Abstract
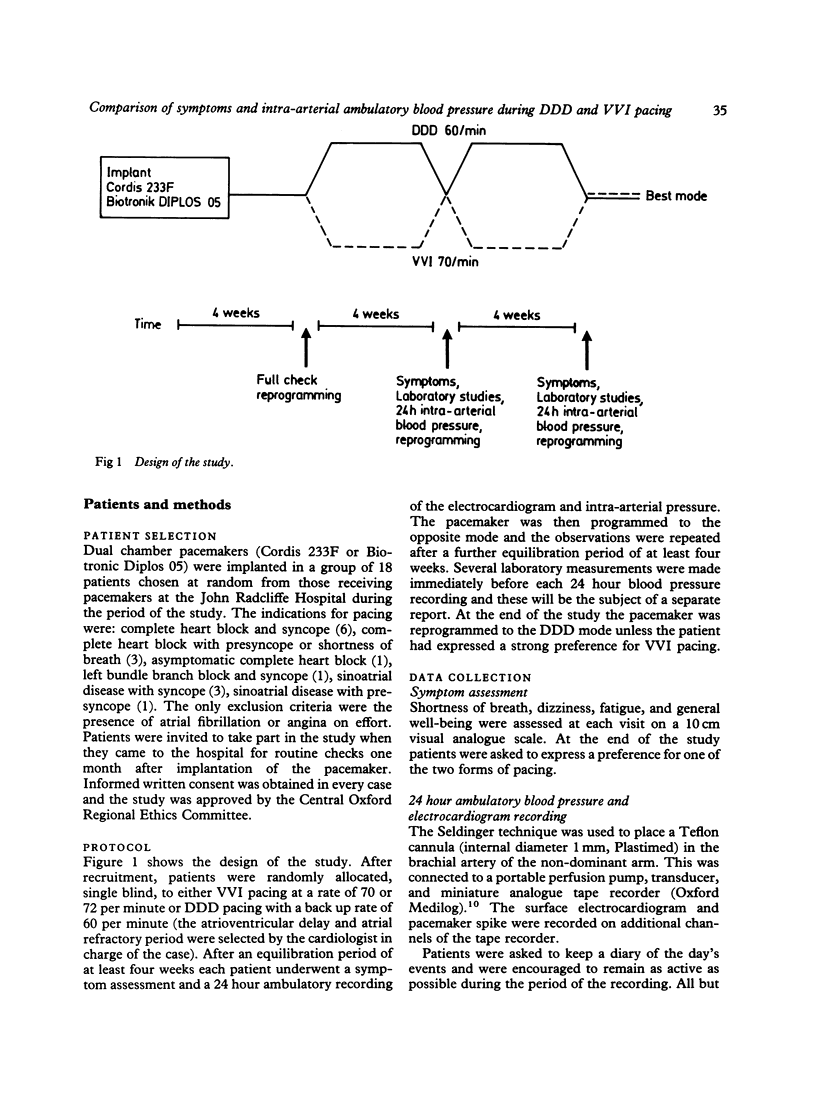
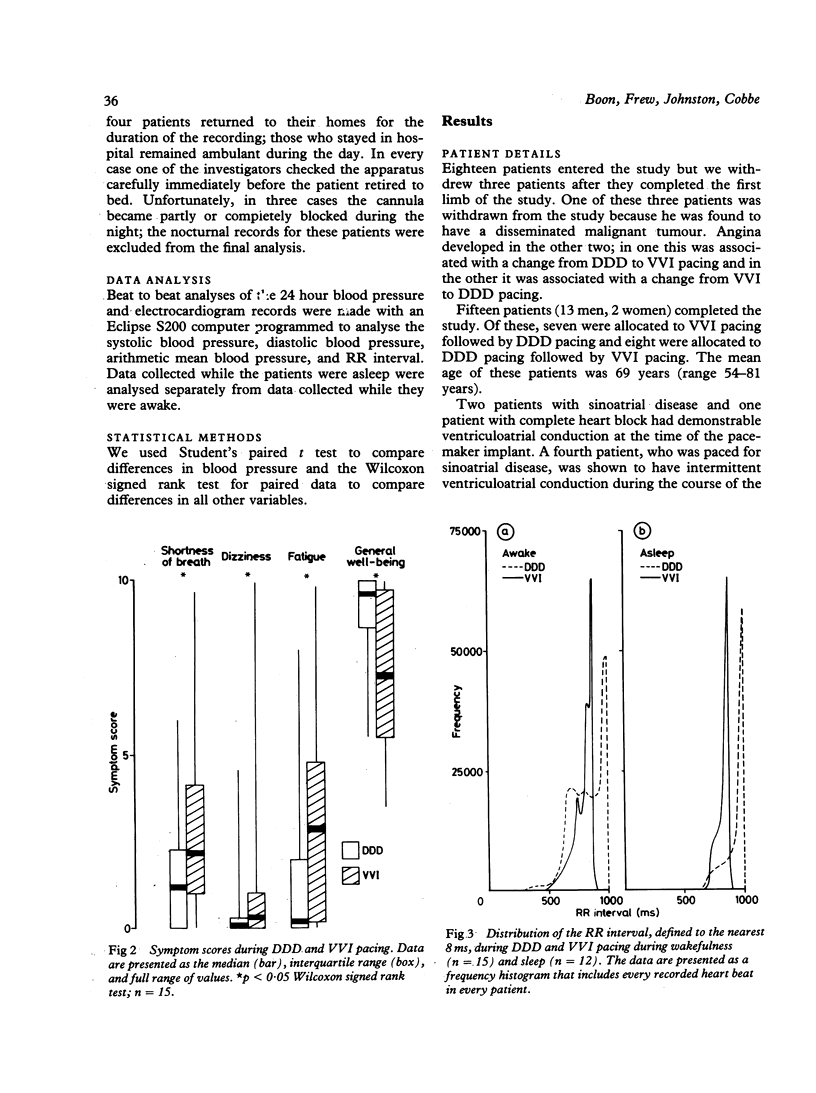
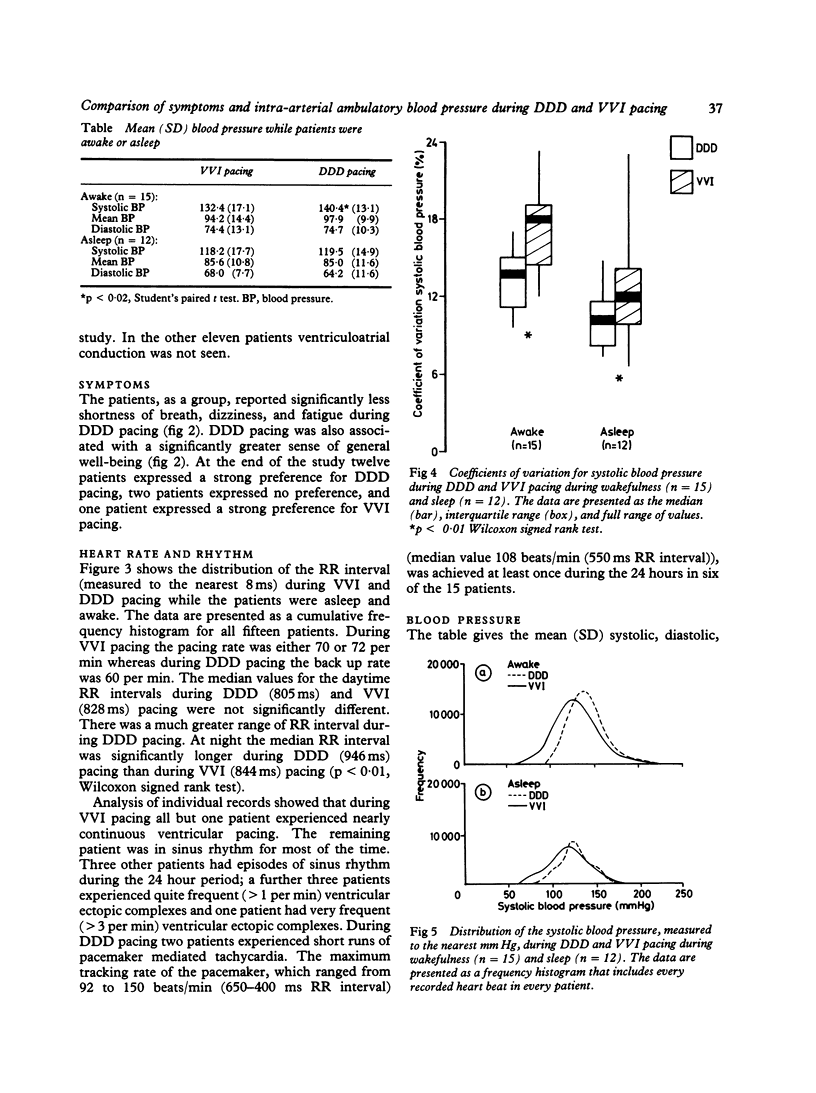
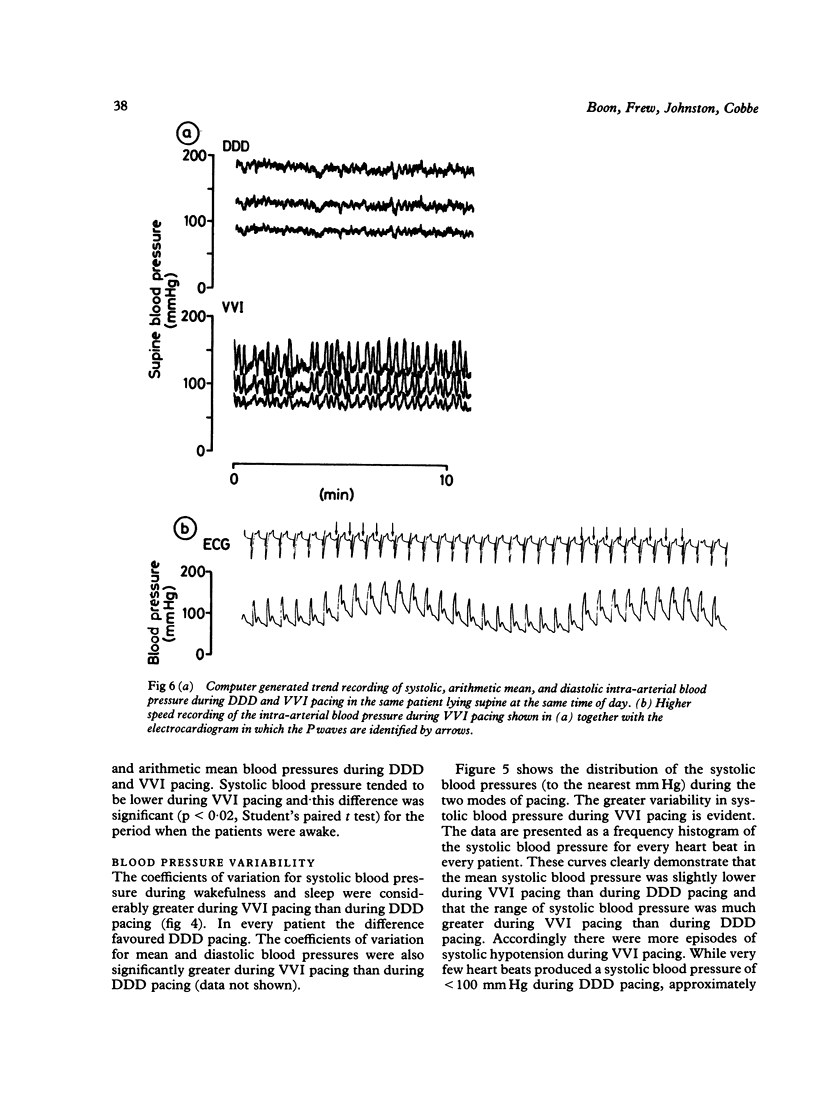
Fifteen patients with dual chamber pacemakers implanted for atrioventricular block (11) or sinoatrial disease (4) completed a single blind within-patient comparison of symptoms and 24 hour intra-arterial blood pressure during long term atrioventricular synchronous (DDD) pacing and long term ventricular demand (VVI) pacing. The patients reported significantly less breathlessness, fatigue, and dizziness and a significantly greater sense of general well-being during DDD pacing than during VVI pacing. Twelve of the fifteen patients expressed a strong preference for DDD pacing. Systolic blood pressure tended to be lower and was significantly more variable during VVI pacing than during DDD pacing (mean (SD) daytime systolic blood pressure 132.4 (17.1) and 140.4 (13.1) mm Hg respectively). Accordingly, episodes of hypotension were more common during VVI pacing, which may partly explain why the patients reported more symptoms during this mode of pacing.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alicandri C., Fouad F. M., Tarazi R. C., Castle L., Morant V. Three cases of hypotension and syncope with ventricular pacing: possible role of atrial reflexes. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Jul;42(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90998-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. S. "Physiological" pacing. Br Heart J. 1983 Aug;50(2):109–111. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. I., Cashman P. M., Hornung R. S., Prince H., Bassein L., Raftery E. B. Ambulatory blood pressure and assessment of pacemaker function. Br Heart J. 1986 May;55(5):462–468. doi: 10.1136/hrt.55.5.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson B. E., Arnman K., Smedgård P., Rydén L. Physiological versus single-rate ventricular pacing: a double-blind cross-over study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1985 Jan;8(1):73–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1985.tb05726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse I., Arnman K., Conradson T. B., Rydén L. A comparison of the acute and long-term hemodynamic effects of ventricular inhibited and atrial synchronous ventricular inhibited pacing. Circulation. 1982 May;65(5):846–855. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.5.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler W. A., Honour A. J., Sleight P., Stott F. D. Continuous recording of direct arterial pressure and electrocardiogram in unrestricted man. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 8;3(5818):76–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5818.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. A., Perrins E. J., Grant P., Chan S. L., McBrien D. J., Sutton R. Carotid sinus syncope treated by pacing. Analysis of persistent symptoms and role of atrioventricular sequential pacing. Br Heart J. 1982 May;47(5):411–418. doi: 10.1136/hrt.47.5.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrins E. J., Morley C. A., Chan S. L., Sutton R. Randomised controlled trial of physiological and ventricular pacing. Br Heart J. 1983 Aug;50(2):112–117. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. B., Stallard T. J., Littler W. A. Continuous ambulatory monitoring of blood pressure and assessment of cardiovascular reflexes in the elderly hypertensive. J Hypertens. 1984 Dec;2(6):615–622. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198412000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. M., Bhakta R. D., Lutgen J. Dual chamber sequential pacing management of sinus node dysfunction: advantages over single-chamber pacing. Am Heart J. 1982 Dec;104(6):1319–1327. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandgaard S., Olesen J., Skinhoj E., Lassen N. A. Autoregulation of brain circulation in severe arterial hypertension. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 3;1(5852):507–510. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5852.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


