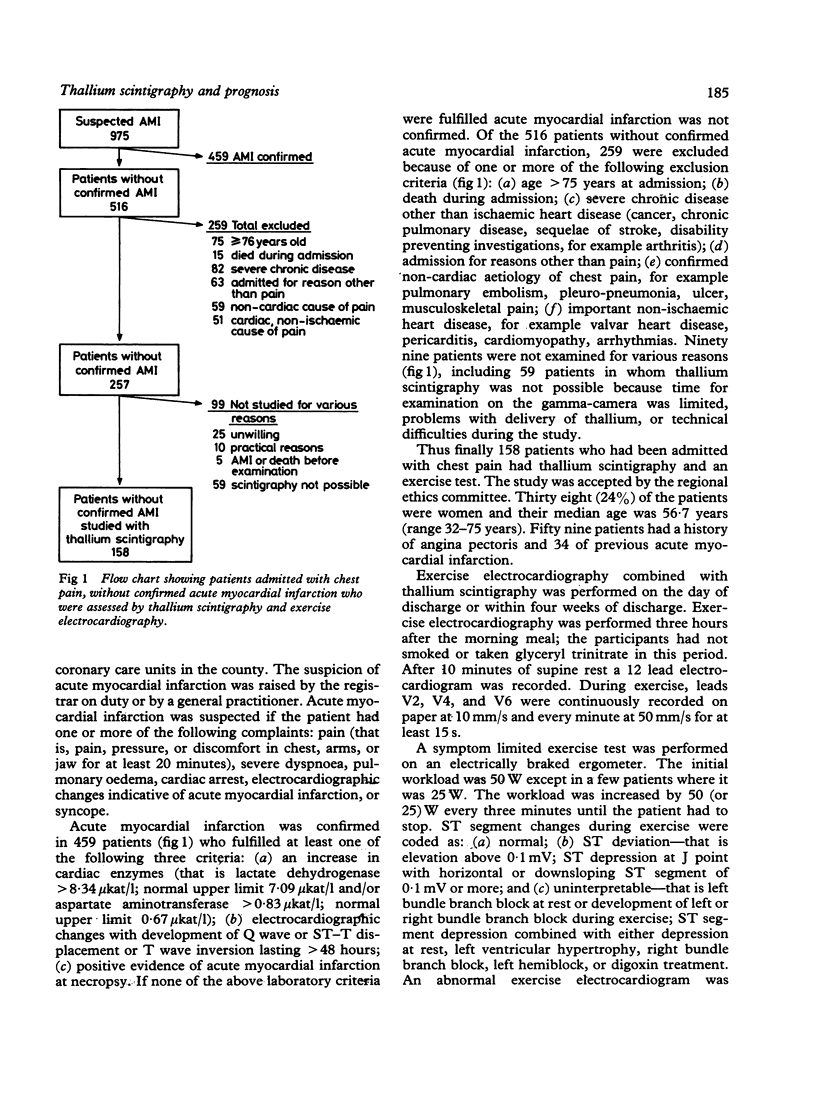
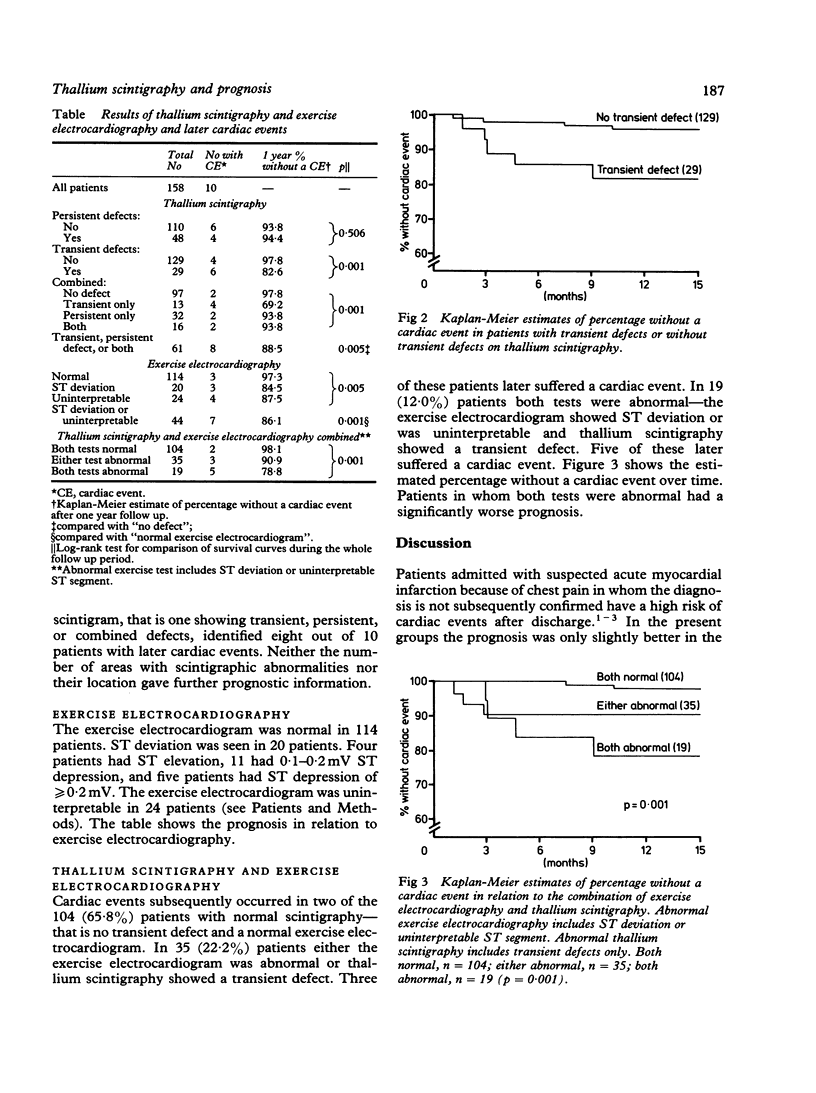
Abstract
Exercise and rest thallium scintigraphy and exercise electrocardiography were performed after discharge in 158 patients aged less than 76 years admitted with chest pain in whom a suspected diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction had not been confirmed. During a follow up of 12-24 months (median 14 months) there were 10 cardiac events--that is, non-fatal acute myocardial infarction or cardiac deaths. Transient thallium defects and abnormal ST response (that is ST segment deviation or uninterpretable ST segment) during exercise were correlated significantly with an unfavourable prognosis. One hundred and four patients with neither of these characteristics were at lower risk of a cardiac event than the 19 patients with both of these characteristics. The percentages of patients in these two groups without a cardiac event after one year were 98.1 and 78.8 respectively. Thallium scintigraphy, alone or in combination with exercise electrocardiography, can be used to identify groups at high and low risk of future cardiac events, in patients with chest pain in whom acute myocardial infarction is suspected but not found.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodenheimer M. B., Banka V. S., Fooshee C. M., Helfant R. H. Extent and severity of coronary heart disease. Determinations by thallous chloride Tl 201 myocardial perfusion scanning and comparison with stress electrocardiography. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Jun;139(6):630–634. doi: 10.1001/archinte.139.6.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Boucher C. A., Okada R. D., Guiney T. E., Newell J. B., Strauss H. W., Pohost G. M. Prognostic value of exercise thallium-201 imaging in patients presenting for evaluation of chest pain. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Apr;1(4):994–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. S., Watson D. D., Craddock G. B., Crampton R. S., Kaiser D. L., Denny M. J., Beller G. A. Prediction of cardiac events after uncomplicated myocardial infarction: a prospective study comparing predischarge exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy and coronary angiography. Circulation. 1983 Aug;68(2):321–336. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilsley C., Stockley A., Clitsakis D., Layton C. Normal coronary arteriogram. An avoidable test? Br Heart J. 1982 Dec;48(6):580–583. doi: 10.1136/hrt.48.6.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iskandrian A. S., Hakki A. H., Kane-Marsch S. Prognostic implications of exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy in patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease. Am Heart J. 1985 Jul;110(1 Pt 1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyst Madsen J., Fischer Hansen J. The prognosis for patients admitted to a coronary care unit due to suspected acute myocardial infarction with and without confirmed diagnosis. Acta Med Scand. 1982;211(6):453–457. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb01981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966 Mar;50(3):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamelia F. X., Gibson R. S., Watson D. D., Craddock G. B., Sirowatka J., Beller G. A. Prognosis with chest pain and normal thallium-201 exercise scintigrams. Am J Cardiol. 1985 Apr 1;55(8):920–926. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90718-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. E., Horowitz S. F., Eng C., Rudin A., Meller J., Halgash D. A., Pichard A. D., Goldsmith S. J., Herman M. V., Gorlin R. Can exercise electrocardiography and thallium-201 myocardial imaging exclude the diagnosis of coronary artery disease? Bayesian analysis of the clinical limits of exclusion and indications for coronary angiography. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Apr 1;49(5):1127–1135. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Gonzalez J., Botvinick E. H., Dunn R., Rahimtoola S., Ports T., Chatterjee K., Parmley W. W. The late prognostic value of acute scintigraphic measurement of myocardial infarction size. Circulation. 1982 Nov;66(5):960–971. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.5.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. L., Zaret B. L., Strauss H. W., Pitt B., Berman D. S., Schelbert H. R., Ashburn W. L., Berger H. J., Hamilton G. W. Myocardial imaging with thallium-201: a multicenter study in patients with angina pectoris or acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Sep;42(3):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. S., Lamb I. H., Hu M. Do patients in whom myocardial infarction has been ruled out have a better prognosis after hospitalization than those surviving infarction? N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackers F. J., Russo D. J., Russo D., Clements J. P. Prognostic significance of normal quantitative planar thallium-201 stress scintigraphy in patients with chest pain. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Jul;6(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. A., Ryan T. J., McCabe C. H., Chaitman B. R., Sheffield L. T., Ferguson J. C., Fisher L. D., Tristani F. Prognostic importance of a clinical profile and exercise test in medically treated patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984 Mar;3(3):772–779. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(84)80254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


