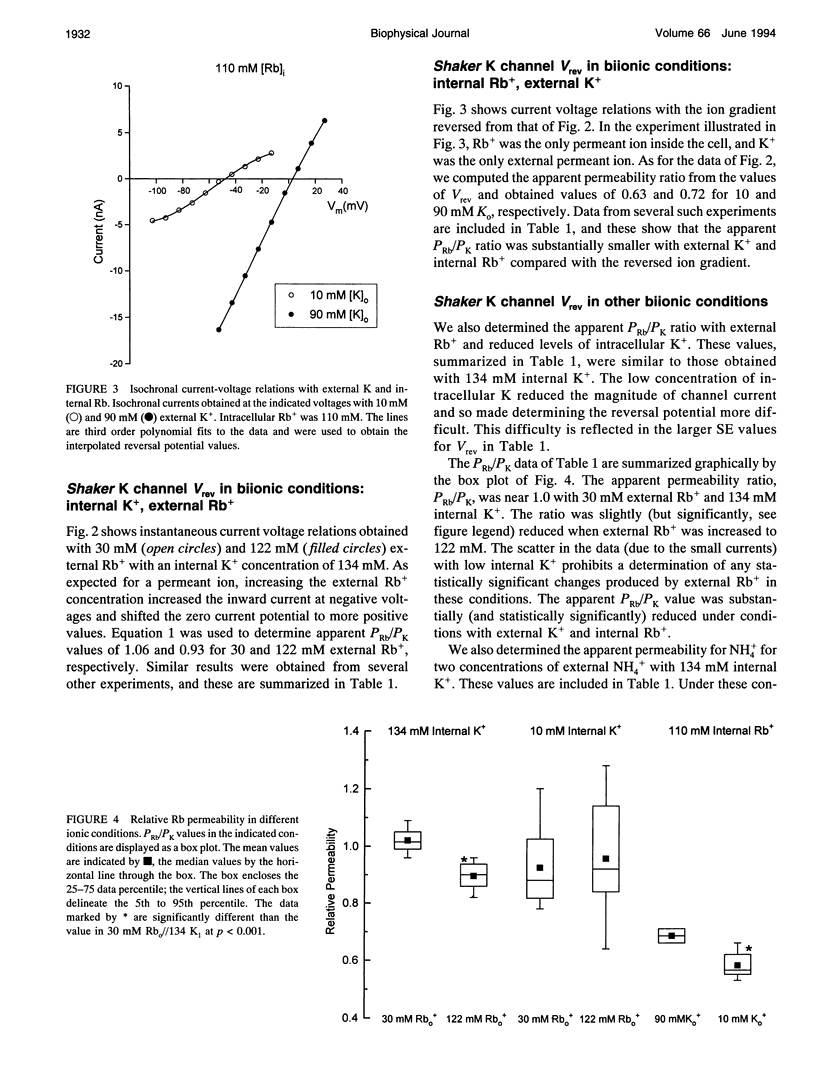
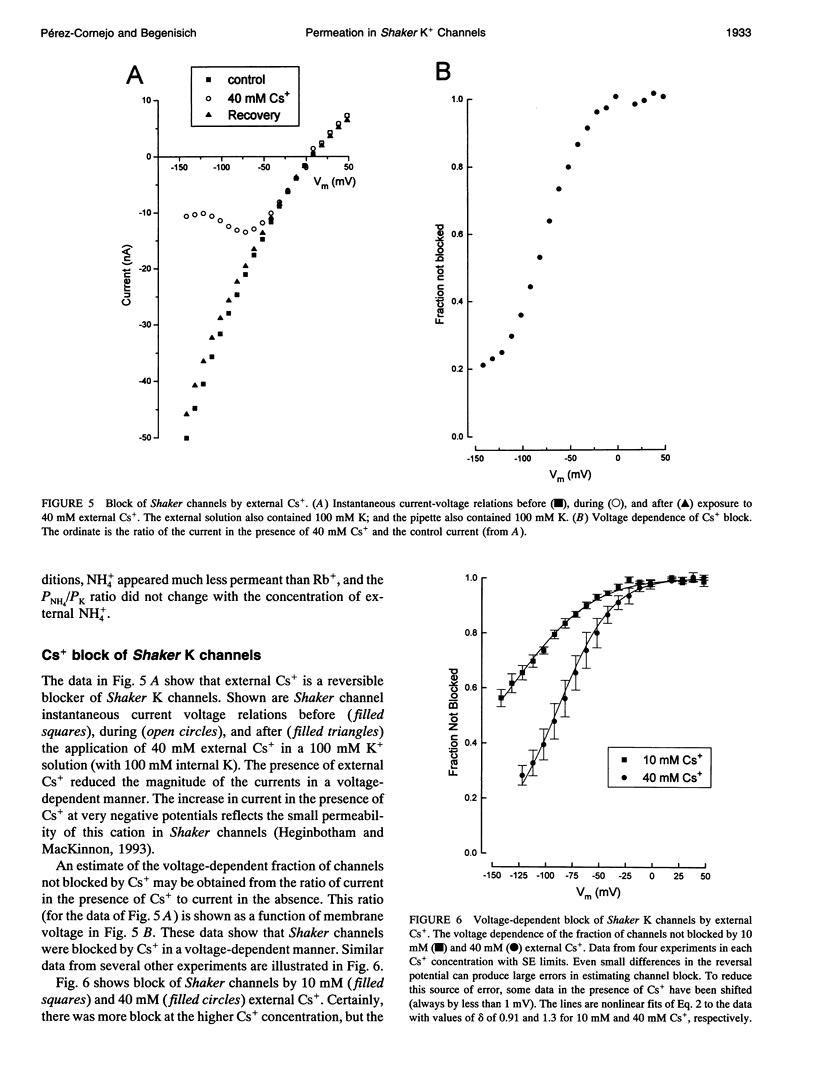
We have investigated some of the permeation properties of the pore in Shaker K channels. We determined the apparent permeability ratio of K+, Rb+, and NH4+ ions and block of the pore by external Cs+ ions. Shaker channels were expressed with the baculovirus/Sf9 expression system and the channel currents measured with the whole-cell variant of the patch clamp technique. The apparent permeability ratio, PRb/PK, determined in biionic conditions with internal K+, was a function of external Rb+ concentration. A large change in PRb/PK occurred with reversed ionic conditions (internal Rb+ and external K+). These changes in apparent permeability were not due to differences in membrane potential. With internal K+, PNH4/PK was not a function of external NH4+ concentration (at least over the range 50-120 mM). We also investigated block of the pore by external Cs+ ions. At a concentration of 20 mM, Cs+ block had a voltage dependence equivalent to that of an ion with a valence of 0.91; this increased to 1.3 at 40 mM Cs+. We show that a 4-barrier, 3-site permeation model can simulate these and many of the other known properties of ion permeation in Shaker channels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, French R. J. Blocking of the squid axon potassium channel by external caesium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:13–25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T. B., Cahalan M. D. Sodium channel permeation in squid axons. I: Reversal potential experiments. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:217–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T. B., Cahalan M. D. Sodium channel permeation in squid axons. II: Non-independence and current-voltage relations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:243–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., De Weer P. Potassium flux ratio in voltage-clamped squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jul;76(1):83–98. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz S., Boxer A., Busath D. D. An SS1-SS2 beta-barrel structure for the voltage-activated potassium channel. Protein Eng. 1992 Jun;5(4):285–293. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.4.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz S., Busath D. Is a beta-barrel model of the K+ channel energetically feasible? Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):19–21. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81765-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. P., Barcilon V., Eisenberg R. S. Constant fields and constant gradients in open ionic channels. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1372–1393. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81944-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. L., Mossman C., Aubé J., Yellen G. The internal quaternary ammonium receptor site of Shaker potassium channels. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):533–541. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90340-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Gates P. Y., Eisenberg R. S. Diffusion theory and discrete rate constants in ion permeation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(2):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01871391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Gates P. Y., Eisenberg R. S. Surmounting barriers in ionic channels. Q Rev Biophys. 1988 Aug;21(3):331–364. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., MacKinnon R. Conduction properties of the cloned Shaker K+ channel. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2089–2096. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81244-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacoff E. Y., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Putative receptor for the cytoplasmic inactivation gate in the Shaker K+ channel. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):86–90. doi: 10.1038/353086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Hartmann H. A., Taglialatela M., de Biasi M., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. Differences between the deep pores of K+ channels determined by an interacting pair of nonpolar amino acids. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90278-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., DeBiasi M., Hartmann H. A., Brown A. M. A single nonpolar residue in the deep pore of related K+ channels acts as a K+:Rb+ conductance switch. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):136–144. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81800-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaiber K., Williams N., Roberts T. M., Papazian D. M., Jan L. Y., Miller C. Functional expression of Shaker K+ channels in a baculovirus-infected insect cell line. Neuron. 1990 Aug;5(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Interpretation of biological ion channel flux data--reaction-rate versus continuum theory. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:29–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Heginbotham L., Abramson T. Mapping the receptor site for charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking potassium channel inhibitor. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):767–771. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90335-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland C. F., Adelman J. P., Tempel B. L., Almers W. Repulsion between tetraethylammonium ions in cloned voltage-gated potassium channels. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):975–982. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90212-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Chemical properties of the divalent cation binding site on potassium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Aug;100(2):181–193. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Pharmacological and kinetic analysis of K channel gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Feb;93(2):263–283. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagoner P. K., Oxford G. S. Cation permeation through the voltage-dependent potassium channel in the squid axon. Characteristics and mechanisms. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Aug;90(2):261–290. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):939–942. doi: 10.1126/science.2000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yool A. J., Schwarz T. L. Alteration of ionic selectivity of a K+ channel by mutation of the H5 region. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):700–704. doi: 10.1038/349700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


